Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical Solvent-Free Synthesis of Quaternary Semiconductor Cu-Fe-Sn-S Nanocrystals
Balaz, Peter; Balaz, Matej; Sayagues, Maria J.; Skorvanek, Ivan; Zorkovska, Anna; Dutkova, Erika; Briancin, Jaroslav; Kovac, Jaroslav; Kovac, Jaroslav, Jr.; Shpotyuk, YaroslavNanoscale Research Letters, 12 (2017) art. 256 DOI: 10.1186/s11671-017-2029-5
Abstract
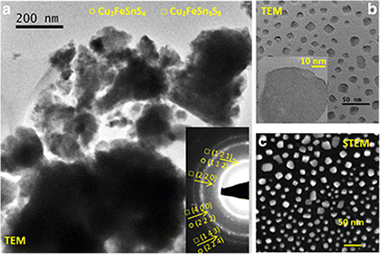
In this study, we demonstrate a one-pot mechanochemical synthesis of the nanocomposite composed of stannite Cu2FeSnS4 and rhodostannite Cu2FeSn3S8 nanocrystals using a planetary ball mill and elemental precursors (Cu, Fe, Sn, S). By this approach, unique nanostructures with interesting properties can be obtained. Methods of XRD, Raman spectroscopy, UV-Vis, nitrogen adsorption, SEM, EDX, HRTEM, STEM, and SQUID magnetometry were applied. Quaternary tetragonal phases of stannite and rhodostannite with crystallite sizes 18-19 nm were obtained. The dominant Raman peaks corresponding to the tetragonal stannite structure corresponding to A-symmetry optical modes were identified in the spectra. The bandgap 1.25 eV calculated from UV-Vis absorption spectrum is very well-acceptable value for the application of the synthesized material. The SEM micrographs illustrate the clusters of particles in micron and submicron range. The formation of agglomerates is also illustrated on the TEM micrographs. Weak ferromagnetic properties of the synthesized nanocrystals were documented.
Abril, 2017 · DOI: 10.1186/s11671-017-2029-5
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically Synthesized CuFeSe2 Nanoparticles and Their Properties
Dutkova, E; Skorvanek, I; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Kovac, J; Balaz, PActa Physica Polonica A, 131 (2017) 1156-1158 DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.131.1156
Abstract
The mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline CuFeSe2 particles prepared by high-energy milling in a planetary mill in an argon atmosphere from copper, iron, and selenium for 60 min is reported for the first time. The CuFeSe2 nanoparticles crystallize in tetragonal structure with mean crystallite size of about 32 +/- 1 nm. High resolution transmission electron microscopy measurements confirmed the presence of agglomerates which are formed by small nanocrystalline domains (5-40 nm). The magnetic data revealed that paramagnetic CuFeSe2 nanoparticles coexist with a small amount of ferromagnetic impurities at room temperature. The magnetic transition towards a weak ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic behavior occurs in CuFeSe2 at approximately 79 K. The band gap of the CuFeSe2 particles is 0.95 eV which is wider than the band gap in bulk materials (0.16 eV), which could be in many aspects of application more beneficial.
Abril, 2017 · DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.131.1156
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
High UV-photocatalytic activity of ZnO and Ag/ZnO synthesized by a facile method
C. Jaramillo-Páez; J.A. Navío; M.C. Hidalgo; M. MacíasCatalysis Today, 284 (2017) 121-128 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.11.021
Abstract
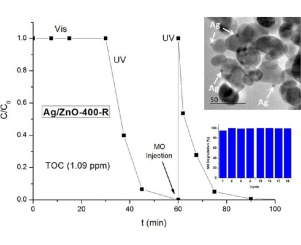
ZnO nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized by a facile precipitation procedure by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn(II) acetate and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7.0 without template addition. We have investigated the effect of annealing temperature in the final surface and structural properties. Photocatalytic studies were performed using two selected substrates, Methyl Orange and Phenol, both as single model substrates and in mixtures of them.
It has been stated that calcination treatments lead to a significant improvement in the photocatalytic properties of the studied samples, even better than TiO2(P25). As expected, the addition of Ag+ during the photocatalytic degradation of MO increases the reaction rate of the degradation of MO, giving a resultant Ag/ZnO photocatalyst which, after recovery, can be reused at least 18 times for the MO degradation tests, being even more photoactive than ZnO.
Abril, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.11.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Thermal Pretreatment and Nanosilica Addition on Limestone Performance at Calcium-Looping Conditions for Thermochemical Energy Storage of Concentrated Solar Power
Valverde, Jose Manuel; Barea-Lopez, Manuel; Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.Enery & Fuels, 31 (2017) 4226-4236 DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03364
Abstract
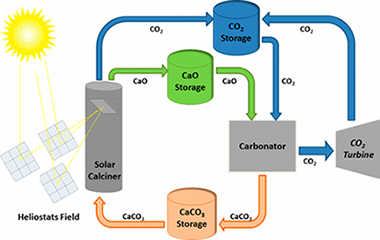
The share of renewable energies is growing rapidly, partly in response to the urgent need for mitigating CO2 emissions from fossil fuel power plants. However, cheap and efficient large-scale energy storage technologies are not yet available to allow for a significant penetration of renewable energies into the grid. Recently, a potentially low-cost and efficient thermochemical energy storage (TCES) system has been proposed, based on the integration of the calcium-looping (CaL) process into concentrated solar power plants (CSPs). The CaL process relies on the multicycle carbonation/calcination of CaO, which can be derived from calcination of widely available, cheap, and nontoxic natural limestone (CaCO3). This work explores the effect on the multicycle activity of limestone-derived CaO of thermal pretreatment under diverse atmospheres and the addition of nanosilica, which would be expected to hinder CaO grain sintering. Importantly, optimum CaL conditions for CSP energy storage differ radically from those used in the application of the CaL process for CO2 capture. Thus, calcination should be ideally carried out under low CO2 partial pressure at moderate temperature (below 750 degrees C), whereas CO2 concentration and temperature should be high for carbonation in order to maximize thermoelectric efficiency. When limestone is subjected to carbonation/calcination cycles at these conditions, its performance is critically dependent on the type of pretreatment. Our results indicate that the multicycle CaO activity is correlated with the size of the particles and the CaO pore size distribution. Thus, CaO activity is impaired as particle size is increased and/or CaO pore size is decreased. These observations suggest that pore plugging poses a main limitation to the multicycle performance of limestone-derived CaO at the optimum CaL conditions for TCES in CSPs, which is supported by scanning electron microscopy analysis. Strategies to enhance the performance of natural limestone at these conditions should be therefore oriented toward minimizing pore plugging rather than CaO grain sintering, which stands as the main limitation at CaL conditions for CO2 capture.
Abril, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03364
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Features of electrical properties of BE-C(Fe) biocarbons carbonized in the presence of an Fe-containing catalyst
Popov, VV; Orlova, TS; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 59 (2017) 703-709 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783417040205
Abstract
The effect of partial graphitization on electrical and galvanomagnetic properties of BE-C(Fe) biomorphic carbons produced by beech wood carbonization at temperatures of 850-1600A degrees C in the presence of an iron-containing catalyst is studied. The use of an Fe catalyst at D cent (carb) ae<yen> 1000A degrees C leads to the formation of nanoscale graphite-phase inclusions; its total volume and nanocrystallite sizes increase with D cent (carb). The data on the carrier concentration and mobility are obtained. It was shown that partially graphitized BE-C(Fe) carbons with D cent (carb) ae<yen> 1000A degrees C in the conductivity type and magnetoresistance features relate to highly disordered metal systems whose conductivity can be described taking into account the contribution of quantum corrections, mainly the correction caused by the electron-electron interaction. It is shown that nonmonotonic dependences of the Hall constant R on the magnetic field are characteristic of BE-C(Fe) samples with 1000 ae<currency> D cent (carb) < 1600A degrees C, which is most probably caused by the contribution of various carrier groups, i.e., electrons and holes. In BE-C(Fe) samples with D cent (carb) = 1600A degrees C, the Hall coefficient corresponds to the metal state, which is associated with conducting medium homogenization resulting from the formation of a significant graphite phase volume.
Abril, 2017 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783417040205
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Formation of nitrile species on Ag nanostructures supported on a-Al2O3: a new corrosion route for silver exposed to the atmosphere
Pelaez, RJ; Espinos, JP; Afonso, CNNanotechnology, 28 (2017) 175709 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa65c0
Abstract
The aging of supported Ag nanostructures upon storage in ambient conditions (air and room temperature) for 20 months has been studied. The samples are produced on glass substrates by pulsed laser deposition (PLD); first a 15 nm thick buffer layer of amorphous aluminum oxide (a-Al2O3) is deposited, followed by PLD of Ag. The amount of deposited Ag ranges from that leading to a discontinuous layer up to an almost-percolated layer with a thickness of <6 nm. Some regions of the as-grown silver layers are converted, by laser induced dewetting, into round isolated nanoparticles (NPs) with diameters of up to ~25 nm. The plasmonic, structural and chemical properties of both as-grown and laser exposed regions upon aging have been followed using extinction spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, respectively. The results show that the discontinuous as-grown regions are optically and chemically unstable and that the metal becomes oxidized faster, the smaller the amount of Ag. The corrosion leads to the formation of nitrile species due to the reaction between NO x species from the atmosphere adsorbed at the surface of Ag, and hydrocarbons adsorbed in defects at the surface of the a-Al2O3 layer during the deposition of the Ag nanostructures by PLD that migrate to the surface of the metal with time. The nitrile formation thus results in the main oxidation mechanism and inhibits almost completely the formation of sulphate/sulphide. Finally, the optical changes upon aging offer an easy-to-use tool for following the aging process. They are dominated by an enhanced absorption in the UV side of the spectrum and a blue-shift of the surface plasmon resonance that are, respectively, related to the formation of a dielectric overlayer on the Ag nanostructure and changes in the dimensions/features of the nanostructures, both due to the oxidation process.
Abril, 2017 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa65c0
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Improving the pollutant removal efficiency of packed-bed plasma reactors incorporating ferroelectric components
Gomez-Ramirez, Ana; Montoro-Damas, Antonio M.; Rodriguez, Miguel A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Cotrino, JoseChemical Engineering Journal, 314 (2017) 311-319 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.065

Abstract
In this work we have studied the plasma removal of air contaminants such as methane, chloroform, toluene and acetone in two parallel plate packed-bed dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactors of different sizes. Removal and energy efficiencies have been determined as a function of the residence time of the contaminated air within the reactor, the kind of packed-bed material (ferroelectrics or classical dielectric materials), the frequency and the incorporation of a ferroelectric plate onto the active electrode together with the inter-electrode ferroelectric pellets filling the gap. Results at low frequency with the small reactor and the ferroelectric plate showed an enhancement in energy efficiency (e.g., it was multiplied by a factor of six and three for toluene and chloroform, respectively) and in removal yield (e.g., it increased from 22% to 52% for chloroform and from 15% to 21% for methane). Such enhancements have been attributed to the higher energy of plasma electrons and a lower reactor capacitance found for this plate-modified configuration. A careful analysis of reaction efficiencies and electron energy distributions for the different investigated conditions and the simulation of the electric field at the necks between ferroelectric/dielectric pellets complete the present study. Overall, the obtained results prove the critical role of the barrier architecture and operating conditions for an enhanced performance of pollution removal processes using DBD systems.
Abril, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.065
Materiales Coloidales
Morphology control of uniform CaMoO4 microarchitectures and development of white light emitting phosphors by Ln doping (Ln = Dy3+, Eu3+)
Laguna, Mariano; Nuñez, Nuria O.; Becerro, Ana I.; Ocaña, ManuelCrystengcomm, 19 (2017) 1590-1600 DOI: 10.1039/c6ce02611g
Abstract
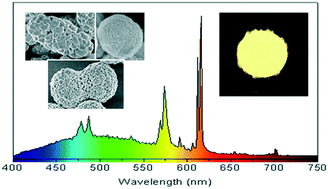
A very simple synthesis procedure based on precipitation reactions at moderate temperature (120 degrees C) from solutions containing calcium nitrate and sodium molybdate, using mixed solvents (polyols and water) has been developed, which produces uniform tetragonal CaMoO4 microarchitectures with different morphologies (peanuts, cocoons, spindles and spheres) composed of self-assembled entities. The morphology and crystal size of such assemblies could be tuned by a simple change of the nature of the components of the solvent mixture or their volumetric ratio in such a mixture. All particles presented similar excitation and emission spectra arising from a charge transfer process within the MoO4 2-groups. The emitted light presented a bluish-green color and its intensity was higher for the spindle-type particles. This synthesis procedure was also suitable for doping peanut-like CaMoO4 architectures with Eu3+ or Dy3+ cations up to a 1% molar ratio (Ln/Ln + Ca), without altering their morphology or crystalline structure. The so prepared phosphors emitted an intense red (Eu-doped) or greenish (Dy-doped) light when excited through the MoO42- group excitation band, indicating the presence of an energy transfer process from such groups to the Ln(3+) cations. Finally, a white light emitting phosphor with chromaticity coordinates x = 0.335 and y = 0.365 and a correlated color temperature of 5407 K was developed by codoping peanut-type CaMoO4 particles with suitable amounts of Dy3+ (0.35%) and Eu3+ (0.15%) cations, which could find applications in white light emitting diodes.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c6ce02611g
Reactividad de Sólidos
A Promising approach to the kinetics of crystallization processes: The sample controlled thermal analysis
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 100 (2017) 1125-1133 DOI: 10.1111/jace.14604
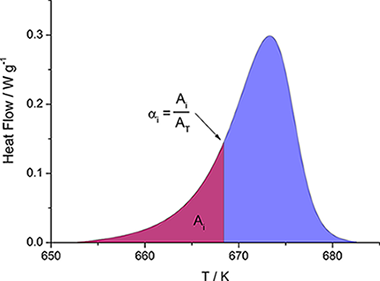
Abstract
Constant Rate Thermal Analysis (CRTA) method implies controlling the temperature in such a way that the reaction rate is maintained constant all over the process. This method allows determining simultaneously both the kinetic parameters and the kinetic model from a single experiment as the shape of the CRTA -T curves strongly depends on the kinetic model. CRTA method has been developed in the market only for thermogravimetric and thermodilatometric systems and, therefore, its use has been limited until now to the kinetic study of processes involving changes in mass or size of the samples, respectively. To overcome this obstacle, a method has been developed in this work for using the DSC signal for controlling the process rate in such a way that CRTA would be applied to the kinetic analysis of either phase transformations or crystallizations. The advantages of CRTA for performing the kinetics of crystallization processes have been here successfully demonstrated for the first time after selecting the crystallization of zirconia gel as test reaction.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.14604
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Antibacterial response of titanium oxide coatings doped by nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation
Esparza, J; Fuentes, GF; Bueno, R; Rodriguez, R; Garcia, JA; Vitas, AI; Rico, V; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface and Coatings Technology, 314 (2017) 67-71 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.11.002
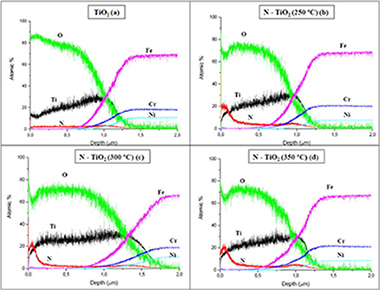
Abstract
Plasma immersion ion implantation technology has been utilized to enhance the photocatalytic activity of the anatase phase of TiO2 thin films deposited by cathodic arc evaporation PVD. The main objective of this study is to shift the light absorbance of the titania in order to obtain antibacterial activity under visible light irradiation. TiO2 thin films, deposited on polished stainless steel AISI 304 and silicon wafers, were implanted with nitrogen ions (N+/N2+) at 20 kV energy and different temperatures between 250 and 350 °C. The antibacterial activity of nitrogen implanted titania coatings has been monitored for Escherichia coli under visible light irradiation. Additionally ultra violet/visible spectrophotometry tests have been carried out to measure the changes in the light absorbance of the doped films. Further characterization has been performed, including X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and glow discharge optical emission spectrometry. As a result of Nitrogen implantation, the light absorption peak shifted from ultra violet region (UV-A) to visible wavelength range, which led to an increase of the antibacterial efficacy under visible light irradiation.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.11.002
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Preferential oxidation of CO on a La-Co-Ru perovskite-type oxide catalyst
Pereniguez, R; Caballero, A; Ferri, DCatalysis Communication, 92 (2017) 75-79 DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.12.020
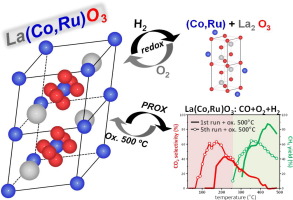
Abstract
A Ru-containing perovskite-type oxide La(Co,Ru)O3 of nominal composition LaCo0.8Ru0.2O3 was prepared by ultrasonic spray combustion and tested for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX). EXAFS indicated that Ru adopted the coordination environment of Co in LaCoO3 while Co was present as LaCoO3 and Co3O4. PROX activity was replaced by CO hydrogenation activity above 250 °C. Short oxidation at 500 °C between temperature programmed reaction ramps did not restore the initial La(Co,Ru)O3 structure but generated a catalyst with improved PROX activity compared to the initial La(Co,Ru)O3. Under reductive PROX conditions the material experienced structural changes that improved its overall catalytic activity only if the catalyst was oxidized after each temperature programmed ramp.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.12.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Monitoring the Reaction Mechanism in Model Biogas Reforming by InSitu Transient and Steady-State DRIFTS Measurements
Bobadilla, LF; Garcilaso, V; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemsuschem, 10 (2017) 1193-1201 DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201601379
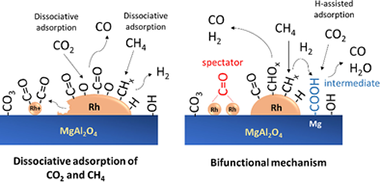
Abstract
In this work, the reforming of model biogas was investigated on a Rh/MgAl2O4 catalyst. In situ transient and steady-state diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) measurements were used to gain insight into the reaction mechanism involved in the activation of CH4 and CO2. It was found that the reaction proceeds through of an initial pathway in which methane and CO2 are both dissociated on Rh metallic sites and additionally a bifunctional mechanism in which methane is activated on Rh sites and CO2 is activated on the basic sites of the support surface via a formate intermediate by H-assisted CO2 decomposition. Moreover, this plausible mechanism is able to explain why the observed apparent activation energy of CO2 is much lower than that of CH4. Our results suggest that CO2 dissociation facilitates CH4activation, because the oxygen-adsorbed species formed in the decomposition of CO2 are capable of reacting with the CHx species derived from methane decomposition.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201601379
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Reliability of new poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) membranes treated with oxygen plasma plus silicon dioxide layers for pre-prosthetic guided bone regeneration processes
Castillo-Dali, G; Castillo-Oyague, R; Batista-Cruzado, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Rodriguez-Gonzalez-Elipe, A; Saffar, JL; Lynch, CD; Gutierrez-Perez, JL; Torres-Lagares, DMedicina Oral Patología Oral y Cirugia Oral, 22 (2017) E242-E250 DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21512
Abstract
Background: The use of cold plasmas may improve the surface roughness of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) membranes, which may stimulate the adhesion of osteogenic mediators and cells, thus accelerating the biodegradation of the barriers. Moreover, the incorporation of metallic-oxide particles to the surface of these membranes may enhance their osteoinductive capacity. Therefore, the aim of this paper was to evaluate the reliability of a new PLGA membrane after being treated with oxygen plasma (PO2) plus silicon dioxide (SiO2) layers for guided bone regeneration (GBR) processes.
Material and Methods: Circumferential bone defects (diameter: 11 mm; depth: 3 mm) were created on the top of eight experimentation rabbits' skulls and were randomly covered with: (1) PLGA membranes (control), or (2) PLGA/ PO2/SiO2 barriers. The animals were euthanized two months afterwards. A micromorphologic study was then performed using ROI (region of interest) colour analysis. Percentage of new bone formation, length of mineralised bone, concentration of osteoclasts, and intensity of ostheosynthetic activity were assessed and compared with those of the original bone tissue. The Kruskal-Wallis test was applied for between-group com asignificance level of a=0.05 was considered.
Results: The PLGA/ PO2/SiO2 membranes achieved the significantly highest new bone formation, length of miner-alised bone, concentration of osteoclasts, and ostheosynthetic activity. The percentage of regenerated bone supplied by the new membranes was similar to that of the original bone tissue. Unlike what happened in the control group, PLGA/PO2/SiO2 membranes predominantly showed bone layers in advanced stages of formation. Conclusions: The addition of SiO2 layers to PLGA membranes pre-treated with PO2 improves their bone-regeneration potential. Although further research is necessary to corroborate these conclusions in humans, this could be a promising strategy to rebuild the bone architecture prior to rehabilitate edentulous areas.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21512
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multicolored Emission and Lasing in DCM-Adamantane Plasma Nanocomposite Optical Films
Alcaire, M; Cerdan, L; Zamarro, FL; Aparicio, FJ; Gonzalez, JC; Ferrer, FJ; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Barranco, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (2017) 8948-8959 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01534
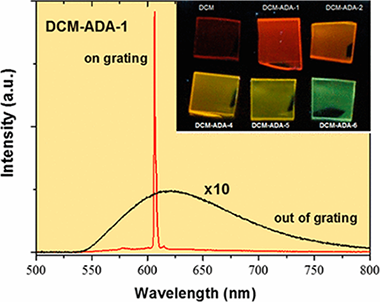
Abstract
We present a low-temperature versatile protocol for the fabrication of plasma nanocomposite thin films to act as tunable emitters and optical gain media. The films are obtained by the remote plasma-assisted deposition of a 4-(dicyano-methylene)-2-methy1-6-(4-dimethylamino-styry1)-4Hpyran (DCM) laser dye alongside adamantane. The experimental parameters that determine the concentration of the dye in the films and their optical properties, including light absorption, the refractive index, and luminescence, are evaluated. Amplified spontaneous emission experiments in the DCM/adamantane nano composite waveguides show the improvement of the copolymerized nano composites' properties compared to films that were deposited with DCM as the sole precursor. Moreover, one-dimensional distributed feed-back laser emission is demonstrated and characterized in some of the nanocomposite films that are studied. These results open new paths for the optimization of the optical and lasing properties of plasma nanocomposite polymers, which can be straightforwardly integrated as active components in optoelectronic devices.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01534
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Aperiodic Metal-Dielectric Multilayers as Highly Efficient Sunlight Reflectors
Alberto Jiménez-Solano; Miguel Anaya; Mauricio E. Calvo; Mercedes Alcon-Camas; Carlos Alcañiz; Elena Guillén; Noelia Martínez; Manuel Gallas; Thomas Preussner; Ramón Escobar-Galindo; Hernán MíguezAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) 1600833 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201600833
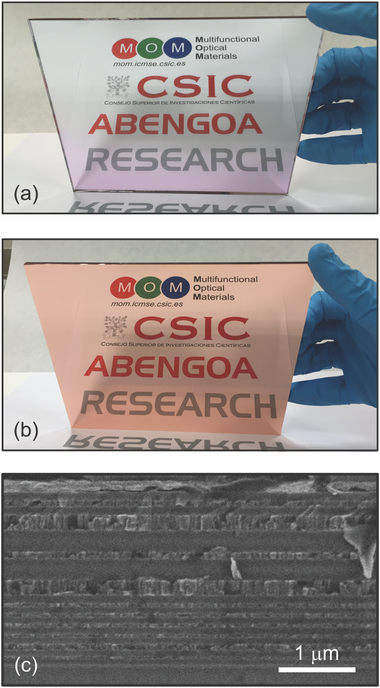
Abstract
The optimum reflection of the solar spectrum at well-defined incident directions as well as its durability in time are, both, fundamental requirements of the optics of thermosolar and photovoltaic energy conversion systems. The stringent high performance needed for these applications implies that, almost exclusively, second face mirrors based on silver are employed for this purpose. Herein, the possibility to develop solar mirrors using other metals, such as copper and aluminum, is theoretically and experimentally analyzed. It is found that reflectors based on these inexpensive metals are capable of reflecting the full solar spectrum with efficiencies comparable to that of silver-based reflectors. The designs herein proposed are based on aperiodic metal-dielectric multilayers whose optimized configuration is chosen employing a code based on a genetic algorithm that allows selecting the best one among 108 tested reflectors. The use of metals with wider spectral absorption bands is compensated by the use of multilayered designs in which metal absorption is almost suppressed, as the analysis of the electric field intensity distribution demonstrates. The feasibility of the proposed mirrors is demonstrated by their actual fabrication by large area deposition techniques amenable for mass production.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201600833
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Ceramics of Ta-doping stabilized orthorhombic ZrO2 densified by spark plasma sintering and the effect of post-annealing in air
Sponchia, G; Moshtaghioun, BM; Benedetti, A; Riello, P; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Ortiz, ALScripta Materialia, 130 (2017) 128-132 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.11.021
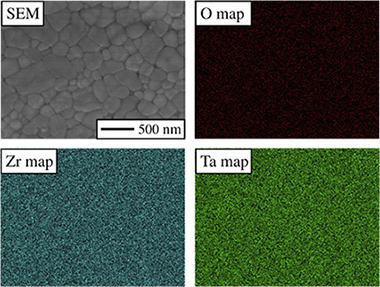
Abstract
16 mol% Ta-doped ZrO2 powders were synthesized and densified by spark-plasma sintering (SPS) in vacuum, followed by post-SPS annealing in air, thus obtaining two ultrafine-grained ceramics consisting of Ta-doping stabilized orthorhombic ZrO2. The as-SPSed ceramic is black because it is actually a suboxide essentially with reduced cations and abundant oxygen vacancies, whereas the post-annealed ceramic is white because it is an oxide without vacancies and with only partially reduced cations. Both ceramics are relatively hard and brittle, but the as-SPSed ceramic was slightly more so, attributable to crystallographic and microstructural differences. Implications of interest for the ceramics community are discussed.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.11.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Large-Scale Storage of Concentrated Solar Power from Industrial Waste
Perejon, Antonio; Valverde, Jose Manuel; Miranda-Pizarro, Juan; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5 (2017) 2265-2272 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02576
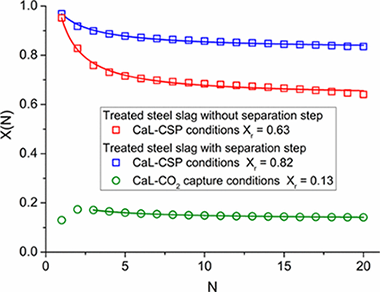
Abstract
Deep penetration of renewable energies into the grid relies on the development of large-scale energy storage technologies using cheap, abundant, and nontoxic materials. Concentrated solar power (CSP) is particularly suitable to massively store thermal energy for dispatchable electricity generation. This is currently accomplished in a few demonstration plants by using molten salts albeit in a not competitive way yet. Process simulation studies indicate that thermochemical energy storage of CSP by means of the calcium looping (CaL) technology would reduce the cost of storage and increase the flexibility of energy supply provided that widely available and cheap CaO precursors with high and stable multicycle activity are used. In this work, we investigate the behavior of calcium rich steel slag at CaL conditions that would expectedly maximize the efficiency of CSP energy storage and power production. When treated with acetic acid, this nontoxic widely abundant waste yields a CaO rich solid with stable conversion near 0.8 over successive carbonation/calcination cycles at these CaL conditions
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02576
Materiales Coloidales
Diverse Applications of Nanomedicine
Pelaz, Beatriz; Alexiou, Christoph; Alvarez -Puebla, Ramon A.; Alves, Frauke; Andrews, Anne M.; Ashraf, Sumaira; Balogh, Lajos P.; Ballerini, Laura; Bestetti, Alessandra; Brendel, Cornelia; Bosi, Susanna; Carril, Monica; Chan, Warren C. W.; Chen, ChunyingACS Nano, 11 (2017) 2312-2381 DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06040
Abstract
The design and use of materials in the nanoscale size range for addressing medical and health-related issues continues to receive increasing interest. Research in nanomedicine spans a multitude of areas, including drug delivery, vaccine development, antibacterial, diagnosis and imaging tools, wearable devices, implants, high-throughput screening platforms, etc. using biological, nonbiological, biomimetic, or hybrid materials. Many of these developments are starting to be translated into viable clinical products. Here, we provide an overview of recent developments in nanomedicine and highlight the current challenges and upcoming opportunities for the field and translation to the clinic.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06040
Tribología y Protección de Superficies - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Strong Quantum Confinement and Fast Photoemission Activation in CH3NH3PbI3 Perovskite Nanocrystals Grown within Periodically Mesostructured Films
Miguel Anaya; Andrea Rubino; Teresa Cristina Rojas; Juan Francisco Galisteo-López; Mauricio Ernesto Calvo; Hernán MíguezAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) 1601087 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201601087
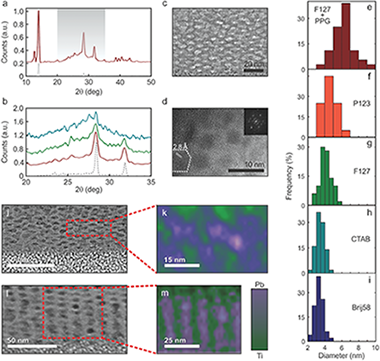
Abstract
In this Communication, a synthetic route is demonstrated to obtain stabilized MAPbI3 nanocrystals embedded in thin metal oxide films that display well-defined and adjustable quantum confinement effects over a wide range of 0.34 eV. Mesostructured TiO2 and SiO2 films displaying an ordered 3D pore network are prepared by evaporation-induced self-assembly of a series of organic supramolecular templates in the presence of metal oxide precursors. The pores in the inorganic films obtained after thermal annealing are then used as nanoreactors to synthesize MAPbI3crystallites with narrow size distribution and average radius comprised between 1 and 4 nm, depending on the template of choice. Both the static and dynamic photoemission properties of the ensemble display features distinctive of the regime of strong quantum confinement. Photoemission maps demonstrate that the spectral and intensity properties of the luminescence extracted from the perovskite quantum dot loaded films are homogeneous over squared centimeters areas. At variance with their bulk counterparts, constant emission intensity is reached in time scales at least four orders of magnitude shorter.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201601087
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Solid lubricant behavior of MoS2 and WSe2-based nanocomposite coatings
Dominguez-Meister, S; Rojas, TC; Brizuela, M; Sanchez-Lopez, JCScience and Tecnology of Advances Materials, 18 (2017) 1 DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2016.1275784
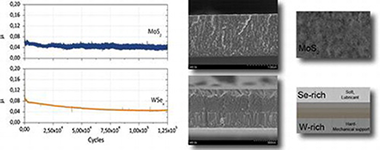
Abstract
Tribological coatings made of MoS2 and WSe2 phases and their corresponding combinations with tungsten carbide (WC) were prepared by non-reactive magnetron sputtering of individual targets of similar composition. A comparative tribological analysis of these multiphase coatings was done in both ambient air (30-40% relative humidity, RH) and dry nitrogen (RH<7%) environments using the same tribometer and testing conditions. A nanostructural study using advanced transmission electron microscopy of the initial coatings and examination of the counterfaces after the friction test using different analytical tools helped to elucidate what governs the tribological behavior for each type of environment. This allowed conclusions to be made about the influence of the coating microstructure and composition on the tribological response. The best performance obtained with a WSe x film (specific wear rate of 2 x 10(-8) mm(3) N(-1)m(-1) and a friction coefficient of 0.03-0.05) was compared with that of the well-established MoS2 lubricant material.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2016.1275784
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
On the effect of wall slip on the determination of the yield stress of magnetorheological fluids
Caballero-Hernandez, J; Gomez-Ramirez, A; Duran, JDG; Gonzalez-Caballero, F; Zubarev, AY; Lopez-Lopez, MTApplied Rheology, 27 (2017) 15001 (8 pages) DOI: 10.3933/ApplRheol-27-15001
Abstract
We study the effect of wall slip on the measured values of the yield stress of magnetorheological (MR) fluids. For this aim we used a rheometer provided with parallel-plate geometries of two types, distinguished by having smooth or rough surfaces. We found that wall slip led to the underestimation of the yield stress when measuring geometries with smooth surfaces were used, and that this underestimation was more pronounced for the static than for the dynamic yield stress. Furthermore, we analysed the effect that both irreversible particle aggregation due to colloidal interactions and reversible magnetic fieldinduced particle aggregation had on the underestimation provoked by wall slip. We found that the higher the degree of aggregation the stronger the underestimation of the yield stress. At low intensity of the applied magnetic field irreversible particle aggregation was dominant and, thus, the underestimation of the yield stress was almost negligible for well-dispersed MR fluids, whereas it was rather pronounced for MR fluids suffering from irreversible aggregation. As the magnetic field was increased the underestimation of the yield stress became significant even for the best dispersed MR fluid.
Marzo, 2017 · DOI: 10.3933/ApplRheol-27-15001
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Fabrication of black-gold coatings by glancing angle deposition with sputtering
Vitrey, A; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Gonzalez, MU; Garcia-Martin, JMBeilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 8 (2017) 434–439 DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.8.46
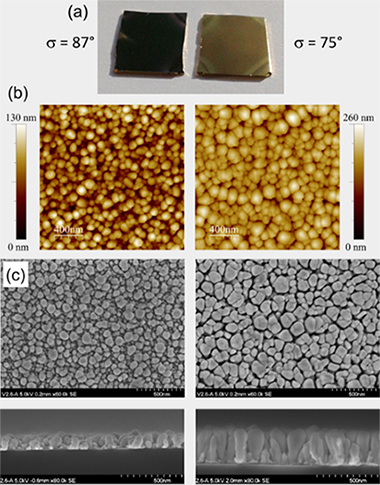
Abstract
The fabrication of black-gold coatings using sputtering is reported here. Glancing angle deposition with a rotating substrate is needed to obtain vertical nanostructures. Enhanced light absorption is obtained in the samples prepared in the ballistic regime with high tilt angles. Under these conditions the diameter distribution of the nanostructures is centered at about 60 nm and the standard deviation is large enough to obtain black-metal behavior in the visible range.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.8.46
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Precision and accuracy of stress measurement with a portable X-ray machine using an area detector
Lee, SY; Ling, JJ; Wang, SH; Ramirez-Rico, JJournal of Applied Crystallography, 50 (2017) 131-144 DOI: 10.1107/S1600576716018914
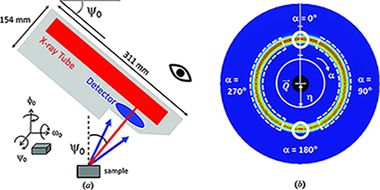
Abstract
The use of portable X-ray stress analyzers, which utilize an area detector along with the newly adopted 'cos alpha' or full-ring fitting method, has recently attracted increasing interest. In laboratory conditions, these measurements are fast, convenient and precise because they employ a single-exposure technique that does not require sample rotation. In addition, the effects of grain size and orientation can be evaluated from the Debye ring recorded on the area detector prior to data analysis. The accuracy of the measured stress, however, has been questioned because in most cases just a single reflection is analyzed and the sample-to-detector distances are relatively short. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of the uncertainty associated with a state-of-the-art commercial portable X-ray device. Annealed ferrite reference powders were used to quantify the instrument precision, and the accuracy of the stress measurement was tested by in situ tensile loading on 1018 carbon steel and 6061 aluminium alloy bar samples. The results show that the precision and accuracy are sensitive to the instrument (or sample) tilt angle (0) as well as to the selected hkl reflection of the sample. The instrument, sample and data analysis methods all affect the overall uncertainty, and each contribution is described for this specific portable X-ray system. Finally, on the basis of the conclusions reached, desirable measurement/analysis protocols for accurate stress assessments are also presented.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1107/S1600576716018914
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Packaging Materials: All‐Natural Sustainable Packaging Materials Inspired by Plant Cuticles (Adv. Sustainable Syst. 1‐2/2017)
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJ; Cataldi, P; Paul, UC; Contardi, M; Cingolani, R; Bayer, IS; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, AAdvanced Sustainable Systems, 1 (2017) DOI: 10.1002/adsu.201770012
Abstract
In article number 1600024, José A. Heredia‐Guerrero, Athanassia Athanassiou, and co‐workers present new, sustainable composite materials inspired by plant cuticles. These materials are fabricated by the impregnation of fibrous cellulose substrates with a naturally occurring polyhydroxylated fatty acid, and subsequent polymerization of the latter into a polyester. In the image a piece of this new material is shown together with tomato and pepper fruits. Cover image created by Dr. Duilio Farina.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adsu.201770012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Cholesterol biosensing with a polydopamine-modified nanostructured platinum electrode prepared by oblique angle physical vacuum deposition
Martin, M; Salazar, P; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Gonzalez-Mora, JL; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 240 (2017) 37-45 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.092
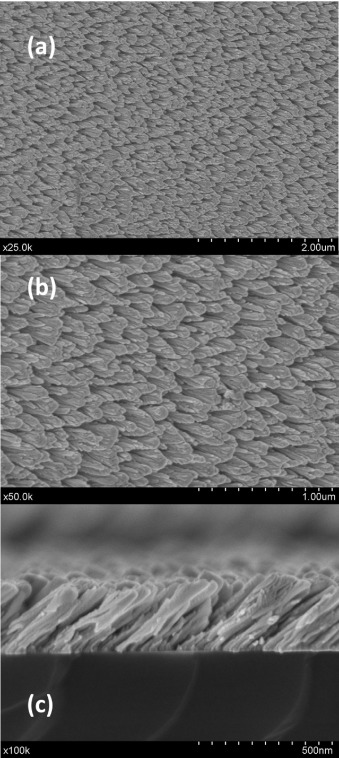
Abstract
This paper reports a novel cholesterol biosensor based on nanostructured platinum (Pt) thin films prepared by Magnetron Sputtering (MS) in an oblique angle (OAD) configuration. Pt thin films were deposited onto a gold screen-printed electrode and characterized using Rutherford Back Scattering (RBS), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Cyclic Voltammetry (CV), X-ray Photo-electron Spectroscopy (XPS), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and wetting analysis. Our results confirmed that the film is highly porous and formed by tilted nanocolumns, with an inclination of around 40 degrees and a total thickness of 280 nm. XRD and CV analysis confirmed the polycrystalline nature of the Pt thin film. Cholesterol oxidase (ChOx) was covalently immobilized using a bioinspired polymer, polydopamine (PDA), via Schiff base formation and Michael-type addition. After being immobilized, ChOx displayed apparent activation energy of 34.09 kJ mol(-1) and Michaelis constant (K-M) values of 34.09 kJ mol(-1) and 3.65 mM, respectively, confirming the high affinity between ChOx and cholesterol and the excellent ability of the PDA film for immobilizing biological material without degradation. Under optimized working conditions the developed biosensor presented a sensitivity of 14.3 mA M(-1)cm(-2) (R-2:0.999) with a linear range up to 0.5 mM and a limit of detection of 10.5 mu M (S/N= 3). Furthermore, the biosensor exhibited a fast response (<8 s), good anti-interference properties and high stability after relatively long-term storage (2 months).
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.092
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
High vacuum synthesis and ambient stability of bottom-up graphene nanoribbons
Fairbrother, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Lauber, B; Shorubalko, I; Ruffieux, P; Hintermann, T; Fasel, RNanoscale, 9 (2017) 2785-2792 DOI: 10.1039/C6NR08975E
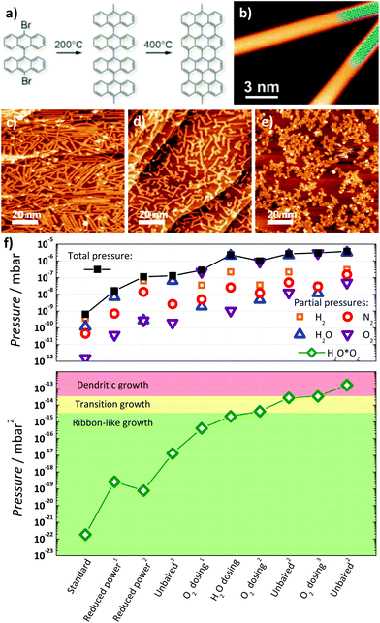
Abstract
Carbon-based nanomaterials such as graphene are at a crucial point in application development, and their promising potential, which has been demonstrated at the laboratory scale, must be translated to an industrial setting for commercialization. Graphene nanoribbons in particular overcome one limitation of graphene in some electronic applications because they exhibit a sizeable bandgap. However, synthesis of bottom-up graphene nanoribbons is most commonly performed under ultra-high vacuum conditions, which are costly and difficult to maintain in a manufacturing environment. Additionally, little is known about the stability of graphene nanoribbons under ambient conditions or during transfer to technologically relevant substrates and subsequent device processing. This work addresses some of these challenges, first by synthesizing bottom-up graphene nanoribbons under easily obtained high vacuum conditions and identifying water and oxygen as the residual gases responsible for interfering with proper coupling during the polymerization step. And second, by using Raman spectroscopy to probe the stability of nanoribbons during storage under ambient conditions, after transfer to arbitrary substrates, and after fabrication of field-effect transistor devices, which shows structurally intact nanoribbons even several months after synthesis. These findings demonstrate the potential of graphene nanoribbon technologies by addressing some limitations which might arise in their commercialization.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/C6NR08975E
Reactividad de Sólidos
Processing and characterization of surrogate nuclear materials with controlled radial porosity
Torres, Y; Garcia-Ostos, C; Arevalo, C; Gotor, FJ; Pavon, JJ; Trueba, P; Rodriguez-Ortiz, JAJournal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54 (2017) 167-173 DOI: 10.1080/00223131.2016.1222918
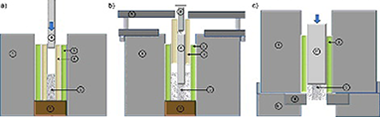
Abstract
Irradiated fuel pellets present radial gradient porosity. CeO2 has been proven as a surrogate material to understand irradiated mixed oxide (MOX) due to its similar structural and mechanical properties. A novel compaction device was developed to produce CeO2 cylindrical pellets with controlled radial porosity. Three blends of CeO2 with different binder contents (0.5, 3 and 7.5 vol.% of ethylene-bis-stearamide, EBS) were prepared and used to obtain three different porosities for the core, intermediate and outer rings of pellets, respectively. Different compaction pressures were employed in each region to get the intended porosities. The whole pellet was subjected to a heating rate up to 500 degrees C to remove the EBS binder. Finally, a pressureless sintering step was performed at 1700 degrees C for 4 h. A microstructural characterization was performed in the three areas, including grain size and porosity. Mechanical properties like hardness, fracture toughness and tribo-mechanical response, as scratch resistance, were also determined. Pellets fabricated from this device have shown microstructural and mechanical properties with a good correlation to those of irradiated nuclear fuel.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1080/00223131.2016.1222918
Reactividad de Sólidos
Preparation of ytterbium substituted BiFeO3 multiferroics by mechanical activation
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Hayward, MA; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 37 (2017) 945-954 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.09.014
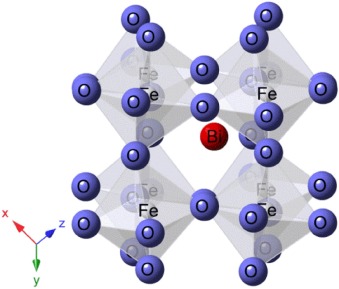
Abstract
Samples in the system Bi1-xYbxFeO3 (0.02 <= x <= 0.07) have for the first time been prepared by mechanical activation followed by sintering. XRD and DSC measurements show that the solubility limit of ytterbium in the R3c Bi1-xYbxFeO3 system is reached at x similar to 0.03. Higher ytterbium contents lead to a two-phase mixture of a main R3c phase of approximate composition Bi0.97Yb0.03FeO3 and ytterbium enriched secondary phases that cannot be readily indexed or quantified due to their small amount. DSC and temperature-dependent XRD showed that while the magnetic ordering temperature, T-N, was unaffected by Yb substitution, the ferroelectric ordering, T-C, declined. Temperature-dependent XRD patterns show that all samples exhibit rhombohedral R3c to orthorrhombic Pnma phase transitions. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy suggests the potential use of the samples in photocatalytic applications due to their low band gap energy. Impedance spectroscopy and magnetic measurements show that samples are electrically homogenous and highly insulating, exhibiting antiferromagnetic behaviour at room temperature.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.09.014
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Identification of Outer and Inner Nickel Particles in a Mesoporous Support: How the Channels Modify the Reducibility of Ni/SBA-15 Catalysts
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Caballero, AChemnanomat, 3 (2017) 94-97 DOI: 10.1002/cnma.201600297
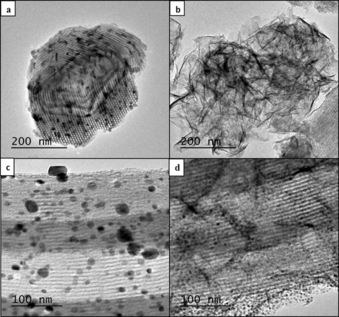
Abstract
Two different nickel supported on SBA-15 catalytic systems have been prepared by means of impregnation (Ni/SBA-15-ImU) and deposition-precipitation (Ni/SBA-15-DP) methodologies. Upon calcination, Ni/SBA-15DP presents a well-developed nickel phyllosilicate phase, which after reduction gives rise to a dispersed and homogeneous metallic phase, mainly located inside the 5 nm in diameter mesoporous structure of the support. On the contrary, as evidenced by XRD and a double temperature programmed reduction (TPR) peak, the Ni/SBA-15-ImU catalyst presents two different NiO phases, which after reduction in hydrogen generate nickel particles in a wide range of sizes. In situ XAS and XPS have unambiguously showed that the distinct TPR profiles obtained for each system are related with particles located in and out the mesoporous structure of the SBA-15 channels. The particles inside the porous are more difficult to reduce, clearly showing a kind of confinement effect of the SBA-15 mesostructure, modifying the reducibility of the NiO phase.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/cnma.201600297
Reactividad de Sólidos
A new family of cermets: Chemically complex but microstructurally simple
de la Obra, AG; Aviles, MA; Torres, Y; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 63 (2017) 17-25 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.04.011
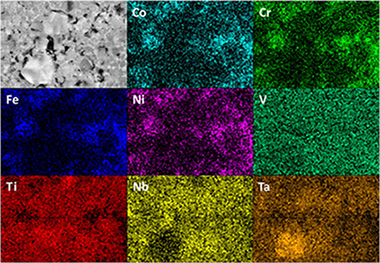
Abstract
Cermets based on Ti(C,N) have interesting properties, such as high wear resistance, high chemical stability and good mechanical strength at high temperature, but to become a viable alternative to cemented carbides, the fracture toughness and damage tolerance must be significantly improved. Complete solid-solution cermets (CSCs) have been proposed to further improve the mechanical properties of these materials. However, to develop this family of cermets with a high level of quality and reliability, using pre-fabricated complex carbonitrides is necessary instead of unalloyed mixtures as the raw ceramic material. A mechanochemical process called mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) is suitable to obtain these complex carbonitrides with high stoichiometric control. On the other hand, high entropy alloys (HEAs), which can also be obtained by mechanochemical processes, are a good candidate to replace the current binder phase in cermets because they exhibit high strength and ductility at high temperature and good resistance to both wear and corrosion. In this work, a new family of CSCs based on (Ti,Ta,Nb)CxN1-x, with HEAs belonging to the Fe-Co-Ni-Cr-Mn-V system as the binder phase is developed by mechanochemical processes. With only two constituent phases, these cermets have a simple microstructure but a high compositional complexity because both the ceramic and binder phases are complex solid solutions with at least five components.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.04.011
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Preparation and Optimization of Fluorescent Thin Films of Rosamine-SiO2/TiO2 Composites for NO2 Sensing
Guillen, MG; Gamez, F; Suarez, B; Queiros, C; Silva, AMG; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Pedrosa, JM; Lopes-Costa, TMaterials, 10 (2017) art 124 DOI: 10.3390/ma10020124
Abstract
The incorporation of a prototypical rosamine fluorescent dye from organic solutions into transparent and microstructured columnar TiO2 and SiO2 (MO2) thin films, prepared by evaporation at glancing angles (GAPVD), was evaluated. The aggregation of the adsorbed molecules, the infiltration efficiency and the adsorption kinetics were studied by means of UV-Vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopies. Specifically, the infiltration equilibrium as well as the kinetic of adsorption of the emitting dye has been described by a Langmuir type adsorption isotherm and a pseudosecond order kinetic model, respectively. The anchoring mechanism of the rosamine to the MO2 matrix has been revealed by specular reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and infiltration from aqueous solutions at different pH values. Finally, the sensing performance towards NO2 gas of optimized films has been assessed by following the changes of its fluorescence intensity revealing that the so-selected device exhibited improved sensing response compared to similar hybrid films reported in the literature.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.3390/ma10020124
Materiales Coloidales
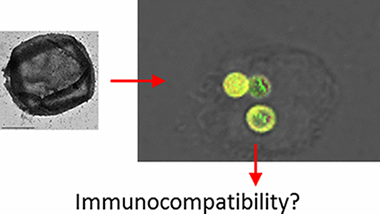
Comprehensive and Systematic Analysis of the Immunocompatibility of Polyelectrolyte Capsules
Zyuzin, MV; Diez, P; Goldsmith, M; Carregal-Romero, S; Teodosio, C; Rejman, J; Feliu, N; Escudero, A; Almendral, MJ; Linne, U; Peer, D; Fuentes, M; Parak, WJBioconjugate Chemistry, 28 (2017) 556-564 DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00657
Abstract
The immunocompability of polyelectrolyte capsules synthesized by layer-by-layer deposition has been investigated. Capsules of different architecture and composed of either non-degradable or biodegradable polymers, with either positively or negatively charged outer surface, and with micrometer size, have been used, and the capsule uptake by different cell lines has been studied and quantified. Immunocompatibility studies were performed with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Data demonstrate that incubation with capsules, at concentrations relevant for practical applications, did not result in a reduced viability of cells, as it did not show an increased apoptosis. Presence of capsules also did not result in an increased expression of TNF-α, as detected with antibody staining, as well as at mRNA level. It also did not result in increased expression of IL-6, as detected at mRNA level. These results indicate that the polyelectrolyte capsules used in this study are immunocompatible.
Febrero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00657
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
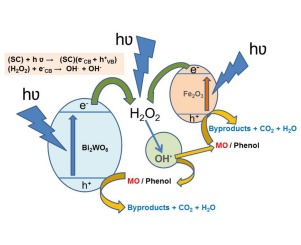
Mixed alpha-Fe2O3/Bi2WO6 oxides for photoassisted hetero-Fenton degradation of Methyl Orange and Phenol
Jaramillo-Paez, C; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MC; Bouziani, A; El Azzouzi, MJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A-Chemistry, 332 (2017) 521-533 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.09.031
Abstract
Mixed oxides, alpha-Fe2O3/Bi2WO6, were prepared using a mechanical mixing procedure by adding to the Bi2WO6 previously obtained by hydrothermal method the corresponding amount of a prepared alpha-Fe2O3, the latter obtained by thermal decomposition of Fe(NO3)center dot 9H(2)O. The physicochemical surface, structural, morphological characteristics and optical properties of the samples, single and mixed, were determined by BET, XRD, FE-SEM, XPS and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra showed that incorporating a 5%wt. of alpha-Fe2O3 to the corresponding amount of Bi2WO6 sample broadened the visible light absorption of Bi2WO6 as expected. The photocatalytic activity, of single and mixed catalysts, to degrade a selected dye such as Methyl Orange (MO) as well as the transparent substrate Phenol (Ph) was studied, in aqueous medium (pH 5.5) under UV and sun-like illumination conditions in the absence and presence of H2O2. In the present study the use of a alpha-Fe2O3/Bi2WO6/H2O2 system demonstrate much higher photocatalytic efficiency to degrade both MO and Ph than pristine Bi2WO6 or alpha-Fe2O3, single or mixed. Using the system alpha-Fe2O3/Bi2WO6/H2O2, around 85% of MO was degraded in 60 min under sun-like illumination whereas 100% was degraded in 60 min under UV-illumination. However, just around 30% of Ph was degraded in 120 min in the alpha-Fe2O3/Bi2WO6/H2O2 system under sun-like illumination whereas around a 95% was degraded in 90 min under UV-illumination. Under UV illumination, the generation of hydroxyl radicals is favorable; whereas under sun-like illumination, only the small fraction of the UV can produces the center dot OH. Under illumination, the H2O2 could react with photoinduced electrons from the photocatalysts leading to the production of hydroxyl radicals (center dot OH).
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.09.031
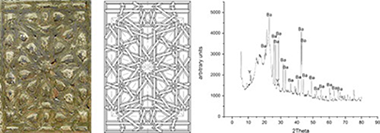
Analytical investigation of Mudejar polychrome on the carpentry in the Casa de Pilatos palace in Seville using non-destructive XRF and complementary techniques
Garrote, MA; Robador, MD; Perez-Rodriguez, JLSpectrochimica Acta Part A-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 173 (2017) 279-291 DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2016.09.027
Abstract
The pigments, execution technique and repainting used on the polychrome wood ceilings and doors in the Casa de Photos (Seville, Spain) were studied using portable X-ray fluorescence equipment. Cross-sections of small samples were also analysed by optical microscopy, SEM with EDX analysis, micro-Raman and micro-infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. These carpentry works are magnificent examples of the Mudejar art made in Spain in the early 16th century. Portable X-ray fluorescence gave good information on the different components of the polychrome. The SEM-EDX study of the surfaces of small samples gave information on their components and also characterized the compounds that had been deposited or formed by environmental contamination or by the alteration of some pigments. The SEM-EDX study of cross-sections facilitated the characterization of all layers and pigments from the support to the most external layer. The following pigments were characterized: red (cinnabar/vermillion, lead oxide, iron oxides and orpiment/realgar), black (carbon black), white (white lead and titanium barium white), yellow-orange-red-brown (orpiment/realgar and iron oxides), green (chromium oxide), blue (indigo blue and ultramarineblue), and gilding (gold leaf on bole). False gold, bronze and brass were also found. The pigments were applied with the oil painting technique over a support layer that had been primed with animal glue. This support layer was gypsum in some cases and white lead in others. This study is essential to the polychrome conservation of the studied artwork, and it will help clarify uncertainties in the history and painting of Mudejar art.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2016.09.027
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
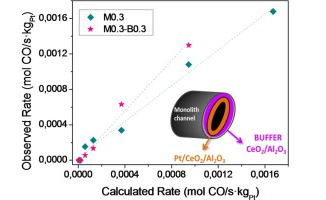
Structuring Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 WGS catalyst: Introduction of buffer layer
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Laguna, OH; Martinez, LM; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 200 (2017) 420-427 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.039
Abstract
This work is devoted to the development of novel structured catalytic system for WGS reaction. The new concept is related to the presence of a pre-catalytic "buffer" layer formed by WGS-inert oxide, i.e. not involved in CO conversion, but able to increase the number of participating sites in water dissociation step during the reaction. The performance of the proposed systems appears to depend strongly on the stream composition, being its effect beneficial in highly reducing atmospheres making it ideal for cleanup application. An increment of the partial kinetic order for water species is observed and reveals the key role of the water activation for superior catalytic behavior.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.039
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Spark plasma sintering of fine-grained alumina ceramics reinforced with alumina whiskers
Tamura, Y; Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Rodriguez, ADCeramis International, 43 (2017) 658-663 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.210
Abstract
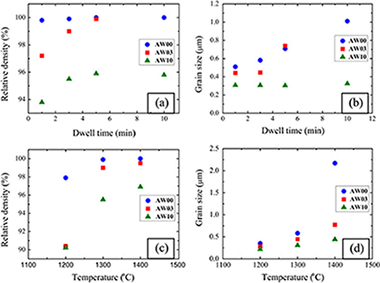
Densification of alumina whisker-reinforced alumina ceramics by spark plasma sintering (SPS) has been investigated with the aim of obtaining a fine-grained microstructure and also studying the effect of whisker addition on the room-temperature mechanical properties. It was found that whisker addition retards slightly the sinterability of alumina by whisker hindering of particle rearrangement. Besides, the internal stress on the alumina matrix particles reduced due to the presence of a whisker network structure of strong rigid boundaries. Nevertheless near fully-dense and fine-grained alumina ceramics with alumina whisker content between 3 wt% and 10 wt% could be obtained under appropriate SPS conditions. The hardness of alumina ceramics with 3 wt% was comparable to that of pure alumina ceramics (similar to 26 GPa) whereas its fracture toughness (5.6 MPa m(1/2)) was higher (4.2 MPa m(1/2)). Crack bridging by well-dispersed whiskers and whiskers pull-out were identified as the main toughening mechanisms.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.210
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Study of the E. coli elimination from urban wastewater over photocatalysts based on metallized TiO2
Murcia, JJ; Avila-Martinez, EG; Rojas, H; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCApplied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 200 (2017) 469-476 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.045
Abstract
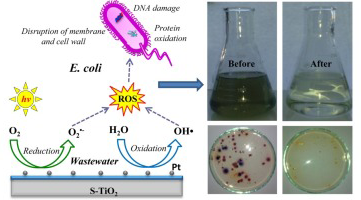
In this study, a series of photocatalysts based on TiO2 was tested in the elimination of Escherichia coli (E. coli) from urban wastewater. Firstly, TiO2 obtained by sol-gel method was modified by sulfation, and then gold or platinum nanoparticles were photodeposited on sulfated titania surface. Platinized samples were also prepared with different Pt content of 0.5 and 2 wt.%. The samples thus obtained were extensively characterized and it was found that sulfation considerably increases the S-BET value of TiO2 and promotes the anatase phase formation; it was also found that 0.5 wt.% Pt-TiO2 sample presents the lowest noble metal particle size and the best particle dispersion. All the photocatalysts synthesized have shown bactericidal effect and the results obtained by using bare and metalized TiO2 were considerably better than the results obtained with the commercial TiO2 P25 Evonic. Different light intensities were also evaluated in the photocatalytic tests and it was found that 120 W/m(2) leads to obtain the highest E. coli elimination from wastewater samples; however no total elimination of E. coli or other species of bacteria was achieved even after 5 h of photocatalytic treatment without catalyst. Total elimination of the E. coli was achieved after 3 h of photocatalytic reaction by using 120 Wim(2) of light intensity and 2 wt.% Pt-TiO2 as photocatalyst; no bacterial regrowth was observed even after 72 h.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.045
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical Gas Sensing of Ammonia and Amines Based on Protonated Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films
Castillero, Pedro; Roales, Javier; Lopes-Costa, Tania; Sanchez-Valencia, Juan R.; Barranco, Angel; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Pedrosa, Jose M.Sensors, 17 (2017) 24 DOI: 10.3390/s17010024
Abstract
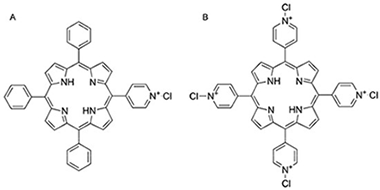
Open porous and transparent microcolumnar structures of TiO2 prepared by physical vapour deposition in glancing angle configuration (GLAD-PVD) have been used as host matrices for two different fluorescent cationic porphyrins, 5-(N-methyl 4-pyridyl)-10,15,20-triphenyl porphine chloride (MMPyP) and meso-tetra (N-methyl 4-pyridyl) porphine tetrachloride (TMPyP). The porphyrins have been anchored by electrostatic interactions to the microcolumns by self-assembly through the dip-coating method. These porphyrin/TiO2 composites have been used as gas sensors for ammonia and amines through previous protonation of the porphyrin with HCl followed by subsequent exposure to the basic analyte. UV-vis absorption, emission, and time-resolved spectroscopies have been used to confirm the protonation-deprotonation of the two porphyrins and to follow their spectral changes in the presence of the analytes. The monocationic porphyrin has been found to be more sensible (up to 10 times) than its tetracationic counterpart. This result has been attributed to the different anchoring arrangements of the two porphyrins to the TiO2 surface and their different states of aggregation within the film. Finally, there was an observed decrease of the emission fluorescence intensity in consecutive cycles of exposure and recovery due to the formation of ammonium chloride inside the film.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.3390/s17010024
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Electron injection and scaffold effects in perovskite solar cells
M. Anaya, W. Zhang, B. Clasen Hames, Y. Li, F. Fabregat-Santiago, M.E. Calvo, H.J. Snaith, H. Míguez, I. Mora-SeróJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 5 (2017) 634-644 DOI: 10.1039/C6TC04639H
Abstract
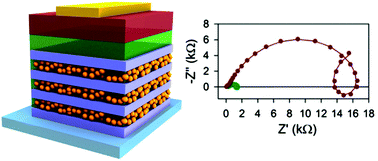
In spite of the impressive efficiencies reported for perovskite solar cells (PSCs), key aspects of their working principles, such as electron injection at the contacts or the suitability of the utilization of a specific scaffold layer, are not yet fully understood. Increasingly complex scaffolds attained by the sequential deposition of TiO2 and SiO2 mesoporous layers onto transparent conducting substrates are used to perform a systematic characterization of both the injection process at the electron selective contact and the scaffold effect in PSCs. By forcing multiple electron injection processes at a controlled sequence of perovskite–TiO2 interfaces before extraction, interfacial injection effects are magnified and hence characterized in detail. An anomalous injection behavior is observed, the fingerprint of which is the presence of significant inductive loops in the impedance spectra with a magnitude that correlates with the number of interfaces in the scaffold. Analysis of the resistive and capacitive behavior of the impedance spectra indicates that the scaffolds could hinder ion migration, with positive consequences such as lowering the recombination rate and implications for the current–potential curve hysteresis. Our results suggest that an appropriate balance between these advantageous effects and the unavoidable charge transport resistive losses introduced by the scaffolds will help in the optimization of PSC performance.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/C6TC04639H
Reactividad de Sólidos
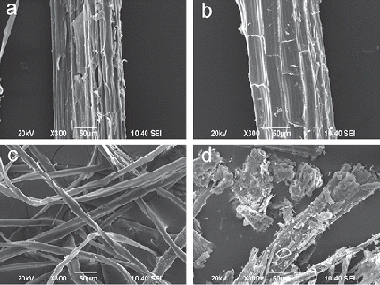
Structural and Chemical Characteristics of Sisal Fiber and Its Components: Effect of Washing and Grinding
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Artiaga, R; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Pascual-Cosp, JJournal of Natural Fibers, 14 (2017) 26-39 DOI: 10.1080/15440478.2015.1137529
Abstract
This work covers the study of microstructural changes of natural sisal fibers induced by different conditioning pre-treatments: mechanical grinding, cryogenic grinding, and hot waterwashing. The aim of the work is to clarify the effects of the pre-treatments on crystallinity and infrared spectra of sisal. Scanning electron microscopy results allowed to identify morphological changes on the fiber surface. Deeper changes of chemical origin were studied by attenuated total reflectance/Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and focused on the main components of cellular walls: cellulose, lignin, and xylan. The work was complemented with crystallinity index (I-c) data determined by two very different methods: the widely used for lignocellulosic fibers Segal equation based on X-ray diffraction measurements, and the other based on FTIR through the 1430/900 cm(-1) band intensity ratio, which is mostly used with cellulosic samples.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1080/15440478.2015.1137529
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Reactividad de Sólidos
Outstanding visible photocatalytic activity of a new mixed bismuth titanatate material
Zambrano, P; Sayagues, MJ; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCApplied Surface Science, 394 (2017) 16-24 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.042
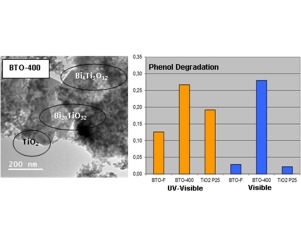
Abstract
In this work, a new photocatalyst based on bismuth titanates with outstanding visible photocatalytic activity was prepared by a facile hydrothermal method. The synthesised material showed visible activity as high as UV activity of commercial TiO2 P25 under the same experimental conditions for phenol degradation. A wide characterisation of the photocatalyst was performed. The material was composed of three phases; majority of Bi20TiO32 closely interconnected to Bi4Ti3O12 and amorphous TiO2. The high visible activity showed by this material could be ascribed to a combination of several features; i.e. low band gap energy value (2.1 eV), a structure allowing a good separation path for visible photogenerated electron-holes pairs and a relatively high surface area. This photocatalyst appeared as a promising material for solar and visible applications of photocatalysis.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.042
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Front contact optimization of industrial scale CIGS solar cells for low solar concentration using 2D physical modeling
Delgado-Sanchez, JM; Lopez-Gonzalez, JM; Orpella, A; Sanchez-Cortezon, E; Alba, MD; Lopez-Lopez, C; Alcubilla, RRenewable Energy, 101 (2017) 90-95 DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.08.046
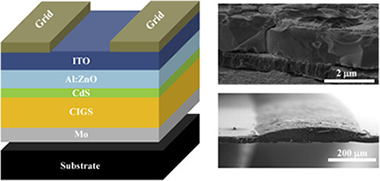
Abstract
Cu(In,Ga)Se-2 (CIGS) technology is one of the best absorber materials with record efficiencies among photovoltaic thin-film technologies (22.3% at lab scale and 16% at large commercial module). Although research on this material was originally motivated by low-cost, glass-glass applications focusing to fixed photovoltaic structures, the high efficiency values make CIGS an interesting alternative for low concentration systems. In this paper a 2D model for Cu(In,Ga)Se-2 (CIGS) solar cells under low solar concentration is described and contrasted with experimental data. Using simulation, the effect of front electric contact design parameters: finger width, finger separation, and number of buses are analyzed for solar concentrations from 1 up to 10 suns. Efficiency maps allowing front contact grid optimization are shown and analyzed for each concentration factor (Cx), assessing the viability of CIGS solar cells for low concentration applications, where commercial CIGS solar cells may exhibit 35% of electrical power increases with proper front grid optimization under low concentration respect to conventional grid design.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.08.046
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold promoted Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts prepared from hydrotalcite precursors: Advanced materials for the WGS reaction
Santos, JL; Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 201 (2017) 310-317 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.017
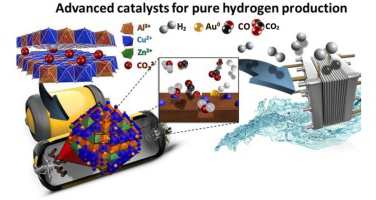
Abstract
Outstanding catalysts for the water was shift reaction are reported in this work. The combination of gold nanoparticles with Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 prepared from hydrotalcite-like precursors leads to very promising systems for pure hydrogen production. Full CO conversion is reached at temperatures as low as 180 degrees C. The key point seems to be the cooperation of Au and Cu and the optimal metal-oxide contact derived from the synthesis method. The high activity of gold for low temperature CO oxidation and the suitability of copper for the WGS results in a perfect synergy. Moreover the materials developed in this work present good stability and tolerance towards start/stop cycles an indispensable requisite for a realistic application in an integrated hydrogen fuel processor.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.017
Materiales Coloidales
Luminescent Eu-doped GdVO4 nanocrystals as optical markers for anti-counterfeiting purposes
Moretti, E; Pizzol, G; Fantin, M; Enrichi, F; Scopece, P; Ocana, M; Polizzi, SChemical Papers, 71 (2017) 149-159 DOI: 10.1007/s11696-016-0081-8
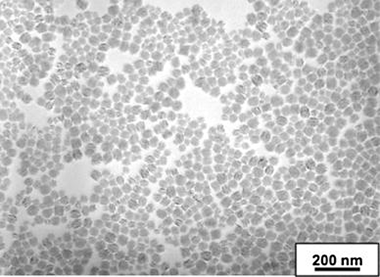
Abstract
Luminescent Eu: GdVO4 nanoparticles, with an average size of 60 nm, were deposited first on monocrystalline silicon wafers, then on four different natural stone materials, by a spray-coating technique and a silica layer was subsequently deposited by atmospheric pressure plasma jet to protect the luminescent layer and improve its adhesion to the substrate. The luminescent films were characterized by photoluminescence excitation and emission, while the surface morphology was examined by FEGSEM microscopy and spectroscopic ellipsometry to determine the coating thickness. The optical appearance of the coatings was also evaluated by colorimetric measurements and the efficacy of the fixing action of the silica layer was estimated by PL measurements performed before and after a Scotch TM tape peeling test. The proposed methodology, easily applied on the surface of stone supports, has led to the realization of a luminescent film displaying good mechanical properties, transparent and undetectable in the presence of visible light, but easily activated by UV light source, indicating that the Eu: GdVO4 nanophosphors could be used as luminescent nanotags for a reliable anti-counterfeiting technology.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1007/s11696-016-0081-8
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Regenerative Endodontic Procedures: A Perspective from Stem Cell Niche Biology
M. Marí-Beffa, J.J. Segura-Egea, A. Díaz-CuencaJournal of Endodontics, 43 (2017) 52-62 DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2016.09.011
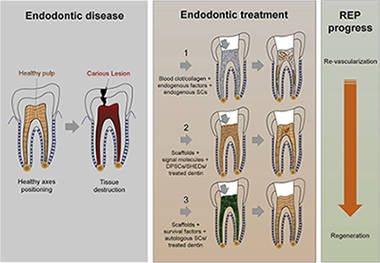
Abstract
Introduction
Endodontics uses cell therapy strategies to treat pulpal and periapical diseases. During these therapies, surgeons aim to reconstruct the natural microenvironments that regulate the activity of dental stem cells.
Methods
We searched for more than 400 articles in PubMed using key words from regenerative endodontics and dental stem cell biology. In 268 articles, we reviewed what factors may influence histologic results after preclinical dental treatments that use regenerative endodontic procedures after pulpectomy.
Results
Several factors, such as the origin of stem cells, the biomimicry of scaffolds used, and the size of lesions, are considered to influence the histologic appearance of the regenerated pulp-dentin complex after treatments. Information is accumulating on transcription factors that generate the pulp-dentin complex and survival/trophic factors that would benefit niche recovery and histologic results.
Conclusions
In this article, we discuss the noninterchangeability of stem cells, the influence of dentin-entrapped molecule release on pulp regeneration and survival of stem cells, and the need of positional markers to assess treatments histologically. The ex vivo amplification of appropriate dental stem cells, the search for scaffolds storing the molecular diversity entrapped in the dentin, and the use of positional transcription factors as histologic markers are necessary to improve future preclinical experiments.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2016.09.011
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Pt-impregnated catalysts on powdery SiC and other commercial supports for the combustion of hydrogen under oxidant conditions
Arzac, G. M.; Montes, O.; Fernandez, A.Applied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 201 (2017) 391-399 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.042
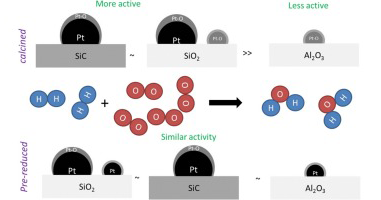
Abstract
We report the study of the catalytic hydrogen combustion over Pt-impregnated powdery silicon carbide (SiC) using H2PtCl6 as precursor. The reaction was conducted in excess of oxygen. beta-SiC was selected for the study because of its thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, chemical inertness and surface area. The obtained Pt particles over SiC were medium size (average particle diameter of 5 nm for 0.5 wt% Pt). The activity of the Pt-impregnated catalyst over SiC was compared to those obtained in oxidized form over TiO2 and Al2O3 commercial supports (Pt particles very small in size, average particle diameter of 1 nm for 0.5 wt% Pt in both cases). The case of a SiO2 support was also discussed. Those Pt/SiC particles were the most active because of their higher contribution of surface Pt, indicating that partially oxidized surfaces have better activity than those totally oxidized in these conditions. SiC was modified with an acid treatment and thus bigger (average particle diameter of 7 nm for 0.5 wt% Pt) and more active Pt particles were obtained. Durability of the SiC and TiO2 supported catalysts was tested upon 5 cycles and both have shown to be durable and even more active than initially. Exposure to the oxidative reaction mixture activates the catalysts and the effect is more pronounced for the completely oxidized particles. This is due to the surface oxygen chemisorption which activates catalystsi surface.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.042
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Insolubilization and thermal stabilization of a long-chain polyester by noncatalyzed melt-polycondensation synthesis in air
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Cruz-Carrillo, MA; Barthel, MJ; Knicker, HE; Heredia, AJournal of Applied Polymer Science, 134 (2017) 1 art 44350 DOI: 10.1002/app.44350

Abstract
Self-standing films of poly(-hydroxyl hexadecanoic acid) [poly(-OHC16)] have been prepared by noncatalyzed melt-polycondensation in air at 150, 175, and 200 degrees C. Poly(-OHC16)s obtained are characterized as polyesters by infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and solid state magic angle spinning C-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (C-13 MAS-NMR). Structurally, poly(-OHC16)s are quite crystalline as revealed by wide angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD). The presence of oxygen in the reaction atmosphere causes a mild oxidation in the form of peroxyester species, tentatively at the interphase between poly(-OHC16) crystallites, and the structure amorphization. The interfacial peroxyester phase ends up in the encapsulation of the polyester grains and provides a barrier towards the action of solvents. Thermal stabilization and insolubility resulting from the synthesis conditions used are interesting features to prepare solvent and heat resistant poly(-OHC16) coatings. Thus, a few microns thick poly(-OHC16) layer has been fabricated on aluminum foil and its resistivity towards a chloroform:methanol (1:1, v:v) mixture has been confirmed.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/app.44350
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold catalysts screening in base-free aerobic oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid
Megias-Sayago, C.; Ivanova, S.; Lopez-Cartes, C.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A.Catalysis Today, 279 (2017) 148-154 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.046
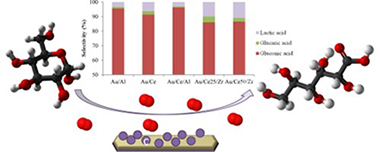
Abstract
Base-free aerobic oxidation of glucose in presence of Au/Al2O3, Au/CeO2, Au/CeO2(20 wt%)/Al2O3, Au/CeO2(25 wt%)/ZrO2 and Au/CeO2(50 wt%)/ZrO2 catalysts using molecular oxygen at atmospheric pressure is studied. Within the whole series high conversion and selectivity to gluconic acid are observed after 18 h of reaction at 120 degrees C. The activity and especially the selectivity changes are related to the support nature in a way that the higher the Lewis acidity of the support the lower the selectivity to gluconic acid and the higher the production of lactic acid. The highest yield to gluconic acid is obtained over Au/Al2O3 for which the influence of the reaction time, temperature and stirring rate are further evaluated and discussed.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.046
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microcalorimetry: A powerful tool for quantitative analysis of aging hardening response of Cu-Ni-Sn alloys
Donoso, E; Dianez, MJ; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sayagues, MJ; Criado, JMJournal of alloys and compounds, 694 (2017) 710-714 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.10.060
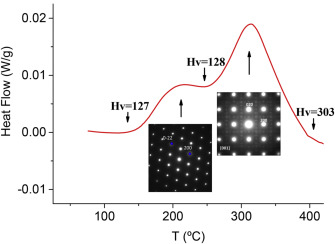
Abstract
The method for the deconvolution of overlapping DSC peaks here proposed has been used by the first time for the quantitative determination of the enthalpies associated to the phase transitions undergone during the aging of an alloy. They have been determined the enthalpies evolved along the first and the second overlapping DSC traces of Cu-10 wt%Ni-5.5 wt%Sn alloy, which are associated, respectively, to the spinodal decomposition of the alloy and the segregation of a DO22 (CuxNi1-x)(3)Sn tetragonal phase. The fraction of the DO22 phase (responsible of the aging hardening of this alloy) has been successfully determined from DSC as a function of the annealing treatment, while TEM and XRD failed for this purpose. It has been demonstrated that a threshold higher than 50% of crystallization of the DO22 phase is required for achieving a significant increase of the hardness as a function of the crystallization percentage. These results suggest that microcalorimetric measurement can be a powerful tool to establish quantitative relationships between the mechanical, electrical or functional properties of alloys and their structural changes undergone by aging.
Enero, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.10.060
2016
2016
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Selectivity control in oxidation of 1-tetradecanol on supported nano Au catalysts
Martinez-Gonzalez, S; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Corberan, VCCatalysis Today, 278 (2016) 113-119 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.019
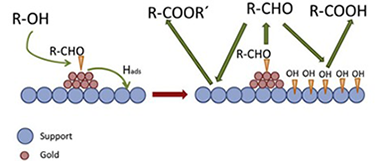
Abstract
Selective oxidation of tetradecanol, a model higher fatty alcohol, on Au/CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst has been investigated to assess the factors that control selectivity. The analysis of the effect of operation conditions (temperature, run time and alcohol/metal (AIM) ratio) on catalytic performance revealed a quite complex reaction network, in which acid formation starts only after a certain level of conversion is reached. This level depends linearly on the total support surface available, indicating that it must be saturated by species generated by the reaction itself to allow acid formation to start. Addition of water to reaction medium did not modify this level, indicating that such species is not adsorbed water, as previously hypothesized, but probably spilled over hydrogen species. The resulting drastic change in the selectivity trends makes the ratio A/M a critical factor to control selectivity to aldehyde and to acid. Selectivity to ester is less sensible to operation parameters. It is noteworthy that aldehyde yields up to 27% with 90% selectivity, and acid yields up to 40% with 81% selectivity can be reached by proper selection of operation parameters.
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.019
Reactividad de Sólidos
The calorimetric analysis as a tool for studying the aging hardening mechanism of a Cu-10wt%Ni-5.5wt%Sn alloy
Dianez, MJ; Donoso, E; Sayagues, MJ; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JMJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 688 (2016) 288-294 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.021
Abstract
The transformations of a Cu-10wt%Ni-5.5wt%Sn alloy as a function of the aging time in the range from room temperature up to 600 degrees C have been followed by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). The results obtained have shown that this alloy undergone two overlapping exothermic phase transitions with DSC peaks at 208 degrees C and 305 degrees C, respectively, followed by an endothermic phase transformation with a DSC peak at 526 degrees C. The structural analysis by TEM, ED, EDX and XRD of the intermediates phases previously discriminated by DSC suggests that the first exothermic peak is associated to the spinodal decomposition of the sample, while the second one is associated to the segregation of a DO22 (Cu-x-Ni1-x)(3)Sn tetragonal phase coherent with the alpha-Cu structure of the starting alloy. The endothermic peak has been associated to the precipitation of cubic DO3 nanocrystals from the DO22 phase previously formed. The microhardness measurements carried out in combination with the structural characterization demonstrate that the aging hardening of the alloy under study is exclusively due to the formation of the coherent DO22 phase. The DO22/DO3 transition leads to a dramatic drop of the hardness of the alloy.
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Stoichiometric Control of SiOx Thin Films Grown by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alvarez, R; Lopez-Santos, C; Ferrer, FJ; Rico, V; Guillen, E; Alcon-Camas, M; Escobar-Galindo, R; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 13 (2016) 1242-1248 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201600077
Abstract
The deposition of SiOx (x <= 2) compound thin films by the reactive magnetron sputtering technique at oblique angles is studied from both theoretical and experimental points of view. A simple mathematical formula that links the film stoichiometry and the deposition conditions is deduced. Numerous experiments have been carried out to test this formula at different deposition pressures and oblique angle geometries obtaining a fairly good agreement in all studied conditions. It is found that, at low deposition pressures, the proportion of oxygen with respect to silicon in the film increases a factor of similar to 5 when solely tilting the film substrate with respect to the target, whereas at high pressures the film stoichiometry depends very weakly on the tilt angle. This behavior is explained by considering the fundamental processes mediating the growth of the film by this technique.
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201600077
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the ionic liquid presence on the selective oxidation of glucose over molybdenum based catalysts
Megias-Sayago, C; Carrasco, CJ; Ivanova, S; Montilla, FJ; Galindo, A; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 278 (2016) 82-90 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.040
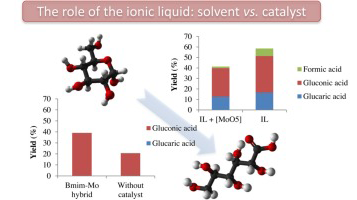
Abstract
Two different approaches are proposed in this work in order to study the influence of the ionic liquid presence in the reaction of glucose oxidation by H2O2 in mild conditions. The ionic liquids are applied either as a solvent by using homogeneous Mo based catalyst, [Mo(O)(O2)2(H2O)n] complex, or by using it as an integral part of a heterogeneous catalyst, organic inorganic hybrids based on Mo Keggin structure. Both catalytic strategies resulted in acceptable glucose transformation degrees but lead to different oxidation products depending on the role of the ionic liquid. The hybrid approach restrains the number of the received products being the most selective one. A detailed study of the effect of the hybrid nature and reaction conditions is proposed in the second part of this study.
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.040
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Three-Dimensional Optical Tomography and Correlated Elemental Analysis of Hybrid Perovskite Microstructures: An Insight into Defect-Related Lattice Distortion and Photoinduced Ion Migration
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Li, YL; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 7 (2016) 5227-5234 DOI: 10.1021/acsjpclett.6b02456
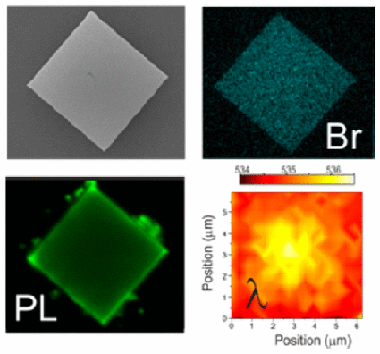
Abstract
Organic lead halide perovskites have recently been proposed for applications in light-emitting devices of different sorts. More specifically, regular crystalline microstructures constitute an efficient light source and fulfill the geometrical requirements to act as resonators, giving rise to waveguiding and optical amplification. Herein we show three-dimensional laser scanning confocal tomography studies of different types of methylammonium lead bromide microstructures which have allowed us to dissect their photoemission properties with a precision of 0.036 mu m(3). This analysis shows that their spectral emission presents strong spatial variations which can be attributed to defect-related lattice distortions. It is also largely enhanced under light exposure, which triggers the migration of halide ions away from illuminated regions, eventually leading to a strongly anisotropic degradation. Our work points to the need for performing an optical quality test of individual crystallites prior to their use in optoelectronics devices and provides a means to do so.
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acsjpclett.6b02456
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Based on Nickel Nanoporous Thin Films Prepared by Physical Vapor Deposition at Oblique Angles for Beverage Industry Applications
Salazar, P; Rico, V; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of the Electrochemical Society, 163 (14) (2016) B704-B709 DOI: 10.1149/2.1241614jes
Abstract
Nickel nanoporous thin films deposited on Indium tin oxide conductive plates have been prepared by physical vapor deposition in an oblique angle configuration. The scanning electron microscopy characterization of these films revealed a microstructure formed by tilted nanocolumns of ca. 40-60 nm of diameter inclined by ca. 26 degrees with respect to the normal. These highly porous films had ca. 30% of void space and provided a large exposed area and outstanding diffusion properties for sensor applications. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the deposition of metallic nickel, while Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies demonstrated that electrochemically treated films presented an oxi/hydroxide outer layer that is the active phase for glucose sensing. The activated electrodes had a high sensitivity (2.05 A M-1 cm(-2)), an excellent coefficient of determination (R-2: 0.999), an outstanding reproducibility (3.2%) and a detection limit of 0.34 mu M. Their glucose selectivity was excellent with regard to common electroactive interferences and other sugars found in agro-alimentary products. Tests carried out with commercial beverages proved the reliability of these electrodes for glucose analysis in real conditions.
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1149/2.1241614jes
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructure, elastic, and inelastic properties of biomorphic carbons carbonized using a Fe-containing catalyst
Orlova, TS; Kardashev, BK; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 58 (2016) 2481-2487 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783416120234
Abstract
The microstructure and amplitude dependences of the Young’s modulus E and internal friction (logarithmic decrement δ), and microplastic properties of biocarbon matrices BE-C(Fe) obtained by beech tree carbonization at temperatures Tcarb = 850–1600°C in the presence of an iron-containing catalyst are studied. By X-ray diffraction analysis and transmission electron microscopy, it is shown that the use of Fe-catalyst during carbonization with Tcarb ≥ 1000°C leads to the appearance of a bulk graphite phase in the form of nanoscale bulk graphite inclusions in a quasi-amorphous matrix, whose volume fraction and size increase with Tcarb. The correlation of the obtained dependences E(Тcarb) and δ(Tcarb) with microstructure evolution with increasing Тcarb is revealed. It is found that E is mainly defined by a crystalline phase fraction in the amorphous matrix, i.e., a nanocrystalline phase at Тcarb < 1150°C and a bulk graphite phase at Tcarb > 1300°C. Maximum values E = 10–12 GPa are achieved for samples with Тcarb ≈ 1150 and 1600°C. It is shown that the microplasticity manifest itself only in biocarbons with Tcarb ≥ 1300°C (upon reaching a significant volume of the graphite phase); in this case, the conditional microyield stress decreases with increasing total volume of introduced mesoporosity (free surface area).
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783416120234
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Intensifying glycerol steam reforming on a monolith catalyst: A reaction kinetic model
Bobadilla, LF; Blay, V; Alvarez, A; Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 306 (2016) 933–941 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.021
Abstract
In this work, a structured monolithic catalyst has been tested under a wide range of conditions (partial pressure, residence time, temperature and time-on-stream), with the aim of modeling its kinetic behavior and assessing its economic and upscaling potential. We have developed a sequential model to help us interpret both main trends and salient features. Unexpected behavior was found for certain parameter values, which led us to consider kinetic parasitic effects such as mass or heat transfer limitations. By independently invoking these effects, a conciliatory view of the results observed could not be reached. A combined explanation may prove successful, although overfitting could not be ruled out at this point. More importantly, however, the observed salient features of this stable and selective monolith catalyst may hold potential for process intensification of glycerol steam reforming, thus contributing to a more sustainable industry.
Diciembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of Ball Milling on CaO Crystal Growth During Limestone and Dolomite Calcination: Effect on CO2 Capture at Calcium Looping Conditions
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; de la Calle, A; Medina, S; Perez-Maqueda, LACryst. Growth Des., 16 (2016) 7025–7036 DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01228
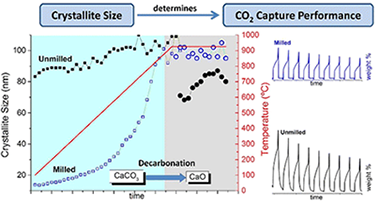
Abstract
Under Calcium-Looping “realistic” operation conditions (high CO2 concentration and temperature), the multicycle CO2 capture capacity performance of CaO derived from limestone and dolomite is inversely related to its crystallite size. Ball-milling the raw sorbents results in the formation of larger nascent CaO nanocrystals during the calcination. Constraint sintering effect due to inert compounds such as dolomitic MgO mitigates the inactivation.
Noviembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01228
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recycling of construction and demolition waste generated by building infrastructure for the production of glassy materials
Dominguez, A; Dominguez, MI; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACeramics International, 42 (2016) 17217-175223 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.157
Abstract
The use of waste materials generated by construction and demolition industry to yield valuable glassy materials, i.e. enamel for glazed ceramic tiles and cellular glasses is presented in this study. Both types of materials are produced by one-step treatment at moderate temperatures after simple waste chemical composition adjust. The enamels are manufactured directly from the initial waste powder by melting, while the expanded materials result from mixing of the vitreous material obtained after waste vitrification with an adequate foaming agent and posterior thermal treatment. Through the manuscript the feasibility of one step production of second generation profit materials is discussed in order to help achieving sustainable development and environmental protection.
Noviembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.157
Materiales Avanzados
Surface functionalizing of a lipid nanosystem to promote brain targeting: step-by-step design and physico-chemical characterization
Cozar-Bernal, MJ; Garcia-Esteban, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Rabasco, AM; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, MLPharmaceutical Development and Technology, 21 (2016) 823-831 DOI: 10.3109/10837450.2015.1063651
Abstract
The use of lipid nanosystems as drug delivery to the central nervous system may be advantageous over the current strategies. The aim of this study was to develop and characterize functionalized liposomes for treatment of brain diseases. The covalent method of coupling IgG to liposomes via the derivatized lipid 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[4-(p-maleimidophenyl)butyramide](MPB-PE) was investigated. Optimized coupling conditions are shown to result in the efficient conjugation of IgG to liposomes containing low concentrations of MPB-PE (3/1 SH:IgG). The qualitative analysis has shown that after the extrusion process, more homogeneous populations of vesicles have been obtained with a nanometric size suitable to be effective to further anchor the protein. Negative values of zeta potential demonstrate that they are stable systems. Lyophilization was used to maintain the stability of the formulation. These very interesting results encourage further investigations to formulate peptide- and protein-loaded immunoliposomes, making targeting of liposomes as an attractive approach for brain drug delivery.
Noviembre, 2016 · DOI: 10.3109/10837450.2015.1063651
- ‹ anterior
- 19 of 37
- siguiente ›














