Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Experimental measurement of the filtration efficiency and pressure drop of wall-flow diesel particulate filters (DPF) made of biomorphic Silicon Carbide using laboratory generated particles
Orihuela, MP; Gomez-Martin, A; Miceli, P; Becerra, JA; Chacartegui, R; Fino, DApplied Thermal Engineering, 131 (2018) 41-53
Show abstract ▽
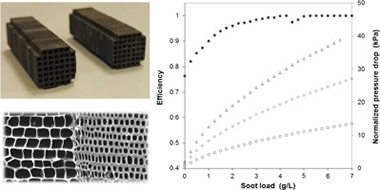
Biomorphic Silicon Carbide (bioSiC) has been recently introduced in the scope of porous ceramic substrates for hot gas filtration applications, where it has demonstrated to have good thermal and mechanical properties, and a high potential to meet the requirements for current Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF). In this experimental study, a small wall-flow bioSiC diesel filter was characterized using a soot generator, the particle size distribution of which being similar to the one generated by a diesel engine. The bioSiC samples were manufactured from Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) following a general manufacturing procedure for bioSiC ceramics, but paying special attention in the mechanizing stage to the geometry and optimal design of the honeycomb structure required for diesel engine applications. The samples had a cell density of 57.59 cell/cm(2) (371.6 cpsi), a square cross section of 9.2 x 9.2 mm, and a length of 31 mm. To generate the particle laden stream and perform the filtration tests, a synthetic Soot Generator (SG) was used. Tests were performed under controlled and reproducible conditions, with a fixed gas flow rate of 5 LPM and a soot mass flow rate of 4 mg/h. The filtration efficiency was determined with the aid of a Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer (SMPS) from the measurements of the particle concentration upstream and downstream the filter samples. During the soot loading process, the pressure drop was also monitored. The results show that, in the initial stage (clean filter), bioSiC wall-flow DPFs may have a filtration efficiency between 0.7 and 0.85 and a pressure drop of around 2 kPa for a normalized wall velocity of 0.01 m/s at ambient temperature. The filtration performance of wall-flow bioSiC particle filters showed in this work can help us to better understand their real potential for automotive applications.
Febrero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.149
Materiales Coloidales
Laterally and Temporally Controlled Intracellular Staining by Light-Triggered Release of Encapsulated Fluorescent Markers
Kantner, K; Rejman, J; Kraft, KVL; Soliman, MG; Zyuzin, MV; Escudero, A; del Pino, P; Parak, WJChemistry-A European Journal, 24 (2018) 2098-2102
Show abstract ▽
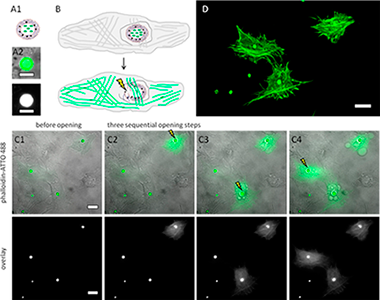
Fluorescent molecular markers were encapsulated. The capsules were additionally modified with plasmonic nanoparticles. The encapsulated markers were endocytosed by cells. Upon light stimulation the plasmonic nanoparticles generated heat, which opened the encapsulation and transiently perforated the endosomal/lysosomal membrane surrounding the capsule, thus allowing for release of the marker into the cytosol. Fluorescence labeling of different intracellular compartments was demonstrated in this way. Most important, the cells do not need to be fixed and perforated, as the molecular markers are introduced into cells by endocytosis and subsequent light-induced release. Thus this technique allows for intracellular fluorescence labeling of living cells.
Febrero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/chem.201706135
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Basicity on the Hydrolysis of the Bi(III) Aqua Ion in Solution: An Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Study
Ayala, R; Martinez, JM; Pappalardo, RR; Refson, K; Marcos, ESJournal of Physical Chemistry A, 122 (2018) 1905-1915
Show abstract ▽
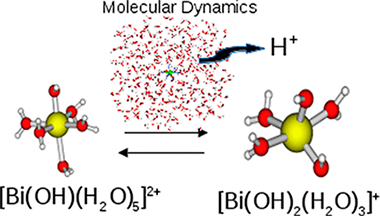
Hydrolysis of the Bi(III) aqua ion under a range of solution conditions has been studied by means of ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. While the Bi(III) aqua ion is stable in pure water, there is an increasing degree of hydrolysis with the number of hydroxide anions in the medium. This is accompanied by a monotonic decrease of the total coordination number to an asymptotic value of similar to 6, reached under extreme basicity conditions. Comparison of the simulated Bi(III) hydrolyzed species with the experimental species distribution at different degrees of basicity suggests that, at the PBE/DFT level of theory here employed, liquid water shows an overly acidic character. Predictions of theoretical EXAFS and XANES spectra were generated from the AIMD trajectories for different Bi hydrolyzed species, [Bi(HO)(m)(H2O)(n)](3-m+), m = 0-3 and n = 7-2. Comparison with available experimental spectra is presented. Spectral features joined to the degree of hydrolysis and hydration are analyzed.
Febrero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b12402
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Self-Assembly of the Nonplanar Fe(III) Phthalocyanine Small-Molecule: Unraveling the Impact on the Magnetic Properties of Organic Nanowires
Filippin, AN; Lopez-Flores, V; Rojas, TC; Saghi, Z; Rico, VJ; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Espinos, JP; Zitolo, A; Viret, M; Midgley, PA; Barranco, A; Borras, AChemistry of Materials, 30 (2018) 879-887
Show abstract ▽
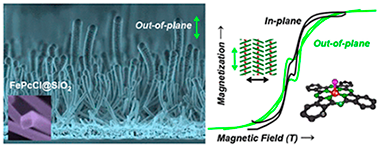
In this article we show for the first time the formation of magnetic supported organic nanowires (ONWs) driven by self-assembly of a nonplanar Fe(III) phthalocyanine chloride (FePcCl) molecule. The ONWs grow by a crystallization mechanism on roughness-tailored substrates. The growth methodology consists of a vapor deposition under low vacuum and mild temperature conditions. The structure, microstructure, and chemical composition of the FePcCl NWs are thoroughly elucidated and compared with those of Fe(II) phthalocyanine NWs by a consistent and complementary combination of advanced electron microscopies and X-ray spectroscopies. In a further step, we vertically align the NWs by conformal deposition of a SiO2 shell. Such orientation is critical to analyze the magnetic properties of the FePcCl and FePc supported NWs. A ferromagnetic behavior below 30 K with an easy axis perpendicular to the phthalocyanine plane was observed in the two cases with the FePcCl nanowires presenting a wider hysteresis. These results open the path to the fabrication of nanostructured one-dimensional small-molecule spintronic devices.
Febrero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04515
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In situ monitoring of the phenomenon of electrochemical promotion of catalysis
Espinos, JP; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Catalysis, 358 (2018) 27-34
Show abstract ▽
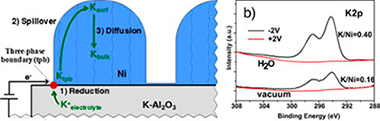
In this work we investigate by in-situ near-ambient pressure photoemission (NAPP) spectroscopy the phenomenon of Electrochemical Promotion of Catalysis (EPOC). We studied the reduction and diffusion kinetics of alkaline ions in a solid electrolyte cell formed by a nickel electrode supported on K+-beta-alumina electrolyte. Experiments in ultra-high vacuum and in the presence of steam showed that the amount of potassium atoms supplied to the surface is probably affected by nickel electronic modifications induced by adsorbed OH- groups. It was also deduced that part of the segregated potassium would be adsorbed at inner interfaces where it would be inaccessible to the photoelectron analyzer. A migration mechanism of the promoter is proposed consisting in: (i) the electrochemical reduction of the alkali ions (potassium) at the Ni/solid electrolyte/gas interface; (ii) the spillover of potassium atoms onto the Ni gas-exposed surface; and (iii) the diffusion of potassium atoms to Ni inner grain boundary interfaces.
Febrero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.11.027
- ‹ anterior
- 174 of 420
- siguiente ›














