Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cutin from agro-waste as a raw material for the production of bioplastics
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Heredia, A; Dominguez, E; Cingolani, R; Bayer, IS; Athanassiou, A; Benitez, JJJournal of Experimental Botany, 68 (2017) 5401-5410
Show abstract ▽
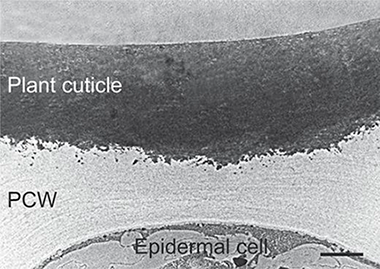
Cutin is the main component of plant cuticles constituting the framework that supports the rest of the cuticle components. This biopolymer is composed of esterified bi- and trifunctional fatty acids. Despite its ubiquity in terrestrial plants, it has been underutilized as raw material due to its insolubility and lack of melting point. However, in recent years, a few technologies have been developed to obtain cutin monomers from several agro-wastes at an industrial scale. This review is focused on the description of cutin properties, biodegradability, chemical composition, processability, abundance, and the state of art of the fabrication of cutin-based materials in order to evaluate whether this biopolymer can be considered a source for the production of renewable materials.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erx272
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties and electronic transitions of zinc oxide, ferric oxide, cerium oxide, and samarium oxide in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Tougaard, SApplied Optics, 56 (2017) 6611-6621
Show abstract ▽
Optical properties and electronic transitions of four oxides, namely zinc oxide, ferric oxide, cerium oxide, and samarium oxide, are determined in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy using primary electron energies in the range 0.3 - 2.0 keV. This technique allows the evaluation of the optical response in these ultraviolet spectral regions of a thin layer of material, and the analysis is straightforward. It is performed within the dielectric response theory by means of the QUEELS-epsilon(k,omega)-REELS software developed by Tougaard and Yubero [Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 824 ( 2004)]. The method consists basically in the fitting of experimentally determined single-scattering electron energy loss cross sections with a parametric energy loss function of the corresponding material, to the one calculated within a dielectric response formalism. The obtained refractive index and extinction coefficients, as well as the identified electronic transitions are compared, when available, with previously published results.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1364/AO.56.006611
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
The role of cobalt hydroxide in deactivation of thin film Co-based catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis
Paladini, M; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 210 (2017) 342-351
Show abstract ▽
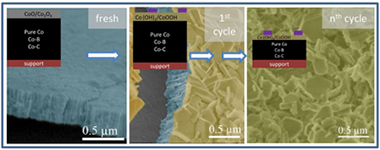
Deactivation of a Co catalyst prepared as thin film by magnetron sputtering was studied for the sodium borohydride (SB) hydrolysis reaction under different conditions. Under high SB concentration in single run experiments, the formation of a B-O passivating layer was observed after 1.5 and 24 h use. This layer was not responsible for the catalyst deactivation. Instead, a peeling-off mechanism produced the loss of cobalt. This peeling-off mechanism was further studied in cycling experiments (14 cycles) under low SB concentrations. Ex-situ study of catalyst surface after use and solid reaction products (precipitates) was performed by X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). The presence of cobalt hydroxide and oxyhydroxide was detected as major components on the catalyst surface after use and as precipitates in the supernatant solutions after washing. Cobalt borate, cobalt carbonate and oxycarbonate were also formed but in lesser amounts. These oxidized cobalt species were formed and further detached from the catalyst at the end of the reaction and/or during catalyst washing by decomposition of the unstable in-situ formed cobalt boride. Leaching of cobalt soluble species was negligible. Thin film mechanical detachment was also found but in a smaller extent. To study the influence of catalyst composition on deactivation processes, cycling experiments were performed with Co-B and Co-C catalysts, also prepared as thin films. We found that the deactivation mechanism proposed by us for the pure Co catalyst also occurred for a different pure Co (prepared at higher pressure) and the Co-B and Co-C samples in our experimental conditions.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.005
Materiales Coloidales
Crystal structure, NIR luminescence and X-ray computed tomography of Nd3+:Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 nanospheres
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Cantelar, E; Cusso, F; Briat, A; Boyer, D; Ocana, MDalton Transactions, 46 (2017) 6580-6587
Show abstract ▽
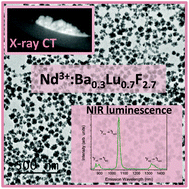
Uniform, hydrophilic 50 nm diameter Nd3+-doped Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 nanospheres are synthesized at 120 degrees C using a singular one-pot method based on the use of ethylene glycol as solvent, in the absence of any additive. The composition and crystal structure of the undoped material are analyzed in detail using ICP and XRD, which reveals a BaF2 cubic crystal structure that is able to incorporate 70 mol% of Lu ions. This finding contrasts with the reported phase diagram of the system, where the maximum solubility is around 30 mol% Lu. XRD proves as well that the Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 structure is able to incorporate Nd3+ ions up to, at least 10 mol%, without altering the uniform particles morphology. The Nd-doped particles exhibit near-infrared luminescence when excited at 810 nm. The maximum emission intensity with the minimum concentration quenching effect is obtained at 1.5% Nd doping level. X-ray computed tomography experiments are carried out on powder samples of the latter composition. The sample significantly absorbs X-ray photons, thus demonstrating that the Nd3+-doped Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 nanospheres are good candidates as contrast agents in computed tomography.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1039/c7dt00453b
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New insights into surface-functionalized swelling high charged micas: Their adsorption performance for non-ionic organic pollutants
Pazos, MC; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 52 (2017) 179-186
Show abstract ▽

The major components of the wastewater from the petroleum refineries are benzene, toluene and phenol and one of the techniques applied to the treatment of effluents is sorption using organo-functionalized clay. The materials exploited in the present study are a family of surface-functionalized synthetic micas and their sorption capacities for non-ionic organic pollutants are analyzed. The organo-functionalization of their surface provides them the capacity to sorb effectively non-ionic pollutants in the interface. Their adsorption performance is a function of the alkylamonium properties such as the chain length, the mass fraction and the organization of the organic cation in the interlayer space of the micas.
Agosto, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.03.042
- ‹ anterior
- 188 of 420
- siguiente ›














