Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust polarization active nanostructured 1D Bragg Microcavities as optofluidic label-free refractive index sensor
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 256 (2018) 590-599
Show abstract ▽
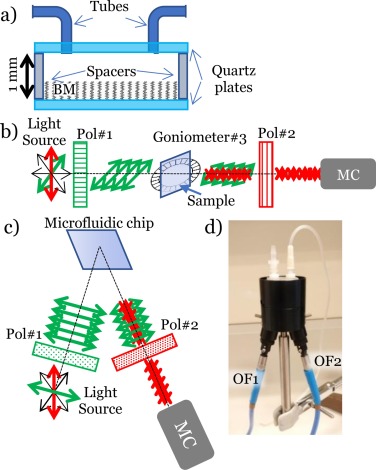
In this work we report the use of polarization active porous 1D Bragg microcavities (BM) prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for the optofluidic analysis of liquid solutions. These photonic structures consist of a series of stacked highly porous layers of two materials with different refractive indices and high birefringence. Their operational principle implies filling the pores with the analyzed liquid while monitoring with linearly polarized light the associated changes in optical response as a function of the solution refractive index. The response of both polarization active and inactive BMs as optofluidic sensors for the determination of glucose concentration in water solutions has been systematically compared. Different methods of detection, including monitoring the BM wave retarder behavior, are critically compared for both low and high glucose concentrations. Data are taken in transmission and reflection modes and different options explored to prove the incorporation of these nanostructured transducers into microfluidic systems and/or onto the tip of an optical fiber. This analysis has proven the advantages of the polarization active transducer sensors for the optofluidic analysis of liquids and their robustness even in the presence of light source instabilities or misalignments of the optical system used for detection.
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.060
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis of Pd-Al/biomorphic carbon catalysts using cellulose as carbon precursor
Cazana, F; Galetti, A; Meyer, C; Sebastian, V; Centeno, MA; Romeo, E; Monzon, ACatalysis Today, 301 (2018) 226-238
Show abstract ▽

This work presents the results obtained with novel Pd and Pd-Al catalysts supported on carbon, which have been prepared using a biomorphic mineralization technique. The catalyst synthesis procedure includes a stage of thermal decomposition under reductive atmosphere of cellulose previously impregnated with the metallic precursors. We have studied the influence of the temperature and time of decomposition, and of the Al precursor addition, on the textural and catalytic properties. The characterisation results indicate that the preparation method used leads to the formation of carbonaceous supports with a high microporosity (up to 97% micropore volume) and values of the BET surface up to 470 m2/g while maintaining the original external structure. The use of low temperatures (ca. 600 °C) during the decomposition step allows the preparation of highly dispersed catalysts with narrow Pd particle size distributions. However, the thermal decomposition at elevated temperatures (ca. 800 °C) increases the Pd particle size due to the sintering of the metallic phase. This phenomenon is augmented with the decomposition time and is not affected by the presence of Al. Consequently, the catalytic activity of these materials in cyclohexene hydrogenation is strongly affected by the operational conditions used during the thermal decomposition step. Unexpectedly, the more sintered catalysts, i.e. those prepared at 800 °C, show the highest activity. According to the characterization results, this fact can be explained considering that the smaller Pd particles obtained after preparation at e.g. 600 °C are quite inactive because they are confined in the internal structure of the micropores of the support and/or embedded inside the carbon matrix. In contrast, after decomposition at 800 °C, the larger Pd particles formed are placed at the external surface of the catalyst, being accessible to the reactants. In addition, for the specific conditions under which the Pd is accessible, the presence of Al favours the cyclohexene conversion due to the enhancement of the adsorption on the Pd surface as a consequence of a charge transfer phenomenon. These results can serve as a guideline for the preparation of these catalysts based on raw lignocellulosic materials in order to maximize their catalytic performance.
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.05.026
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold catalyst recycling study in base-free glucose oxidation reaction
Megias-Sayago, C.; Bobadilla, L. F.; Ivanova, S.; Penkova, A.; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Catalysis Today, 301 (2018) 72-77
Show abstract ▽
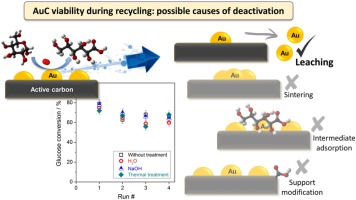
This work is devoted to the study of viability of immobilized gold colloids on carbon as catalysts for the base-free glucose oxidation reaction with a special emphasis made on catalysts' recycling, operational life and possible routes for deactivation/reactivation under batch conditions. The observed catalytic behavior is related to all possible manners of deactivation, like gold metal state changes (particle size agglomeration or leaching), support modifications or active sites blocking by intermediates. In an attempt to recover the initial catalytic activity, the samples are subjected to different treatments such as H2O and NaOH washings and calcination. The failure of the regeneration procedures to recover the initial activity and after detailed catalyst' characterization allows us to find out the main cause of deactivation
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.03.022
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and optical properties of environmentally benign and highly uniform NaCe(MoO4)(2) based yellow nanopigments
Laguna, M; Nuñez, NO; Fernandez, M; Ocaña, MJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 739 (2018) 542-548
Show abstract ▽
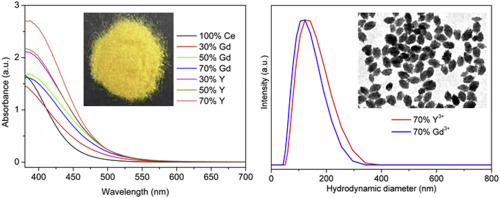
A method for the synthesis of uniform and aggregation free NaCeMoO4 based nanospheroids with tunable size is reported. The procedure is based on a precipitation reaction at 120 degrees C for 20 h from solutions containing Na2MoO4, sodium citrate and Ce(NO3)(3) and different amounts of Y(NO3)(3) or Gd(NO3)(3). The role played by the later compounds on the formation of the particles and their morphological and structural characteristics is analyzed through the analysis of the mechanism of particle formation. The chromaticity coordinates of the obtained samples are also evaluated showing that the here reported nanoparticles constitute an ecofriendly alternative to more toxic commercial yellow pigments. The synthesized nanoparticles are also free of aggregation in water suspensions and might be suitable for injet-printing technologies.
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.158
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO2 reforming of methane over Ni-Ru supported catalysts: On the nature of active sites by operando DRIFTS study
Alvarez, A; Bobadilla, LF; Garcilaso, V; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of CO2 utilization, 24 (2018) 509-515
Show abstract ▽
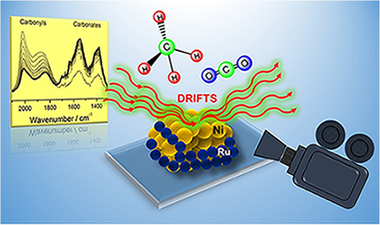
The present paper addresses the nature of the active sites of a bimetallic Ni-Ru supported catalyst on the dry reforming of methane (DRM). The structural characterization by XRD and Raman spectroscopy, along with the reducibility study (TPR-H-2) of the samples, evidenced the existence of a strong Ni-Ru interaction in the bimetallic system. We have assumed that Ru atoms block the most reactive Ni sites (step-edge sites) leaving less reactive centers for methane activation (terraces). In this way, operando DRIFTS measurements revealed that Ru decreases the catalytic activity but favors the carbon gasification and prevents the CO dissociation.
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.01.027
- ‹ anterior
- 173 of 420
- siguiente ›














