Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photo-induced processes on Nb2O5 synthesized by different procedures
Jaramillo-Páez, C., Sánchez-Fernández, F.J., Navío, J.A., Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 359 (2018) 40-52
Show abstract ▽
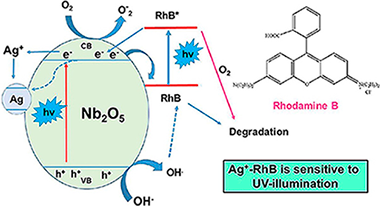
The properties of Nb2O5 strongly depend on its synthesis procedure as well as the conditions of ulterior thermal treatment. We report the synthesis of Nb2O5 powders prepared by sol-gel precipitation method using niobium(V) ethoxide as precursor. Two chemical routes were chosen: the presence of tryethyl amine (TEA) as precipitant/template agent, or the oxidant peroxide method. In addition, microwave-assisted activation was also used. The as-prepared samples by the above procedures were amorphous. Structural changes upon heating from room temperature up to 800 °C were investigated by X-ray powder diffraction technique combined with thermogravimetric analysis. The sequential thermal treatment up to 800 °C promotes the crystallization of hexagonal phase to orthorhombic phase whereas the ulterior cooling to room temperature lead to a mixture of both phases. Samples calcined at selected temperatures of either 600 °C or 800 °C for 2 h, were characterized by XRD, SEM, N2-adsorption and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). The synthetic approach routes as well as the combined microwave activation followed by ulterior thermal treatment lead to changes not only on particle size but also on the textural properties of the synthesized catalysts. The catalysts synthesized have been evaluated using Rhodamine B (RhB) as a substrate, under both UV and visible lighting conditions. None of the catalysts synthesized showed activity in the visible. Under UV-illumination conditions, some of the catalysts exhibited a relatively low photoactivity in the degradation of RhB, which is associated with a photo-sensitizing effect. However, the addition of Ag+ ions considerably increased the activity of all the catalysts in the degradation of RhB under UV-illumination conditions. A mechanism is proposed to explain the photo-induced processes obtained, leaving the door open to the possible implications of the observed results in relation to the interaction of RhB dye with noble metal nanoparticles such as silver.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.040
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Chemical CO2 recycling via dry and bi reforming of methane using Ni-Sn/Al2O3 and Ni-Sn/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts
Stroud, T; Smith, TJ; Le Sache, E; Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Arellano-Garcia, H; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 224 (2018) 125-135
Show abstract ▽
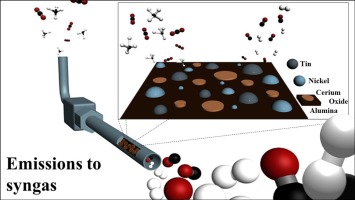
Carbon formation and sintering remain the main culprits regarding catalyst deactivation in the dry and bi-reforming of methane reactions (DRM and BRM, respectively). Nickel based catalysts (10 wt.%) supported on alumina (Al2O3) have shown no exception in this study, but can be improved by the addition of tin and ceria. The effect of two different Sn loadings on this base have been examined for the DRM reaction over 20 h, before selecting the most appropriate Sn/Ni ratio and promoting the alumina base with 20 wt.% of CeO2. This catalyst then underwent activity measurements over a range of temperatures and space velocities, before undergoing experimentation in BRM. It not only showed good levels of conversions for DRM, but exhibited stable conversions towards BRM, reaching an equilibrium H-2/CO product ratio in the process. In fact, this work reveals how multicomponent Ni catalysts can be effectively utilised to produce flexible syngas streams from CO2/CH4 mixtures as an efficient route for CO2 utilisation.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.047
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of a novel TiNbTa material potentially suitable for bone replacement implants
Chicardi, E; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, CF; Sayagues, MJ; Garcia-Garrido, CMaterials & Design, 145 (2018) 88-96
Show abstract ▽
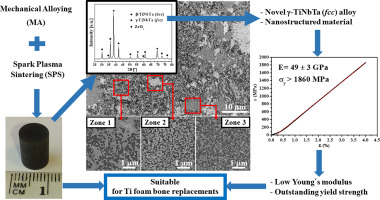
A novel (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa alloy has been developed by a combined low energy mechanical alloying (LEMA) and pulsed electric current sintering process (PECS). Microstructurally, this material presents interesting characteristics, such as a submicrometric range of particle size, a body-centered phase (beta-TiNbTa) and, mainly, a novel face-centered cubic Ti-based alloy (gamma-TiNbTa) not previously reported. Related to mechanical performance, the novel (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa shows a lower E (49 +/- 3 GPa) and an outstanding yield strength (sigma(y) 1860 MPa). This combination of original microstructure and properties makes to the (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa a novel material potentially suitable as biomaterial to fabricate bone replacement implants, avoiding the undesirable and detrimental stressshielding problem and even the usual damage on the mechanical strength of Ti-based foams biomaterials.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.02.042
Reactividad de Sólidos
Carbonation of Limestone Derived CaO for Thermochemical Energy Storage: From Kinetics to Process Integration in Concentrating Solar Plants
Ortiz, C; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6 (2018) 6404-6417
Show abstract ▽
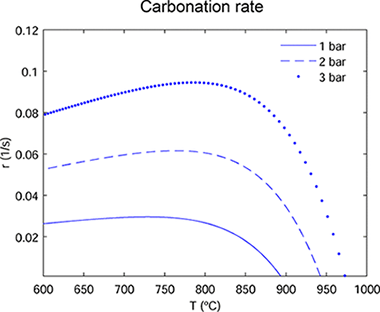
Thermochemical energy storage (TCES) is considered as a promising technology to accomplish high energy storage efficiency in concentrating solar power (CSP) plants. Among the various possibilities, the calcium-looping (CaL) process, based on the reversible calcination–carbonation of CaCO3 stands as a main candidate due to the high energy density achievable and the extremely low price, nontoxicity, and wide availability of natural CaO precursors such as limestone. The CaL process is already widely studied for CO2 capture in fossil fuel power plants or to enhance H2 production from methane reforming. Either one of these applications requires particular reaction conditions to which the sorbent performance (reaction kinetics and multicycle conversion) is extremely sensitive. Therefore, specific models based on the conditions of any particular application are needed. To get a grip on the optimum conditions for the carbonation of limestone derived CaO in the CaL-CSP integration, in the present work is pursued a multidisciplinary approach that combines theoretical modeling on reaction kinetics, lab-scale experimental tests at relevant CaL conditions for TCES, process modeling, and simulations. A new analytic equation to estimate the carbonation reaction rate as a function of CO2 partial pressure and temperature is proposed and validated with experimental data. Using the kinetics analysis, a carbonator model is proposed to assess the average carbonation degree of the solids. After that, the carbonator model is incorporated into an overall process integration scheme to address the optimum operation conditions from thermodynamic and kinetics considerations. Results from process simulations show that the highest efficiencies for the CaL-CSP integration are achieved at carbonator absolute pressures of ∼3.5–4 bar, which leads to an overall plant efficiency (net electric power to net solar thermal power) around 41% when carbonation is carried out at 950 °C under pure CO2
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00199
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribological properties of TiC/a-C:H nanocomposite coatings prepared via HiPIMS
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Dominguez-Meister, S; Rojas, TC; Colasuonno, M; Bazzan, M; Patelli, AApplied Surface Science, 440 (2018) 458-466
Show abstract ▽
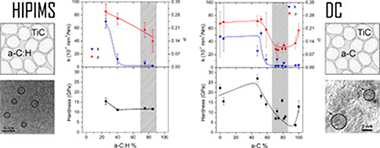
High power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) technology has been employed to prepare TiC/a-C:H nanocomposite coatings from a titanium target in acetylene (C2H2) reactive atmospheres. Gas fluxes were varied from 1.3 to 4.4 sccm to obtain C/Ti ratios from 2 to 15 as measured by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA). X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy demonstrate the presence of TiC nanocrystals embedded in an amorphous carbon-based matrix. The hardness properties decrease from 17 to 10 GPa as the carbon content increases. The tribological properties were measured using a pinon-disk tribometer in ambient air (RH = 30-40%) at 10 cm/s with 5 N of applied load against 6-mm 100Cr6 balls. The friction coefficient and the film wear rates are gradually improved from 0.3 and 7 x 10(-6) mm(3)/N m to 0.15 and 2 x 10(-7) mm(3)/N m, respectively, by increasing the C2H2 flux. To understand the tribological processes appearing at the interface and to elucidate the wear mechanism, microstructural and chemical investigations of the coatings were performed before and after the friction test. EPMA, X-ray photoelectron and electron energy-loss spectroscopies were employed to obtain an estimation of the fraction of the a-C:H phase, which can be correlated with the tribological behavior. Examination of the friction counterfaces (ball and track) by Raman microanalysis reveals an increased ordering of the amorphous carbon phase concomitant with friction reduction. The tribological results were compared with similar TiC/a-C(:H) composites prepared by the conventional direct current process.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.135
- ‹ anterior
- 165 of 420
- siguiente ›














