Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Iron-Catalyzed Graphitic Carbon Materials from Biomass Resources as Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Gomez-Martin, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ruttert, M; Heckmann, A; Winter, M; Placke, T; Ramirez-Rico, JChemsuschem, 11 (2018) 2776-2787
Show abstract ▽
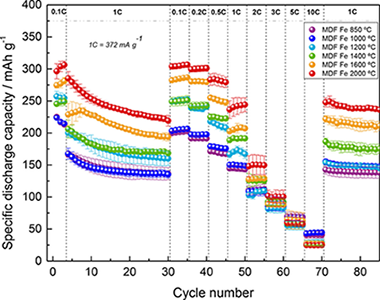
Graphitized carbon materials from biomass resources were successfully synthesized with an iron catalyst, and their electrochemical performance as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) was investigated. Peak pyrolysis temperatures between 850 and 2000 degrees C were covered to study the effect of crystallinity and microstructural parameters on the anodic behavior, with a focus on the first-cycle Coulombic efficiency, reversible specific capacity, and rate performance. In terms of capacity, results at the highest temperatures are comparable to those of commercially used synthetic graphite derived from a petroleum coke precursor at higher temperatures, and up to twice as much as that of uncatalyzed biomass-derived carbons. The opportunity to graphitize low-cost biomass resources at moderate temperatures through this one-step environmentally friendly process, and the positive effects on the specific capacity, make it interesting to develop more sustainable graphite-based anodes for LIBs.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201800831
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis and characterization of SiC/Si3N4 composites from rice husks
Real, C; Cordoba, JM; Alcala, MDCeramics International, 44 (2018) 14645-14651
Show abstract ▽
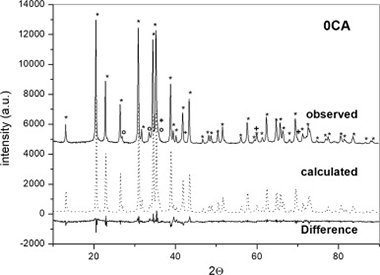
SiC-Si3N4 composites have been obtained by carbothermal reduction of rice husk under a nitrogen-argon atmosphere at 1450 degrees C, which is a lower temperature than those used by other authors. On the other hand, tailoring the argon/nitrogen ratio led to the obtained of SiC-Si3N4 composites across the whole range of compositions. Phosphoric acid treatment permited the synthesis of the composite without a pyrolysis step. The final products were characterized by X-ray diffractometry, IR spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.090
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Solar pilot plant scale hydrogen generation by irradiation of Cu/TiO2 composites in presence of sacrificial electron donors
Maldonado, MI; Lopez-Martin, A; Colon, G; Peral, J; Martinez-Costa, JI; Malato, SApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 229 (2018) 15-23
Show abstract ▽
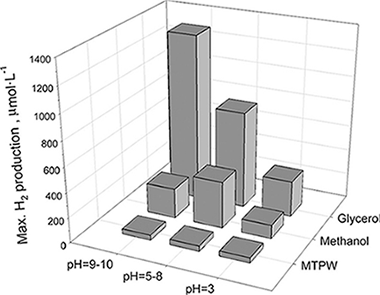
A Cu/TiO2 photocatalyst has been synthesised by reducing a Cu precursor with NaBH4 onto the surface of a sulphate pretreated TiO2 obtained by a sol-gel procedure. The catalyst, that shows a clearly defined anatase phase with high crystallinity and relatively high surface area, and contains Cu2O and CuO deposits on its surface, has been used to produce hydrogen in a solar driven pilot plant scale photocatalytic reactor. Different electron donor aqueous solutions (methanol, glycerol, and a real municipal wastewater treatment plant influent) have been tested showing similar or even higher energy efficiency than those obtained using more expensive noble metal based photocatalytic systems. The glycerol solutions have provided the best reactive environments for hydrogen generation.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.02.005
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of milling mechanism on the CO2 capture performance of limestone in the Calcium Looping process
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 346 (2018) 549-556
Show abstract ▽
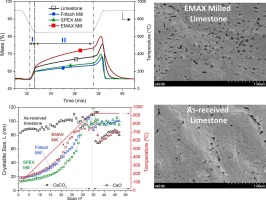
This work analyzes the relevant influence of milling on the CO2 capture performance of CaO derived from natural limestone. Diverse types of milling mechanisms produce contrasting effects on the microstructure of the CaO formed after calcination of the milled limestone samples, which affects crucially the kinetics of carbonation at conditions for CO2 capture. The capture capacity of CaO derived from limestone samples milled using either shear or impact based mills is impaired compared to as-received limestone. After calcination of the milled samples, the resulting CaO porosity is increased while crystallinity is enhanced, which hinders carbonation. Conversely, if the material is simultaneously subjected to intense impact and shear stresses, CaO porosity is promoted whereas CaO cristanillity is reduced, which enhances carbonation in both the reaction and solid-state diffusion controlled regimes.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.146
Reactividad de Sólidos
On the determination of thermal degradation effects and detection techniques for thermoplastic composites obtained by automatic lamination
Martin, MI; Rodriguez-Lence, F; Guemes, A; Fernandez-Lopez, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, AComposites part A-Applied science and manufacturing, 111 (2018) 23-32
Show abstract ▽
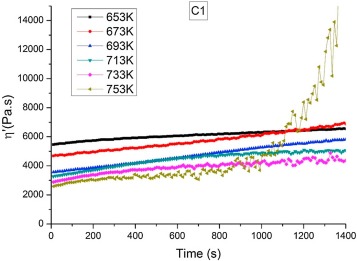
Automatic lay-up and in-situ consolidation with thermoplastic composite materials is a technology under research for its expected use in the profitable manufacturing of structural aeronautical parts. This study is devoted to analysing the possible effects of thermal degradation produced by this manufacturing technique.
Rheological measurements showed that there is negligible degradation in PEEK for the temperatures reached during the process. Thermogravimetric analysis under linear heating and constant rate conditions show that thermal degradation is a complex process with a number of overlapping steps. A general kinetic equation that describes the degradation of the material with temperature has been proposed and validated. Attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirmed that there is no remarkable degradation. The use of a combination of in-situ and ex-situ experimental techniques, including kinetic modelling, not only provides reliable information about degradation but also allows setting optimal processing conditions.
Agosto, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.05.006
- ‹ anterior
- 159 of 420
- siguiente ›














