Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Structural control in porous/compact multilayer systems grown by magnetron sputtering
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Alvarez, R; Rico, V; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 28 (2017) 46
Show abstract ▽
In this work we analyze a phenomenon that takes place when growing magnetron sputtered porous/compact multilayer systems by alternating the oblique angle and the classical configuration geometries. We show that the compact layers develop numerous fissures rooted in the porous structures of the film below, in a phenomenon that amplifies when increasing the number of stacked layers. We demonstrate that these fissures emerge during growth due to the high roughness of the porous layers and the coarsening of a discontinuous interfacial region. To minimize this phenomenon, we have grown thin interlayers between porous and compact films under the impingement of energetic plasma ions, responsible for smoothing out the interfaces and inhibiting the formation of structural fissures. This method has been tested in practical situations for compact TiO2/porous SiO2 multilayer systems, although it can be extrapolated to other materials and conditions.
Noviembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa8cf4
Materiales Avanzados
Characterization of ashes from greenhouse crops plant biomass residues using X-ray fluorescence analysis and X-ray diffraction
Garzon, E; Morales, L; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Sanchez-Soto, PJX-ray spectrometry, 46 (2017) 569-578
Show abstract ▽
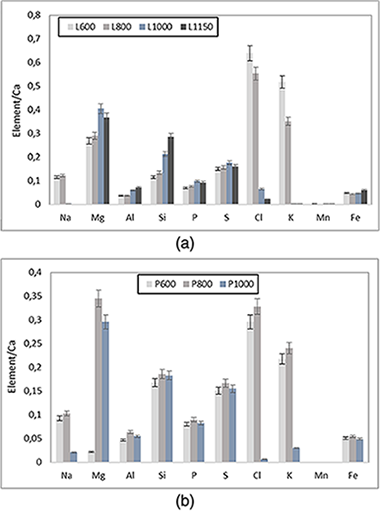
A characterization of ashes obtained by thermal treatments on greenhouse crops plant biomass residues is presented. The chemical analysis, by X-ray fluorescence (wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence), and phase analysis, by X-ray diffraction, of the resultant ashes are reported. Thermal treatments of selected samples of these residues increase the relative amounts of inorganic Mg, Si, P, and S in the ashes, being these amounts as high as increasing temperature. As an opposite effect, Na, Cl, and K contents decrease as increasing temperature by a volatilization process of the chlorides, as confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The crystalline phase analysis of the ashes demonstrates the formation of inorganic constituents of the biomass, including alkaline chlorides and calcium salts (calcite, anhydrite, and apatite). Progressive thermal treatments induce the formation of new silicate phases (akermanite and grossularite) and silica (-quartz and cristobalite). Furthermore, the particle size of the starting biomass samples does not influence the evolution of the crystalline phases by thermal treatments. In contrast, a previous leaching using water and subsequent heating at 1,000 degrees C produces the formation of periclase (MgO), lime (CaO), and the silicate gehlenite, without the presence of anhydrite. This study is interesting for future investigations on the residues as a profitable biomass source for energy production and sustainable large-scale management. Some potential applications of the resultant ashes can be proposed.
Noviembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/xrs.2801
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of the crystal chemistry on the hydration mechanism of swelling micas
Pavon, E; Alba, MD; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pazos, MCGeochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 217 (2017) 231-239
Show abstract ▽
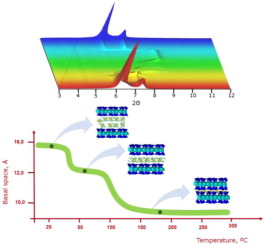
Swelling and dehydration under minor changes in temperature and water vapor pressure is an important property that clays and clay minerals exhibit. In particular, their interlayer space, the solid-water interface and the layers' collapse and re-expansion have received much attention because it affects to the dynamical properties of interlayer cations and thus the transfer and fate of water and pollutants. In this contribution, the dehydration and rehydration mechanism of a swelling high-charge mica family is examined by in situ X-ray Diffraction. The effect of the aluminosilicate layer charge and the physicochemical properties of the interlayer cations on these processes are analyzed. The results showed that the dehydration temperature and the number of steps involved in this process are related to the layer charge of the silicate and the physicochemical properties of the interlayer cations. Moreover, the ability to adsorb water molecules in a confined space with high electric field by the interlayer cations does not only depend on their hydration enthalpy but also on the electrostatic parameters of these cations.
Noviembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.08.028
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Over Zr-Promoted Co/gamma-Al2O3 Catalysts
Barrientos, J; Garcilaso, V; Venezia, B; Aho, A; Odriozola, JA; Boutonnet, M; Jaras, STopics in Catalysis, 60 (2017) 1285-1298
Show abstract ▽
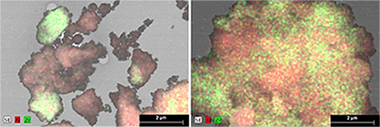
Two Zr-modified alumina supports were synthetized containing the same amount of Zr but a different distribution of this modifier over the alumina surface. These supports, together with the unmodified alumina carrier, were used to prepare three cobalt-based catalysts which were characterized and tested under relevant Fischer-Tropsch conditions. The three catalysts presented very similar porosity and cobalt dispersion. The addition of Zr nor its distribution enhanced the catalyst reducibility. The catalyst activity was superior when using a carrier consisting of large ZrO2 islands over the alumina surface. The use of a carrier with a homogeneous Zr distribution had however, a detrimental effect. Moreover, a faster initial deactivation rate was observed for the Zr-promoted catalysts, fact that may explain this contradictory effect of Zr on activity. Finally, the addition of Zr showed a clear enhancement of the selectivity to long chain hydrocarbons and ethylene, especially when Zr was well dispersed.
Noviembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1007/s11244-017-0813-1
Tribología y Protección de Superficies - Materiales Coloidales
HoF3 and DyF3 Nanoparticles as Contrast Agents for High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, Daniel; Becerro, Ana I.; Rojas, T. Cristina; Garcia-Martin, Maria L.; de la Fuente, Jesus M.; Ocana, ManuelParticle & particle systems characterization, 34 (2017) art. 1700116
Show abstract ▽
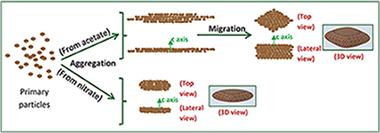
Clinical contrast agents (CAs) currently used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at low fields are less effective at high magnetic fields. The development of new CAs is mandatory to improve diagnostic capabilities of the new generation of high field MRI scanners. The purpose of this study is to synthesize uniform, water dispersible LnF3 (Ln = Ho, Dy) nanoparticles (NPs) and to evaluate their relaxivity at high magnetic field (9.4 T) as a function of size and composition. Two different types of HoF3 NPs are obtained by homogeneous precipitation in ethylene glycol at 120 °C. The use of holmium acetate as holmium precursor leads to rhombus-like nanoparticles, while smaller, ellipsoid-like nanoparticles are obtained when nitrate is used as the holmium salt. To explain this behavior, the mechanism of formation of both kinds of particles is analyzed in detail. Likewise, rhombus-like DyF3 nanoparticles are prepared following the same method as for the rhombus-like HoF3 nanoparticles. We have found, to the best of knowledge, the highest transverse relaxivity values at 9.4 T described in the literature for this kind of CAs. Finally, the LnF3 NPs have shown negligible cytotoxicity for C6 rat glioma cells for concentrations up to 0.1 mg mL−1.
Octubre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/ppsc.201700116
- ‹ anterior
- 182 of 420
- siguiente ›














