Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of milling parameters on the solid-gas synthesis of TiCxN1-x by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Alcala, MD; Cordoba, JMPowder Technology, 319 (2017) 12-18
Show abstract ▽
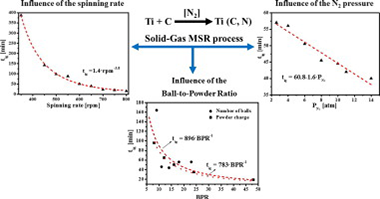
The synthesis of a titanium carbonitride solid solution (TiCxN1 − x) performed in a high-energy planetary mill by a solid-gas Mechanically induced Self-sustaining Reaction (MSR) was used to study the influence of a full set of experimental milling parameters on the ignition time (tig) as a measure of the mechanical dose rate provided by the mill. The highly exothermic Ti-C-N mixture was selected to ensure no competitiveness between MSR and diffusion-controlled routes under the milling conditions employed. The results showed that the dependence of tig on the spinning rate followed a potential function, with a potential factor higher than the value of 3 that would be obtained if a perfect collision model is assumed. The scalability of milling processes performed using planetary mills was confirmed. The results suggested that to define a milling experiment, it is necessary to provide not only the Ball-to-Powder mass Ratio (BPR) and spinning rate values, as is usually performed, but also the full set of milling parameters including the nature of the milling media (vial and balls), the number and size of balls, the mass of the powder charge, the pressure of the reactive gas and even the volume of the vial.
Septiembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.06.035
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Carbon nanofibers replacing graphene oxide in ceramic composites as a reinforcing-phase: Is it feasible?
Cano-Crespo, Rafael; Malmal Moshtaghioun, Bibi; Gomez-Garcia, Diego; Dominguez-Rodriguez, Arturo; Moreno, RodrigoJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 37 (2017) 3791-3796
Show abstract ▽
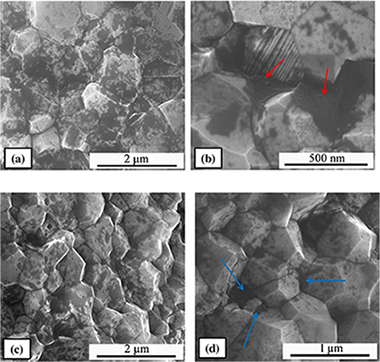
In recent years, the interest of graphene and graphene-oxide has increased extraordinarily due to the outstanding properties concurring in this material. In ceramic science, the possibility of combining excellent electrical conductivities together with an enhancement of mechanical properties has motivated the research in fabrication of graphene oxide-reinforced ceramic composites despite the intrinsic difficulties for sintering. In this work a comparison is made between graphene oxide-reinforced alumina composites and carbon nanofiber-reinforced alumina ones. It will be concluded that the improvement of mechanical properties is scarce, if any. Since carbon nanofibers have also a good electrical conductivity their importance for future applications as a replacement of more sophisticated but expensive graphene-based ceramic composites will be stressed.
Septiembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.03.027
Reactividad de Sólidos
Multicycle activity of natural CaCO3 minerals for thermochemical energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power plants
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LASolar Energy, 153 (2017) 188-199
Show abstract ▽
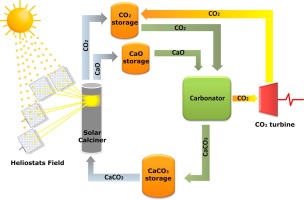
Thermochemical energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power plants by means of the Calcium-Looping process is a promising novel technology that would allow for a higher share of renewables. A main benefit of this technology is the use of widely available, non-toxic and environmentally friendly calcium carbonate minerals as raw materials to store energy. Efficient integration of the Calcium-Looping process into Concentrated Solar Power plants involves the endothermic calcination of CaCO3 in the solar receiver while the exothermic carbonation of CaO is carried out at high temperature under high CO2 partial pressure. The heat released by this reaction is carried out by the excess CO2 and employed for power generation by means of a closed CO2 cycle. This work explores the multicycle Calcium-Looping performance of naturally occurring CaCO3 minerals such as limestone, chalk and marble for thermochemical energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power plants. Despite their similar composition (almost pure CaCO3), these minerals exhibit a significant difference in their Calcium-Looping multicycle activity, which may be attributed to differences in particle size and microstructure. Pore plugging at the Calcium-Looping conditions for thermochemical energy storage tested in our work is a main limiting mechanism on the multicycle CaO carbonation activity.
Septiembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2017.05.068
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
High performance novel gadolinium doped ceria/yttria stabilized zirconia/nickel layered and hybrid thin film anodes for application in solid oxide fuel cells
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Beltran, AM; Yubero, E; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMJournal of Power Sources, 363 (2017) 251-259
Show abstract ▽
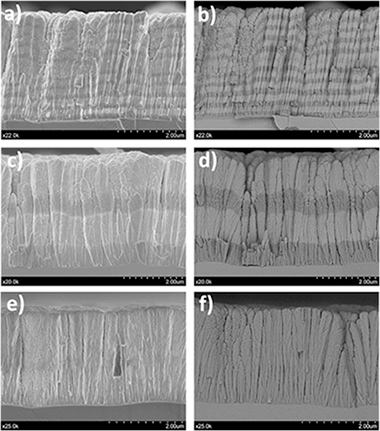
Magnetron sputtering under oblique angle deposition was used to produce Ni-containing ultra thin film anodes comprising alternating layers of,gadolinium doped ceria (GDC) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) of either 200 nm or 1000 nm thickness. The evolution of film structure from initial deposition, through calcination and final reduction was examined by XRD, SEM, TEM and TOF-SIMS. After subsequent fuel cell usage, the porous columnar architecture of the two-component layered thin film anodes was maintained and their resistance to delamination from the underlying YSZ electrolyte was superior to that of corresponding single component Ni-YSZ and Ni-GDC thin films. Moreover, the fuel cell performance of the 200 nm layered anodes compared favorably with conventional commercially available thick anodes. The observed dependence of fuel cell performance on individual layer thicknesses prompted study of equivalent but more easily fabricated hybrid anodes consisting of simultaneously deposited Ni-GDC and Ni-YSZ, which procedure resulted in exceptionally intimate mixing and interaction of the components. The hybrids exhibited very unusual and favorable I-V characteristics, along with exceptionally high power densities at high currents. Their discovery is the principal contribution of the present work.
Septiembre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.07.085
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New insights into surface-functionalized swelling high charged micas: Their adsorption performance for non-ionic organic pollutants
Pazos, MC; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 52 (2017) 179-186
Show abstract ▽

The major components of the wastewater from the petroleum refineries are benzene, toluene and phenol and one of the techniques applied to the treatment of effluents is sorption using organo-functionalized clay. The materials exploited in the present study are a family of surface-functionalized synthetic micas and their sorption capacities for non-ionic organic pollutants are analyzed. The organo-functionalization of their surface provides them the capacity to sorb effectively non-ionic pollutants in the interface. Their adsorption performance is a function of the alkylamonium properties such as the chain length, the mass fraction and the organization of the organic cation in the interlayer space of the micas.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.03.042
- ‹ anterior
- 186 of 420
- siguiente ›














