Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Reactividad de Sólidos
Fabrication and characterization of WC-HEA cemented carbide based on the CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy
Velo, IL; Gotor, FJ; Alcala, MD; Real, C; Cordoba, JMJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 746 (2018) 1-8
Show abstract ▽
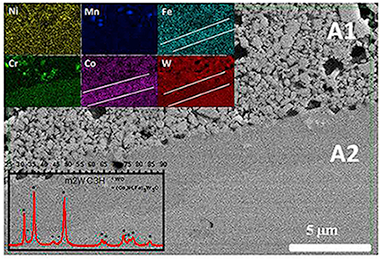
A high entropy alloy (HEA, CoCrFeNiMn) synthesized by mechanical alloying was used as the binder for the densification of WC by a pressureless high temperature procedure. Three different WC were used by modifying its microstructure with a high energy ball milling treatment. The alloy content in the HEA-WC mixture was varied from 10 to 30% vol. The microstructure and properties of the sintered composites were studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and microindentation.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.292
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Study of the effectiveness of the flocculation-photocatalysis in the treatment of wastewater coming from dairy industries
Murcia, J.J., Hernández-Laverde, M., Rojas, Muñoz, E., Navío, J.A., Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 358 (2018) 256-264
Show abstract ▽
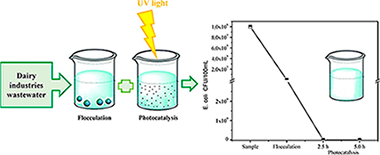
The aim of the present work was to evaluate the effectiveness of flocculation-photocatalysis as combined processes in the treatment of dairy industries wastewater. Different commercial and lab prepared flocculants and photocatalysts were evaluated. All the materials prepared were extensively characterized. Commercial materials presented the best physicochemical properties and performance in the treatment of the studied wastewater. On one hand, all the photocatalysts evaluated showed bactericidal activity for E. Coli, total coliforms and other enterobacteriaceae. Total elimination of E. coli was obtained by using commercial TiO2 P25 Evonik, under 120 W/m2 of UV–vis light intensity and 5 h of total illumination time. Other species of bacteria remained after treatment under these conditions. It was also found that the highest light intensity of 120 W/m2 led to increase the Chemical Oxygen Demand and Total Organic Carbon in the samples treated, it can be due to the faster formation of new organic compounds as intermediaries during the photocatalytic reactions at the highest photonic flux. Flocculation pre-treatment of the wastewater samples led to improve the effectiveness of the photocatalytic treatment; thus, the combination of flocculation-photocatalysis treatments at low light intensity of 30 W/m2 leads to achieve the total elimination of E. coli, and under this intensity the elimination of total coliforms and other enterobacteriaceae increased 5.48% compared to the photocatalytic treatment alone. These treatment conditions led to comply the Colombian regulations for dairy wastewater.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.034
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the Mn content on the TiNbxMn alloys with a novel fcc structure
Chicardi, E; Aguilar, C; Sayagues, MJ; Garcia-Garrido, CJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 746 (2018) 601-610
Show abstract ▽

This work studies the structural evolution of TiNbxMn alloys (x: 0-12 wt%) synthetized by mechanical alloying in a planetary ball mill with different milling times between 1 h and 120 h. The specimens were characterized by X-ray diffraction patterns, scanning and transmission electron microscopies and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. It was observed an evolution of the alloys developed from the raw Ti, Nb and Mn elements to bcc-TiNbxMn alloys and, finally, novel fcc-TiNbxMn alloys, with Fm3m space group symmetry, not previously observed. The presence of Mn promotes other interesting effects: a) the decreasing of the crystallite and the particle sizes, reaching values close to 4 nm and 400 nm, respectively, b) the partial amorphization of the fcc-TiNbxMn alloys due to the combined effect of the Mechanical Alloying and the difference of Mn atomic size in comparison with Ti and Nb and c) the presence of Mn that decreases the Fe amount (from milling media) in the as-milled powders.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.306
Reactividad de Sólidos
Crystallization Kinetics of Nanocrystalline Materials by Combined X-ray Diffraction and Differential Scanning Calorimetry Experiments
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Medina-Carrasco, S; Kupcik, J; Subrt, J; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LACrystal Growth & Design, 18 (2018) 3107-3116
Show abstract ▽
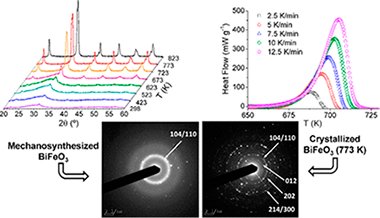
Crystallization is one key aspect in the resulting properties of nanocrystalline functional materials, and much effort has been devoted to understanding the physical mechanisms involved in these processes as a function of temperature. The main problems associated with crystallization kinetic studies come from the limitations of the employed techniques, and the obtained results may vary significantly depending on the choice of the measurement method. In this work, a complete description of the thermal crystallization event of nanocrystalline BiFeO3 has been performed by combining the information obtained from three different experimental techniques: in situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry. Interestingly, the kinetic analysis of the X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry data yields almost identical results, although the physical properties measured by both techniques are different. This allows the unambiguous determination of the kinetic parameters. The importance of a proper definition of the conversion degree, which is limited by the employed measurement technique, is also highlighted.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00241
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photo-induced processes on Nb2O5 synthesized by different procedures
Jaramillo-Páez, C., Sánchez-Fernández, F.J., Navío, J.A., Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 359 (2018) 40-52
Show abstract ▽
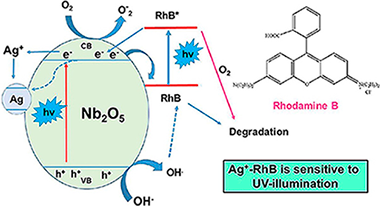
The properties of Nb2O5 strongly depend on its synthesis procedure as well as the conditions of ulterior thermal treatment. We report the synthesis of Nb2O5 powders prepared by sol-gel precipitation method using niobium(V) ethoxide as precursor. Two chemical routes were chosen: the presence of tryethyl amine (TEA) as precipitant/template agent, or the oxidant peroxide method. In addition, microwave-assisted activation was also used. The as-prepared samples by the above procedures were amorphous. Structural changes upon heating from room temperature up to 800 °C were investigated by X-ray powder diffraction technique combined with thermogravimetric analysis. The sequential thermal treatment up to 800 °C promotes the crystallization of hexagonal phase to orthorhombic phase whereas the ulterior cooling to room temperature lead to a mixture of both phases. Samples calcined at selected temperatures of either 600 °C or 800 °C for 2 h, were characterized by XRD, SEM, N2-adsorption and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). The synthetic approach routes as well as the combined microwave activation followed by ulterior thermal treatment lead to changes not only on particle size but also on the textural properties of the synthesized catalysts. The catalysts synthesized have been evaluated using Rhodamine B (RhB) as a substrate, under both UV and visible lighting conditions. None of the catalysts synthesized showed activity in the visible. Under UV-illumination conditions, some of the catalysts exhibited a relatively low photoactivity in the degradation of RhB, which is associated with a photo-sensitizing effect. However, the addition of Ag+ ions considerably increased the activity of all the catalysts in the degradation of RhB under UV-illumination conditions. A mechanism is proposed to explain the photo-induced processes obtained, leaving the door open to the possible implications of the observed results in relation to the interaction of RhB dye with noble metal nanoparticles such as silver.
Mayo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.040
- ‹ anterior
- 166 of 420
- siguiente ›














