Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Reactividad de Sólidos
Combined kinetic analysis of multistep processes of thermal decomposition of polydimethylsiloxane silicone
Garcia-Garrido, C; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PEPolymer, 153 (2018) 558-564
Show abstract ▽
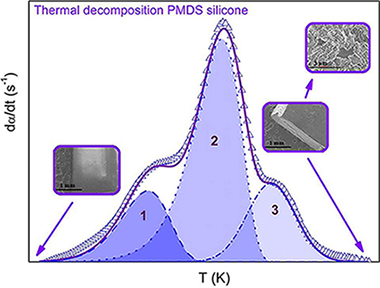
In this work, we studied the thermal decomposition of a widely employed silicone elastomer, polydimethylsiloxane, in an inert atmosphere. This silicone elastomer has several applications due to its high thermal stability such as MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) precursors, microfluidic components, adhesives, lubricants, and precursors for non-porous ceramics. Therefore, a reliable description of the thermal decomposition kinetics is important to prevent or control the decomposition in such applications. While the decomposition has been amply reported as a complex process, most kinetic studies published on this system use simplified methods that avoid the fact that the entire process cannot be described by a single kinetic triplet. Here, we have studied the decomposition process by first separating the overall reaction into its three constituent steps which were subsequently analysed independently. The deconvolution was carried out using Fraser-Suzuki function that is capable of fitting an asymmetric peak fitting function. The resulting kinetic parameters proved to be able to reconstruct the original experimental curves but are also capable of producing accurate predictions of curves recorded at heating schedules different from those employed to record the experimental data used in the kinetic analysis. Finally, it was found that the rate limiting step of all stages is the diffusion of the gases released during the polymer decomposition through the transforming polymeric matrix.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2018.08.045
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Operando DRIFTS-MS Study of WGS and rWGS Reaction on Biochar-Based Pt Catalysts: The Promotional Effect of Na
Santos, JL; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAC-Journal of Carbon Research, 4 (2018) 47
Show abstract ▽
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis, characterization and combined kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition of hydrotalcite (Mg6Al2(OH)(16)CO3 center dot 4H(2)O)
Yahyaoui, R; Jimenez, PES; Maqueda, LAP; Nahdi, K; Luque, JMCThermochimica Acta, 667 (2018) 177-184
Show abstract ▽
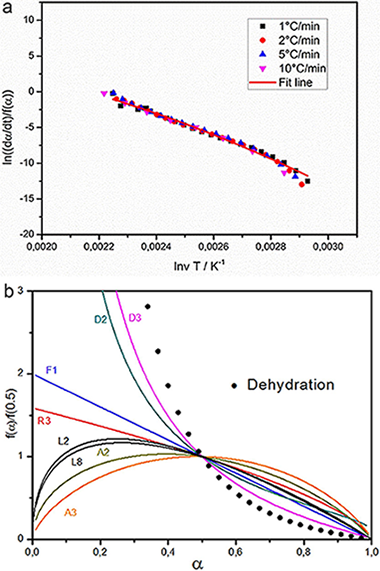
Here, a kinetic study of the thermal decomposition of synthesized hydrotalcite, Mg-6 Al-2 CO3(OH)(16)center dot H2O, has been carried out using thermogravimetric experiments in air atmosphere. It is shown that the thermal decomposition occurs in two well differentiated stages. The first one is a single-step dehydration process that comprises the release of four water molecules. On the other hand, the second stage is complex and corresponds to both dehydroxylation and decarbonation processes which occur simultaneously. The kinetic parameters describing all processes were calculated by means of a combined approach comprising isoconversional, model-fitting and deconvolution methods. It was concluded that dehydroxilation and decarbonization cannot be separated by TG experiments and the two stages contributing to the complex process do not apparently match the expected stoichiometry of the process. Therefore, it is proposed that such stages mark a change on the reaction mechanism due to the structural collapse of the laminar double hydroxide.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2018.07.025
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Adhesion enhancement of DLC hard coatings by HiPIMS metal ion etching pretreatment
Santiago, JA; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Wennberg, A; Molina-Aldareguia, JM; Castillo-Rodriguez, M; Rojas, TC; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Gonzalez, MU; Garcia-Martin, JM; Li, H; Bellido-Gonzalez, V; Monclus, MA; Gonzalez-Arrabal, RSurface & Coatings Technology, 349 (2018) 787-796
Show abstract ▽
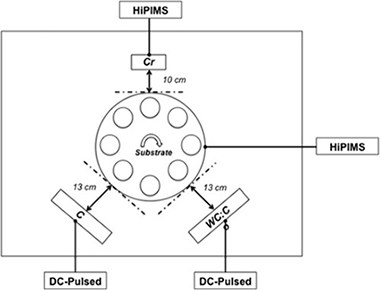
Poor adhesion is a recurrent problem for the wider use of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings in industrial applications. In this work, we investigate the effectiveness of high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) metal ion etching to improve the adhesion of DLC coatings on high speed steel substrates. The influence of HiPIMS pretreatment parameters, the metal ion selection for the process and the addition of bonding layers on the adhesion properties were studied. Daimler-Benz and nanoscratch test methods were used to evaluate the adhesion. The elemental composition, morphology and microstructure of the samples were evaluated by EELS, SEM, AFM and HRTEM. In general, samples pretreated with HiPIMS metal ion etching withstand larger critical loads than those pretreated by conventional Ar + glow discharge and bonding layers. The pretreatment is proven to be very effective at removing surface contaminants and providing a gradual interface. The selection of Cr over Ti contributes to a significant improvement on the adhesion due to the reduction of the oxygen level at the interface thus ensuring an optimal coating-substrate contact and a more compliant structure, which prevents the delamination failure.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.04.090
Materiales Avanzados
An approach to the heating dynamics of residues from greenhouse-crop plant biomass originated by tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum, L.)
Garzon, E; Morales, L; Ortiz-Rodriguez, IM; Sanchez-Soto, PJEnvironmental Science and Pollution Research, 25 (2018) 25880-25887
Show abstract ▽
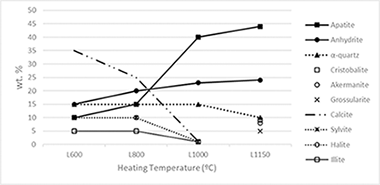
The most representative of greenhouse-crop plant biomass residues of tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) were selected for this study by using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The heating dynamics in air in the 600-1150 degrees C range of these residues for the production of renewable energy and the resultant ashes have been investigated. A total of 11 elements were determined by XRF in the biomass ashes and some minor elements. The content of alkaline elements and chlorides decreased as increasing heating temperature and disappeared at 1150 degrees C. Alkaline salts, NaCl and KCl, were volatilized by heating since 800 degrees C. The total contents of S and P in the biomass ashes were associated to CaSO4, and a complex phosphate identified by XRD. CaCO3 present at 600 degrees C was decomposed to CaO with disappearance at 1000 degrees C. By heating, new silicates were formed by solid-state reactions in the biomass residue. The minor elements have been found in a relative proportion lower than 0.9wt.% and they characterized the obtained ashes, with potential use as micronutrients.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-2577-y
- ‹ anterior
- 157 of 420
- siguiente ›














