Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Materiales Avanzados
Thermal study of residues from greenhouse crops plant biomass
Morales, Laura; Garzon, Eduardo; Maria Martinez-Blanes, Jose; Jose Sanchez-Soto, PedroJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 129 (2017) 1111-1120
Show abstract ▽

The principal aim of this work is to examine the effect of thermal treatments using a muffle furnace (static heating) and by simultaneous TG/DTA (dynamic heating) on selected greenhouse crops plant biomass investigated here as the first time. The effect of fractionation by sieving (<25 and <2.5 mm), preheating at 150 °C for 48 h and leaching with water on the thermal behavior has been studied. The observation of similar profiles of mass variation corresponding to several samples heated in air up to 1150 °C allows to conclude that particle size did not influence the thermal evolution, but the effect of heating cycle is evidenced. Thermal analysis in air of a representative sample showed the several mass variation steps and DTA exothermic effects produced by the complex thermal decomposition and pyrolysis of the organic matter. Elemental analysis (CHNS and O) of the starting samples and thermally treated revealed the effect of the temperature, with formation of ashes with lower C content from 44.37 to 0.70 mass% as a minimum after elimination of organic matter by heating. Leaching increased the thermal mass variation as an effect of elimination of water-soluble components. According to the present results, the size fractionation of the greenhouse crops biomass did not influence the results of elemental composition. The present study has provided results of interest concerning this biomass source of renewable energy originated by the remains of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.), being estimated the highest of all the biomass produced by the greenhouse crops agricultural industry in Almería (SE Spain).
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-017-6243-2
Reactividad de Sólidos
Simultaneous adsorption and photocatalytic behavior of hybrid mesoporous ZnS-SiO2 nanocomposite
Emrooz, HBM; Gotor, FJMaterials Research Express, 4 (2017) art. 085037
Show abstract ▽
Mesoporous ZnS-SiO2 nanocomposite was synthesized with a facile process. At first a large pore volume (1.86 cm(3).g(-1)), moderate pore size (about 12.8 nm) and moderate surface area (586 m(2).g(-1)) mesoporous SiO2 was synthesized in an acidic PH using cationic surfactant. ZnS nanoparticles were infiltrated in the porosities of the synthesized SiO2, with a room temperature post grafting method. The synthesized particles have been characterized with transmission electron microscopy (TEM), x-ray diffraction (XRD), x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), furrier transformation infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). Results confirm the mesoporous characteristics of ZnS-SiO2 nanocomposite with specific surface area as high as 248 m(2).g(-1), pore volume of 0.89 cm(3).g(-1) and average pore diameter of about 14.4 nm. Simultaneous adsorption-photocatalytic behavior of this hybrid mesoporous nanocomposite for degradation of methylene blue (MB) was investigated. The efficiency of this material was compared with that of mesoporous SiO2 and also lone ZnS nanoparticles. Results showed that by using ultraviolet irradiation, ZnS-SiO2 can degrade greater than 85% of MB only after 3 min. The case for lone ZnS is less than 5% after 30 min. Degradation mechanism of MB using ZnS-SiO2 and ultraviolet radiation was explained with simultaneous adsorption and photocatalytic phenomena. Ultraviolet irradiation can degrade adsorbed MB of mesoporous SiO2 which can prevent it from saturation.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/aa85cf
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties and electronic transitions of zinc oxide, ferric oxide, cerium oxide, and samarium oxide in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Tougaard, SApplied Optics, 56 (2017) 6611-6621
Show abstract ▽
Optical properties and electronic transitions of four oxides, namely zinc oxide, ferric oxide, cerium oxide, and samarium oxide, are determined in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy using primary electron energies in the range 0.3 - 2.0 keV. This technique allows the evaluation of the optical response in these ultraviolet spectral regions of a thin layer of material, and the analysis is straightforward. It is performed within the dielectric response theory by means of the QUEELS-epsilon(k,omega)-REELS software developed by Tougaard and Yubero [Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 824 ( 2004)]. The method consists basically in the fitting of experimentally determined single-scattering electron energy loss cross sections with a parametric energy loss function of the corresponding material, to the one calculated within a dielectric response formalism. The obtained refractive index and extinction coefficients, as well as the identified electronic transitions are compared, when available, with previously published results.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1364/AO.56.006611
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cutin from agro-waste as a raw material for the production of bioplastics
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Heredia, A; Dominguez, E; Cingolani, R; Bayer, IS; Athanassiou, A; Benitez, JJJournal of Experimental Botany, 68 (2017) 5401-5410
Show abstract ▽
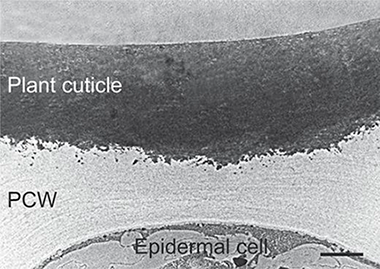
Cutin is the main component of plant cuticles constituting the framework that supports the rest of the cuticle components. This biopolymer is composed of esterified bi- and trifunctional fatty acids. Despite its ubiquity in terrestrial plants, it has been underutilized as raw material due to its insolubility and lack of melting point. However, in recent years, a few technologies have been developed to obtain cutin monomers from several agro-wastes at an industrial scale. This review is focused on the description of cutin properties, biodegradability, chemical composition, processability, abundance, and the state of art of the fabrication of cutin-based materials in order to evaluate whether this biopolymer can be considered a source for the production of renewable materials.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erx272
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
The role of cobalt hydroxide in deactivation of thin film Co-based catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis
Paladini, M; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 210 (2017) 342-351
Show abstract ▽
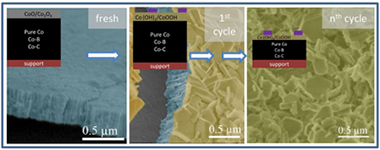
Deactivation of a Co catalyst prepared as thin film by magnetron sputtering was studied for the sodium borohydride (SB) hydrolysis reaction under different conditions. Under high SB concentration in single run experiments, the formation of a B-O passivating layer was observed after 1.5 and 24 h use. This layer was not responsible for the catalyst deactivation. Instead, a peeling-off mechanism produced the loss of cobalt. This peeling-off mechanism was further studied in cycling experiments (14 cycles) under low SB concentrations. Ex-situ study of catalyst surface after use and solid reaction products (precipitates) was performed by X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). The presence of cobalt hydroxide and oxyhydroxide was detected as major components on the catalyst surface after use and as precipitates in the supernatant solutions after washing. Cobalt borate, cobalt carbonate and oxycarbonate were also formed but in lesser amounts. These oxidized cobalt species were formed and further detached from the catalyst at the end of the reaction and/or during catalyst washing by decomposition of the unstable in-situ formed cobalt boride. Leaching of cobalt soluble species was negligible. Thin film mechanical detachment was also found but in a smaller extent. To study the influence of catalyst composition on deactivation processes, cycling experiments were performed with Co-B and Co-C catalysts, also prepared as thin films. We found that the deactivation mechanism proposed by us for the pure Co catalyst also occurred for a different pure Co (prepared at higher pressure) and the Co-B and Co-C samples in our experimental conditions.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.005
- ‹ anterior
- 187 of 420
- siguiente ›














