Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Flexible and Adaptable Light-Emitting Coatings for Arbitrary Metal Surfaces based on Optical Tamm Mode Coupling
Jiménez-Solano, A.; Galisteo-López, J.; Míguez, H.Advanced Optical Materials, 6 (2018) 1700560
Show abstract ▽
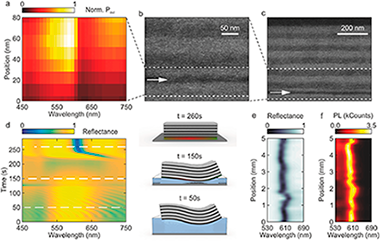
This study demonstrates a design that maximizes the power radiated into free space from a monolayer of nanoemitters embedded in a flexible distributed Bragg reflector conformably attached to a metal surface. This is achieved by positioning the light source at the precise depth within the multilayer for which optical Tamm states provide enhanced quantum yield and outcoupling efficiency, which are combined to optimize the luminous power radiated by the surface of the ensemble. This approach, based on the adhesion of flexible multilayer stacks onto metal surfaces with an arbitrary curvature, is versatile and permits the realization of spectrally narrow monodirectional or self-focusing light-emitting surfaces.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700560
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanostructured hybrid device mimicking bone extracellular matrix as local and sustained antibiotic delivery system
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Romero-Sanchez, LB; Blazquez, J; Diaz-Cuenca, AMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 256 (2018) 165-176
Show abstract ▽
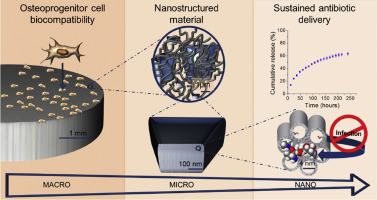
A fluidic permeable and stable in wet media, MBG-NfGel, device consisting of a mesoporous ceramic embodied in a nanofibrillar biodegradable polymer has been processed using appropriate thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) processing variables of 5.4% (wt/v) gelatin in 50/50 water/ethanol (v/v) ratio. The device comprises high surface area mesoporous bioactive glass (MBG) microparticles within a fibrous matrix of 170 nm average diameter nanofibers gelatin, forming a meshwork of 0.2-1.6 mu m range voids. Gentamicin sulphate (GS) antibiotic high loading capacity and sustained release ability, as well as in vitro bioactivity and osteoprogenitor cells biocompatibility supports long-term antibacterial and bone growth stimulation properties. Antibiotic local delivery functionality in vitro of this device has been analysed and discussed in relation to other systems previously reported. The presented device properties as well as its industrial scalability potential, in terms of process reliability and absence of toxic chemical agents, low raw material biopolymer cost and immunogenicity, are other important advantages. These advantages rank MBG-NfGel device as a potential candidate to further development for application as local antibiotic device in bone surgery and therapy.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.08.010
2017
2017
Materiales Coloidales
Local Disorder and Tunable Luminescence in Sr1–x/2Al2–xSixO4 (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) Transparent Ceramics
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Al Saghir, K; Veron, E; Becerro, AI; Porcher, F; Wisniewsld, W; Matzen, G; Fayon, F; Allix, MInorganic Chemistry, 56 (2017) 14446-14458
Show abstract ▽
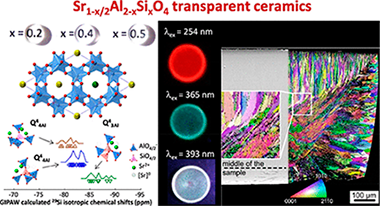
Eu-doped Sr1–x/2Al2–xSixO4 (x = 0.2, 0.4, and 0.5) transparent ceramics have been synthesized by full and congruent crystallization from glasses prepared by aerodynamic levitation and laser-heating method. Structural refinements from synchrotron and neutron powder diffraction data show that the ceramics adopt a 1 × 1 × 2 superstructure compared to the SrAl2O4 hexagonal polymorph. While the observed superstructure reflections indicate a long-range ordering of the Sr vacancies in the structure, 29Si and 27Al solid-state NMR measurements associated with DFT computations reveal a significant degree of disorder in the fully polymerized tetrahedral network. This is evidenced through the presence of Si–O–Si bonds, as well as Si(OAl)4 units at remote distances of the Sr vacancies and Al(OAl)4 units in the close vicinity of Sr vacancies departing from local charge compensation in the network. The transparent ceramics can be doped by europium to induce light emission arising from the volume under UV excitation. Luminescence measurements then reveal the coexistence of Eu2+ and Eu3+ in the samples, thereby allowing tuning the emission color depending on the excitation wavelength and suggesting possible applications such as solid state lighting.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01881
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of acid-treatment and colloidal-processing conditions on the room temperature mechanical and electrical properties of 3YTZP/MWNT ceramic nanocomposites
Poyato, R.; Morales-Rodríguez, A.; Gutiérrez-Mora, F.; Muñoz, A.; Gallardo-López, A.Ceramics International, 43 (2017) 16560-16568
Show abstract ▽
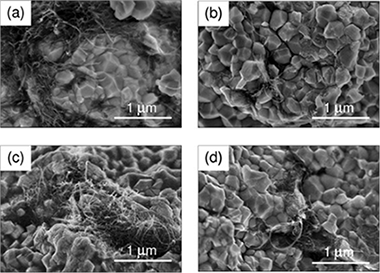
Different colloidal powder processing routines have been used to prepare composites of 3 mol% Y2O3 -ZrO2 (tetragonal zirconia polycrystals, 3YTZP) with 2.5 vol% multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWNT) with the aim of achieving a homogeneous distribution of the MWNTs in the ceramic, eliminating agglomerates but also minimizing carbon nanotube (CNT) damage during processing. Modifications of the acid treatment applied to the nanotubes, including subjecting them to stirring or ultrasonic agitation, and use of acid or basic pH during composite powder mixing have been approached.
No MWNT damage during processing was detected by Raman spectroscopy. CNT bundles were found in all the composites forming different patterns depending on the processing route. Similar values of hardness were obtained for all the composites, while different anisotropy in fracture propagation was found when studying parallel and perpendicular directions to the sintering pressing axis on the cross sections of the composites due to the MWNT preferential alignment. The CNT bundles were found to act as fracture short paths. A similar anisotropic behavior was observed for the electrical conductivity. These results have been correlated to the different microstructures obtained in the composites prepared with different processing routines.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.043
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High temperature compressive strength and creep behavior of Si-Ti-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Ramirez-Rico, JJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 37 (2017) 4442-4448
Show abstract ▽
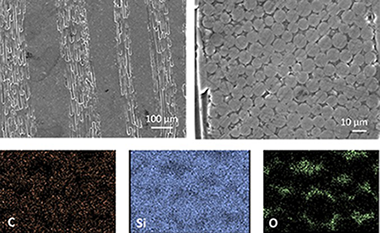
Fiber bonded silicon carbide ceramic materials provide cost-advantage over traditional ceramic matrix composites and require fewer processing steps. Despite their interest in extreme environment thermostructural applications no data on long term mechanical reliability other than static fatigue is available for them. We studied the high temperature compressive strength and creep behavior of a fiber bonded SiC material obtained by hot-pressing of Si Ti-C-O fibers. The deformation mechanism and onset of plasticity was evaluated and compared with other commercial SiC materials. Up to 1400 degrees C, plasticity is very limited and any macroscopic deformation proceeds by crack formation and damage propagation. A transient viscous creep stage is observed due to flow in the silica matrix and once steady state is established, a stress exponent n similar to 4 and an activation energy Q similar to 700 kJ mol(-1) are found. These results are consistent with previous data on creep of polymer derived SiC fibers and polycrystals.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.06.037
- ‹ anterior
- 179 of 420
- siguiente ›














