Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping performance of steel and blast furnace slags for thermochemical energy storage in concentrated solar power plants
Valverde, JM; Miranda-Pizarro, J; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of CO2 Utilization, 22 (2017) 143-154
Show abstract ▽
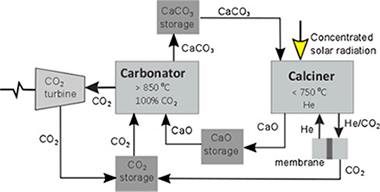
The Calcium Looping (CaL) process, based on the carbonation/calcination of CaO, has been proposed as a feasible technology for Thermochemical Energy Storage (TCES) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants. The CaL process usually employs limestone as CaO precursor for its very low cost, non-toxicity, abundance and wide geographical distribution. However, the multicycle activity of limestone derived CaO under relevant CaL conditions for TCES in CSP plants can be severely limited by pore plugging. In this work, the alternative use of calcium-rich steel and blast furnace slags after treatment with acetic acid is investigated. A main observation is that the calcination temperature to regenerate the CaO is significantly reduced as compared to limestone. Furthermore, the multicycle activity of some of the slags tested at relevant CaL conditions for TCES remains high and stable if the treated samples are subjected to filtration. This process serves to remove silica grains, which helps decrease the porosity of the CaO resulting from calcination in the mesoporous range thus mitigating pore plugging.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2017.09.021
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Photochemical methane partial oxidation to methanol assisted by H2O2
López Martin, A.; Caballero, A.; Colón, G.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 349 (2017) 216-223
Show abstract ▽
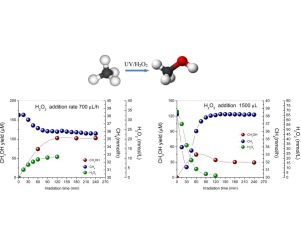
The photochemical conversion of methane into methanol from H2O2 aqueous solution as well as the effect of the addition mode were studied. Direct addition of different amounts H2O2 leads to increasing methanol production at the first stage of the reaction. The excess of H2O2 would lead to the reactive oxygen species scavenging and the subsequent O2 production. It was also corroborated that extra hydroxyl radicals in the aqueous medium do not improve the formation of methanol but a noticeable increase in the formation of HCOOH with respect to methanol was evidenced. In contrast, dosing addition at relatively low rates leads to constant methane consumption towards methanol. Methanol formation would be in this case in equilibrium with further oxidation to HCOOH or CO2. This suggests that only a controlled constant availability of HO’s at low concentration can enhance the performance of methanol generation in the photochemical process.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.09.039
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Silver and gold nanoparticles in nanometric confined templates: synthesis and alloying within the anisotropic pores of oblique angle deposited films
Parra-Barranco, J., Sánchez-Valencia, J.R., Barranco, A., González-Elipe, A.R.Nanotechnology, 28 (2017) 485602
Show abstract ▽
In this work we have developed an infiltration methodology to incorporate metal nanoparticles (NPs) of controlled size and shape into the open voids available in oblique angle deposited thin films. These NPs exhibited well-defined surface plasmon resonances (SPRs). The nanometric confined space provided by their porous microstructure has been used as a template for the growth of anisotropic NPs with interesting SPR properties. The fabrication methodology has been applied for the preparation of films with embedded Ag and Au NPs with two associated plasmon resonance features that developed a dichroic behaviour when examined with linearly polarized light. A confined alloying process was induced by near IR nanosecond laser irradiation yielding bimetallic NPs with SPR features covering a large zone of the electromagnetic spectrum. The possibilities of the method for the tailored fabrication of a wide range colour palette based on SPR features are highlighted.
Diciembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa92af
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Redox and Catalytic Properties of Promoted NiO Catalysts for the Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethane
Delgado, D; Solsona, B; Ykrelef, A; Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Caballero, A; Rodriguez-Aguado, E; Rodriguez-Castellon, E; Nieto, JMLJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 121 (2017) 25132-25142
Show abstract ▽
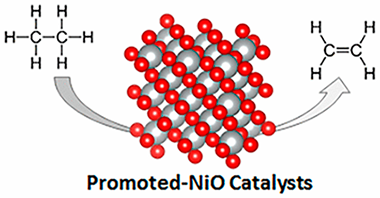
NiO and metal-promoted NiO catalysts (M-NiO, with a M/(M+Ni) atomic ratio of 0.08, with M = Nb, Sn, or La) have been prepared, tested in the oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of ethane, and characterized by means of XRD, TPR, HRTEM, Raman, XPS, and in situ XAS (using H-2/He, air or C2H6/He mixtures). The selectivity to ethylene during the ODH of ethane decreases according to the following trend: Nb NiO Sn NiO > La NiO > NiO, whereas the catalyst reducibility (determined by both TPR and XAS using H-2/He mixtures) shows the opposite trend. However, different reducibility and catalytic behavior in the absence of oxygen (ethane/He mixtures) have been observed, especially when comparing Nb- and Sn-promoted NiO samples. These differences can be ascribed mainly to a different phase distribution of the promoter. The results presented here are discussed in terms of the nature of active and selective sites for ODH of ethane in selective and unselective catalysts, but also the role of promoters and the importance of their phase distribution.
Noviembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07066
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Determination of the thickness of the embedding phase in 0D nanocomposites
Martinez-Martinez, D; Sanchez-Lopez, JCApplied Surface Science, 421 (2017) 179-184
Show abstract ▽
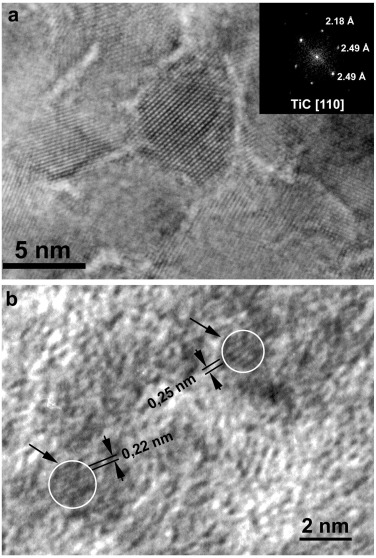
0D nanocomposites formed by small nanoparticles embedded in a second phase are very interesting systems which may show properties that are beyond those observed in the original constituents alone. One of the main parameters to understand the behavior of such nanocomposites is the determination of the separation between two adjacent nanoparticles, in other words, the thickness of the embedding phase. However, its experimental measurement is extremely complicated. Therefore, its evaluation is performed by an indirect approach using geometrical models. The ones typically used represent the nanoparticles by cubes or spheres.
In this paper the used geometrical models are revised, and additional geometrical models based in other parallelohedra (hexagonal prism, rhombic and elongated dodecahedron and truncated octahedron) are presented. Additionally, a hybrid model that shows a transition between the spherical and tessellated models is proposed. Finally, the different approaches are tested on a set of titanium carbide/amorphous carbon (TiC/a-C) nanocomposite films to estimate the thickness of the a-C phase and explain the observed hardness properties.
Noviembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.081
- ‹ anterior
- 181 of 420
- siguiente ›














