Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synergy achieved in silver-TiO2 nanocomposites for the inhibition of biofouling on limestone
Becerra, J; Zaderenko, AP; Sayagues, MJ; Ortiz, R; Ortiz, PBuilding and Environment, 141 (2018) 80-90
Show abstract ▽

Biodeterioration of stone monuments is estimated to be as high as 20-30% of the total degradation suffered by Cultural Heritage constructions. With regard to this problem, bactericidal treatments are mainly based on cleaning. These processes, while effective in the short term, require frequent reapplications increasing potential damages to the monument. Silver nanoparticles offer many advantages over traditionally employed products, such as their prolonged biocide efficacy and their low toxicity to humans and environment. The aim of this study was to evaluate the applicability and effectiveness of seven nanocomposite treatments based on titanium dioxide and/or silver nanoparticles to prevent biodeterioration of limestone monuments. These nanocomposites were characterized by UV Visible spectrophotometry, Dynamic Light Scattering and Electron Microscopy. To assess their bactericidal activity, accelerated weathering tests were performed on limestones from the quarry of Utrera, a source widely employed in such iconic monuments as the Cathedral of Seville (Spain). Furthermore, the samples of biopatina employed in our assays stemmed from the fa ades of historical buildings from Seville. Our results show that silver and titanium dioxide nanocomposites stabilized by citrate achieve a high biocide effect while maintaining color alterations at a low level.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.05.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Unravelling the Role of Oxygen Vacancies in the Mechanism of the Reverse Water-Gas Shift Reaction by Operando DRIFTS and Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy
Bobadilla, LF; Santos, JL; Ivanova, S; Odriozola, JA; Urakawa, AACS Catalysis, 8 (2018) 7455-7467
Show abstract ▽
The reaction mechanism of the reverse water gas shift (RWGS) reaction was investigated using two commercial gold-based catalysts supported on Al2O3 and TiO2. The surface species formed during the reaction and reaction mechanisms were elucidated by transient and steady-state operando DRIFTS studies. It was revealed that RWGS reaction over Au/Al2O3 proceeds through the formation of formate intermediates that are reduced to CO. In the case of the Au/TiO2 catalyst, the reaction goes through a redox mechanism with the suggested formation of hydroxycarbonyl intermediates, which further decompose to CO and water. The Ti-3+ species, the surface hydroxyls, and oxygen vacancies jointly participate. The absence of carbonyl species adsorbed on gold particles during the reaction for both catalysts indicates that the reaction pathway involving dissociative adsorption of CO2 on Au particles can be discarded. To complete the study, operando ultraviolet visible spectroscopy was successfully applied to confirm the presence of Ti3+ and to understand the role of the oxygen vacancies of TiO2 support in activating CO2 and thus the subsequent RWGS reaction.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02121
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Structural Reversibility of LaCo1-xCuxO3 Followed by In Situ X-ray Diffraction and Absorption Spectroscopy
Pereniguez, Rosa; Ferri, DavideChemphyschem, 19 (2018) 1876-1885
Show abstract ▽
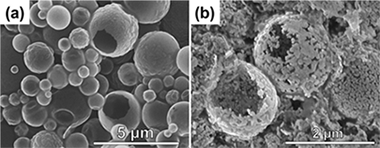
Combinations of perovskite-type oxides with transition and precious metals exhibit a remarkable self-regenerable property that could be exploited for numerous practical applications. The objective of the present work was to study the reversibility of structural changes of perovskite-type oxides under cyclic reducing/oxidizing atmosphere by taking advantage of the reducibility of LaCoO3. LaCoO3 +/- and LaCo0.8Cu0.2O3 +/- were prepared by ultrasonic spray combustion and were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and temperature-programmed reduction (TPR). XRD and XAS data confirmed that copper adopted the coordination environment of cobalt at the B-site of the rhombohedral LaCoO3 under the selected synthesis conditions. The structural evolution under reducing atmosphere was studied by insitu XRD and XANES supporting the assignment of the observed structural changes to the reduction of the perovskite-type oxide from ABB'O-3 (B'=Cu) to B'(0)/ABO(3) and to B'B-0(0)/A(2)O(3). Successive redox cycles allowed the observation of a nearly complete reversibility of the perovskite phase, i.e. copper was able to revert into LaCoO3 upon oxidation. The reversible reduction/segregation of copper and incorporation at the B-site of the perovskite-type oxides could be used in chemical processes where the material can be functionalized by segregation of Cu and protected against irreversible structural changes upon re-oxidation.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201800069
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis, structural, magnetic, optical and electrooptical properties of CuFeS2 nanoparticles
Dutkova, E; Bujnakova, Z; Kovac, J; Skorvanek, I; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Kovac, J; Balaz, PAdvanced Powder Technology, 29 (2018) 1820-1826
Show abstract ▽
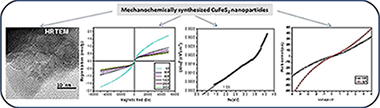
The rapid mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline CuFeS2 particles prepared by high-energy milling for 60 min in a planetary mill from copper, iron and sulphur elements is reported. The CuFeS2 nanoparticles crystallize in tetragonal structure with mean crystallite size of about 38 ± 1 nm determined by XRD analysis. HRTEM study also revealed the presence of nanocrystals with the size of 5–30 nm with the tendency to form agglomerates. The Raman spectrum confirms the chalcopyrite structure. Low temperature magnetic data for CuFeS2 support the coexistence of antiferromagnetic and paramagnetic spin structure. Moreover, the hysteresis loops taken at temperatures from 5 K to 300 K revealed a presence of very small amount of ferromagnetic phase, which seems to be associated with the non-consumed elemental Fe in as-prepared nanoparticles. The optical band gap of CuFeS2nanoparticles has been detected to be 1.05 eV, larger than band gap of the bulk material. The wider gap possibly resulted from the nano-size effect. Photoresponses of CuFeS2nanoparticles were confirmed by I-V measurements under dark and light illumination. It was demonstrated that mechanochemical synthesis can be successfully employed in the one step preparation of nanocrystalline CuFeS2 with good structural, magnetic, optical and electrooptical properties.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2018.04.018
Reactividad de Sólidos
Surface modification of Ti-6Al-4V alloys manufactured by selective laser melting: Microstructural and tribo-mechanical characterization
Torres, Y; Sarria, P; Gotor, FJ; Gutierrez, E; Peon, E; Beltran, AM; Gonzalez, JESurface & Coatings Technology, 348 (2018) 31-40
Show abstract ▽
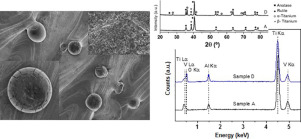
Medical grade of both titanium (Ti) and Ti6A14V alloy are recognized as the metallic biomaterials with the better outcomes for clinical repair of bone tissue thanks to their suitable mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. However, those Ti advantages are not enough to avoid failure risks of bone implants; between 5 and 10% of Ti implants fail due to a deficient osseointegration, within 5 years of post-implantation. Most of these failures indicate the necessity of getting a better biomechanical-biofunctional balance. Microstructural and tribo-mechanical characterizations were performed on Ti6A14V samples obtained by selective laser melting and subjected to different surface treatments (thermal stress relief, acid etching, chemical treatment and thermochemical treatment). Scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction were used for detailed characterization of the elemental composition, phase analysis and surface morphology. Micro-hardness and scratch tests were employed to evaluate the tribo-mechanical properties, which were improved after consecutive surface treatments. Protuberances with spherical morphology, as a remainder of the original powder, were present on the surface. The resulting modified surfaces were constituted by rutile (major phase) and anatase (minor phase). Submicro-nano-topographies were obtained after the chemical and thermochemical treatments.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.05.015
- ‹ anterior
- 160 of 420
- siguiente ›














