Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales Coloidales
Structural, optical and X-ray attenuation properties of Tb3+: BaxCe1-xF3-x (x=0.18-0.48) nanospheres synthesized in polyol medium
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Genevois, C; Allix, M; Corral, A; Parrado-Gallego, A; Ocana, MDalton Transactions, 47 (2018) 8382-8391
Show abstract ▽
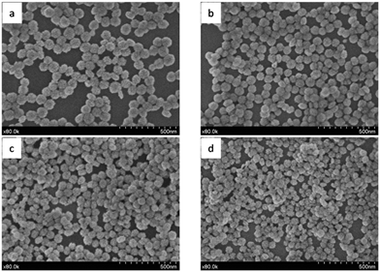
Uniform Ba0.18Ce0.82F2.82 nanospheres have been obtained after aging a solution of barium and cerium nitrates and sodium tetrafluoroborate in a mixture of ethylene glycol and water at 120 degrees C for 20 hours. The diameter of the spheres could be tailored from 65 nm to 80 nm by varying the NaBF4 concentration while maintaining their colloidal stability in aqueous suspension. Increasing the aging temperature led to a phase transformation from hexagonal to cubic symmetry and to a concomitant increase of the Ba/Ce ratio, which reached a value close to the nominal one (50/50) at 240 degrees C. The same method was successful in obtaining Tb3+-doped nanospheres with homogeneous cation distribution and the same morphological features as the undoped material. An intense green emission was observed after the excitation of the Tb3+-doped samples through the Ce3+-Tb3+ energy transfer (ET) band. The ET efficiency increased with increasing Tb content, the maximum emission being observed for the 10% Tb-doped nanospheres. Aqueous suspensions of the latter sample showed excellent X-ray attenuation values that were superior to those of an iodine-based clinically approved contrast agent. Their fluorescence and X-ray attenuation properties make this material a potential dual bioprobe for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography.
Julio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1039/c8dt01202d
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Comparison of solvent extraction and extraction chromatography resin techniques for uranium isotopic characterization in high-level radioactive waste and barrier materials
Hurtado-Bermudez, S; Villa-Alfageme, M; Mas, JL; Alba, MDApplied Radiation and Isotopes, 137 (2018) 177-183
Show abstract ▽
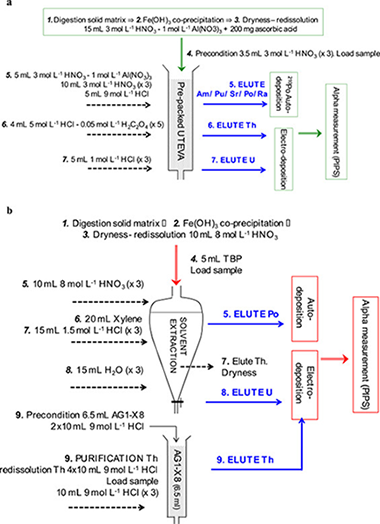
The development of Deep Geological Repositories (DGP) to the storage of high-level radioactive waste (HLRW) is mainly focused in systems of multiple barriers based on the use of clays, and particularly bentonites, as natural and engineered barriers in nuclear waste isolation due to their remarkable properties.
Due to the fact that uranium is the major component of HLRW, it is required to go in depth in the analysis of the chemistry of the reaction of this element within bentonites. The determination of uranium under the conditions of HLRW, including the analysis of silicate matrices before and after the uranium-bentonite reaction, was investigated. The performances of a state-of-the-art and widespread radiochemical method based on chromatographic UTEVA resins, and a well-known and traditional method based on solvent extraction with tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP), for the analysis of uranium and thorium isotopes in solid matrices with high concentrations of uranium were analysed in detail.
In the development of this comparison, both radiochemical approaches have an overall excellent performance in order to analyse uranium concentration in HLRW samples. However, due to the high uranium concentration in the samples, the chromatographic resin is not able to avoid completely the uranium contamination in the thorium fraction.
Julio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2018.04.008
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Photonic structuring improves the colour purity of rare-earth nanophosphors
Geng, DL; Cabello-Olmo, E; Lozano, G; Miguez, HMaterials Horizons, 5 (2018) 661-667
Show abstract ▽
Nanophosphor integration in an optical cavity allows unprecedented control over both the chromaticity and the directionality of the emitted light, without modifying the chemical composition of the emitters or compromising their efficiency. Our approach opens a route towards the development of nanoscale photonics based solid state lighting.
Julio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1039/c8mh00123e
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Design of Ag/ and Pt/TiO2-SiO2 nanomaterials for the photocatalyti degradation of phenol under solar irradiation
Matos, J; Llano, B; Montana, R; Poon, PS; Hidalgo, MCEnvironmental Science and Pollution Research, 25 (2018) 18894-18913
Show abstract ▽

The design of hybrid mesoporous TiO2-SiO2(TS1) materials decorated with Ag and Pt nanoparticles was performed. The photocatalytic degradation of phenol under artificial solar irradiation was studied and the activity and selectivity of the intermediate products were verified. TiO2-SiO(2)was prepared by sol-gel method while Ag- and Pt-based photocatalysts (TS1-Ag and TS1-Pt) were prepared by photodeposition of the noble metals on TS1. Two series of photocatalysts were prepared varying Ag and Pt contents (0.5 and 1.0 wt%). An increase in the photocatalytic activity up to two and five times higher than TS1 was found on TS1-Ag-1.0 and TS1-Pt-1.0, respectively. Changes in the intermediate products were detected on Ag- and Pt-based photocatalysts with an increase in the catechol formation up to 3.3 and 6.6 times higher than that observed on TS1, respectively. A two-parallel reaction mechanism for the hydroquinone and catechol formation is proposed. A linear correlation between the photocatalytic activity and the surface concentration of noble metals was found indicating that the electron affinity of noble metals is the driven force for both the increase in the photoactivity and for the remarkable changes in the selectivity of products.
Julio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-2102-3
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Plant cuticle under global change: Biophysical implications
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Guzman-Puyol, S; Benitez, JJ; Athanassiou, A; Heredia, A; Dominguez, EGlobal Change Biology, 24 (2018) 2749-2751
Show abstract ▽
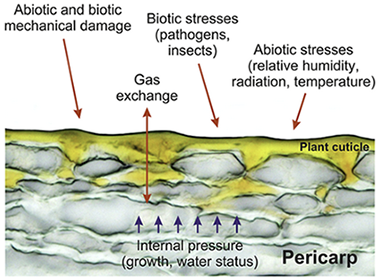
Climatic stressors due to global change induce important modifications to the chemical composition of plant cuticles and their biophysical properties.
In particular, plant cuticles can become heavier, stiffer and more inert, improving plant protection.
The climatic stressors that modify the chemical composition of plant tissues have been recently reviewed by Suseela and Tharayil (2018). In particular, the authors stated that the response of plants to global change effects (viz. increasing temperatures and frequent drought periods) can induce important modifications in plant cuticles such as an increase of the main cuticle components (cutin and polysaccharides), a preponderance of cutan, heavier wax loads, and changes in the chemical composition of waxes, mainly the accumulation of longer aliphatic compounds. In this letter, we would like to emphasize the biophysical consequences that this new scenario involves and how it would affect plant performance.
Julio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1111/gcb.14276
- ‹ anterior
- 161 of 420
- siguiente ›














