Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nickel/Copper Bilayer-modified Screen Printed Electrode for Glucose Determination in Flow Injection Analysis
Salazar, P.; Rico, V.; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Electroanalysis, 30 (2018) 187-193
Show abstract ▽
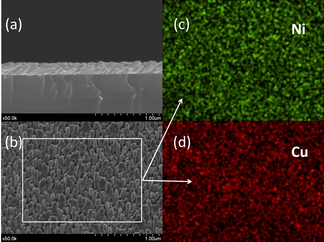
This work reports about the performance of a Ni/Cu-modified screen printed electrodes (SPE/Ni/Cu), prepared by physical vapor deposition (PVD) in an oblique angle configuration (OAD), for non-enzymatic glucose sensing applications. SPE/Ni/Cu electrodes showed an excellent reversibility and a catalytic behavior for detection of glucose that were controlled by the diffusion of reactants up to the active sites at the electrode surface. The study with a flow injection analysis (FIA) setup of the main experimental variables affecting the detection process has shown that the developed electrode system had an excellent glucose sensitivity of 1.04AM(-1)cm(-2) (R-2:0.999), a linear response up to 1mM, a limit of detection of 0.33M and a time of analysis of ca. 30s per sample. The selectivity of the sensor was checked against various interferences, including ascorbic acid, uric acid, acetaminophen and other sugars, in all cases with excellent results. The feasibility of using this sensor for practical applications was successfully confirmed by determining the glucose concentration in different commercial beverages.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/elan.201700592
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Outstanding performance of rehydrated Mg-Al hydrotalcites as heterogeneous methanolysis catalysts for the synthesis of biodiesel
Navajas, A; Campo, I; Moral, A; Echave, J; Sanz, O; Montes, M; Odriozola, JA; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LMFuel, 211 (2018) 173-181
Show abstract ▽
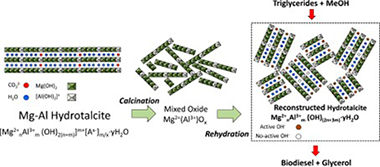
There is still a need for active, selective and stable heterogeneous catalysts for the synthesis of biodiesel. In this work, magnesium-aluminium hydrotalcites with Mg/Al molar ratios within the 1.5-5 range were synthesized by coprecipitation and used as transesterification catalysts for the synthesis of biodiesel. The mixed oxides obtained after calcination recovered the hydrotalcite structure in the form of meixnerite after rehydration in boiling water. The solids were characterized by XRD, TGA, N-2 adsorption-desorption, and SEM. Basic properties were assessed by means of Hammett indicators and CO2-TPD. Rehydrated materials with the highest Mg/Al ratios showed some distinctive features: low surface area, well defined flake-like crystals, high basicity and strong basic sites with H_ values above 11. They were also the most active catalysts allowing to achieve 51-75% sunflower oil methanolysis conversion after 8 h of reaction under mild conditions (60 degrees C, 1 atm), methanol/oil molar ratio of 12 using between 2 and 6 wt% of catalyst. The conversion increased up to 96% (92% fatty acid methyl esters yield) using 2 wt% catalyst and methanol/oil molar ratio of 48. Catalyst leaching was not a serious problem with these solids that could be reutilized maintaining very good activities. A general accordance between solids basic properties and their catalytic performance has been observed. These results are among the best reported in the literature for heterogeneous methanolysis catalysts and have been attributed to the high basicity of the rehydrated solids and the presence of strong and accessible basic sites probably consisting in interlayer hydroxide anions at the edges of the crystals.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.09.061
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Ir-Catalysed Nitrous oxide (N2O) Decomposition: Effect of Ir Particle Size and Metal-Support Interactions
Yentekakis, IV; Goula, G; Kampouri, S; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I; Panagiotopoulou, P; Taylor, MJ; Kyriakou, G; Lambert, RMCatalysis Letters, 148 (2019) 341-347
Show abstract ▽
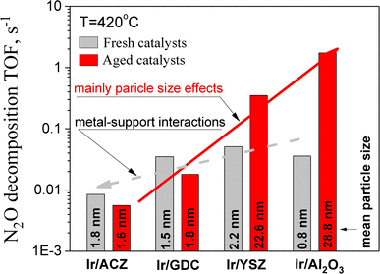
The effect of the morphology of Ir particles supported on.-Al2O3, 8 mol% Y2O3-stabilized -ZrO2 (YSZ), 10 mol%Gd2O3-doped CeO2 (GDC) and 80 wt%Al2O3-10 wt%CeO2-10 wt%ZrO2 (ACZ) on their stability on oxidative conditions, the associated metal-support interactions and activity for catalytic decomposition of N2O has been studied. Supports with intermediate or high oxygen ion lability (GDC and ACZ) effectively stabilized Ir nanoparticles against sintering, in striking contrast to supports offering negligible or low oxygen ion lability (gamma-Al2O3 and YSZ). Turnover frequency studies using size-controlled Ir particles showed strong structure sensitivity, de-N2O catalysis being favoured on large catalyst particles. Although metallic Ir showed some de-N2O activity, IrO2 was more active, possibly present as a superficial overlayer on the iridium particles under reaction conditions. Support-induced turnover rate modifications, resulted from an effective double layer [O delta--delta(+)](Ir) on the surface of iridium nanoparticles, via O2- backspillover from the support, were significant in the case of GDC and ACZ.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1007/s10562-017-2233-z
Reactividad de Sólidos
Core-rim structure formation in TiC-Ni based cermets fabricated by a combined thermal explosion/hot-pressing process
Lemboub, S; Boudebane, S; Gotor, FJ; Haouli, S; Mezrag, S; Bouhedja, S; Hesser, G; Chadli, H; Chouchane, TInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 70 (2018) 84-92
Show abstract ▽
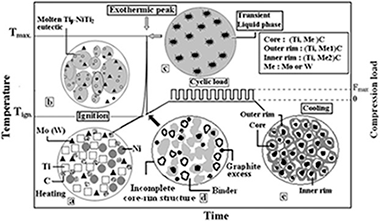
TiC-Ni-based cermets were obtained by thermal explosion from different elemental mixtures (Ti, C, Ni and X, where X = Cr, Mo or W) and subsequently densified by hot-pressing under a cyclic load. The whole process was performed in a single stage in the same experimental device according to the following thermal and pressure procedure: a heating rate ramp up to 1573 K without applying any load followed by an isothermal dwelling under a compressive cyclic load of 32 MPa. The thermal explosion synthesis occurred during the heating ramp at a temperature close to 1273 K that was practically independent of the starting nominal composition. The influence of different refractory elements on the chemical composition and microstructure of cermets was studied. SEM characterization showed that only with Mo and W, the cermets developed the characteristic core-rim structure. A high densification was achieved, but decreased when the refractory elements were added. Nevertheless, in these cases higher hardness values were obtained.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.09.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
A new combustion route for synthesis of TaB2 nanoparticles
Jalaly, M; Gotor, FJCeramics International, 44 (2018) 1142-1146
Show abstract ▽

Tantalum diboride (TaB2) nanoparticles were synthesized through a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). In this method, the ternary system of Mg/Ta2O5/B was employed in which, magnesium was used as a reducing agent for reduction of tantalum oxides in a combustive regime. The processing route of TaB2 by the solid-state combustion was very short-term and the product purification was extremely easy and rapid. The synthesis mechanism was studied and revealed that magnesiothermic reduction of tantalum oxide is the initiator of the total reaction, while borothermic reduction of the oxide may occur in parallel.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.074
- ‹ anterior
- 178 of 420
- siguiente ›














