Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of acid-treatment and colloidal-processing conditions on the room temperature mechanical and electrical properties of 3YTZP/MWNT ceramic nanocomposites
Poyato, R.; Morales-Rodríguez, A.; Gutiérrez-Mora, F.; Muñoz, A.; Gallardo-López, A.Ceramics International, 43 (2017) 16560-16568
Show abstract ▽
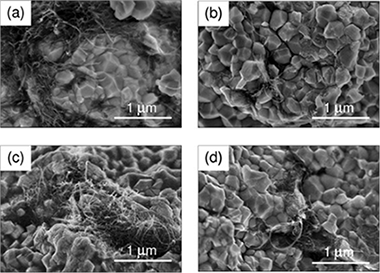
Different colloidal powder processing routines have been used to prepare composites of 3 mol% Y2O3 -ZrO2 (tetragonal zirconia polycrystals, 3YTZP) with 2.5 vol% multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWNT) with the aim of achieving a homogeneous distribution of the MWNTs in the ceramic, eliminating agglomerates but also minimizing carbon nanotube (CNT) damage during processing. Modifications of the acid treatment applied to the nanotubes, including subjecting them to stirring or ultrasonic agitation, and use of acid or basic pH during composite powder mixing have been approached.
No MWNT damage during processing was detected by Raman spectroscopy. CNT bundles were found in all the composites forming different patterns depending on the processing route. Similar values of hardness were obtained for all the composites, while different anisotropy in fracture propagation was found when studying parallel and perpendicular directions to the sintering pressing axis on the cross sections of the composites due to the MWNT preferential alignment. The CNT bundles were found to act as fracture short paths. A similar anisotropic behavior was observed for the electrical conductivity. These results have been correlated to the different microstructures obtained in the composites prepared with different processing routines.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.043
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High temperature compressive strength and creep behavior of Si-Ti-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Ramirez-Rico, JJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 37 (2017) 4442-4448
Show abstract ▽
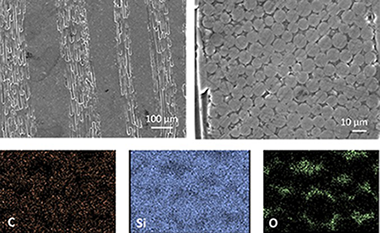
Fiber bonded silicon carbide ceramic materials provide cost-advantage over traditional ceramic matrix composites and require fewer processing steps. Despite their interest in extreme environment thermostructural applications no data on long term mechanical reliability other than static fatigue is available for them. We studied the high temperature compressive strength and creep behavior of a fiber bonded SiC material obtained by hot-pressing of Si Ti-C-O fibers. The deformation mechanism and onset of plasticity was evaluated and compared with other commercial SiC materials. Up to 1400 degrees C, plasticity is very limited and any macroscopic deformation proceeds by crack formation and damage propagation. A transient viscous creep stage is observed due to flow in the silica matrix and once steady state is established, a stress exponent n similar to 4 and an activation energy Q similar to 700 kJ mol(-1) are found. These results are consistent with previous data on creep of polymer derived SiC fibers and polycrystals.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.06.037
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Micron-scale wedge thin films prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition
Lopez-Santos, MC; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Borras, A; del Campo, RC; Holgado, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 14 (2017) e1700043
Show abstract ▽
Wedge-shaped materials are currently employed for optical analyses and sensing applications. In this paper, we present an easy to implement plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition procedure to grow wedge-shaped thin films with controlled slope at the scale of few hundred microns. The method relies on the use of few tenths micron height obstacles to alter the laminar flow of precursor gas during deposition and is applied for the fabrication of wedge-shaped ZnO thin films. Local interference patterns, refractive index, and birefringence of the films have been measured with one micron resolution using a specially designed optical set-up. Their micro- and nano-structures have been characterized by means of scanning electron microscopy and theoretically reproduced by Monte Carlo calculations.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201700043
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance of biomorphic Silicon Carbide as particulate filter in diesel boilers
Orihuela, M Pilar; Gomez-Martin, Aurora; Becerra, Jose A; Chacartegui, Ricardo; Ramirez-Rico, JoaquinJournal of Environmental Management, 203 (2017) 907-919
Show abstract ▽
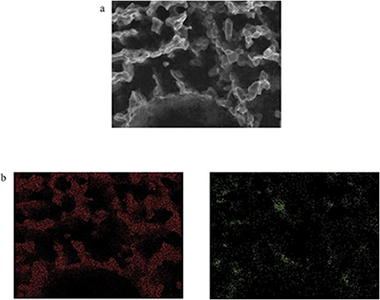
Biomorphic Silicon Carbide (bioSiC) is a novel porous ceramic material with excellent mechanical and thermal properties. Previous studies have demonstrated that it may be a good candidate for its use as particle filter media of exhaust gases at medium or high temperature. In order to determine the filtration efficiency of biomorphic Silicon Carbide, and its adequacy as substrate for diesel particulate filters, different bioSiC-samples have been tested in the flue gases of a diesel boiler. For this purpose, an experimental facility to extract a fraction of the boiler exhaust flow and filter it under controlled conditions has been designed and built. Several filter samples with different microstructures, obtained from different precursors, have been tested in this bench. The experimental campaign was focused on the measurement of the number and size of particles before and after placing the samples. Results show that the initial efficiency of filters made from natural precursors is severely determined by the cutting direction and associated microstructure. In biomorphic Silicon Carbide derived from radially cut wood, the initial efficiency of the filter is higher than 95%. Nevertheless, when the cut of the wood is axial, the efficiency depends on the pore size and the permeability, reaching in some cases values in the range 70–90%. In this case, the presence of macropores in some of the samples reduces their efficiency as particle traps. In continuous operation, the accumulation of particles within the porous media leads to the formation of a soot cake, which improves the efficiency except in the case when extra-large pores exist. For all the samples, after a few operation cycles, capture efficiency was higher than 95%. These experimental results show the potential for developing filters for diesel boilers based on biomorphic Silicon Carbide.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.003
Materiales Coloidales
Microemulsion-Mediated Synthesis and Properties of Uniform Ln:CaWO4 (Ln = Eu, Dy) Nanophosphors with Multicolor Luminescence for Optical and CT Imaging
Laguna, M; Nuñez, NO; Garcia, FJ; Corral, A; Parrado-Gallego, A; Balcerzyk, M; Becerro, AI; Ocaña, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 44 (2017) 5158-5168
Show abstract ▽
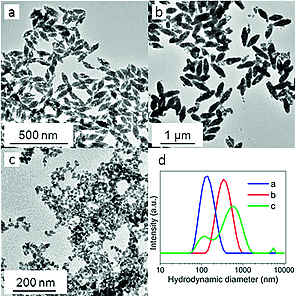
A new room-temperature method has been developed that yields, for the first time in the literature, uniform and well-dispersed CaWO4 nanospindles. This method is based on the use of microemulsions consisting of aqueous solutions of Ca2+ and WO42- precursors, cyclohexane as the organic medium, Triton X-100 as the surfactant, and n-octanol as the cosurfactant. We show that the formation of uniform nanospindles requires a restrictive set of experimental conditions. These particles crystallize into the tetragonal CaWO4 phase and emit blue-green luminescence when excited by UV radiation. The reported method is also useful for doping the CaWO4 spindles with Eu3+ or Dy3+ cations, resulting in multicolor emissions (red for Eu3+; white for Dy3+). The luminescence is much stronger when excited through a WO42--Ln(3+) (Ln = Eu or Dy) energy-transfer band than through the f-f transition bands of the Ln(3+) cations. Interestingly, because of the white luminescence associated with the Dy:CaWO4 nanophosphor, it might be useful for LED technologies. Luminescence dynamics and energy-transfer efficiency have been analyzed to determine the optimum phosphors. Finally, the Eu-doped CaWO4 nanospindles also showed excellent X-ray attenuation efficacy, which confers double functionality to this material as both a luminescence bioprobe and as a contrasting agent for X-ray computed-tomography.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201700650
- ‹ anterior
- 180 of 420
- siguiente ›














