Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Characterization of of mechanosynthesized Bi1-xSmxFeO3 samples unencumbered by secondary phases or compositional inhomogeneity
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Hayward, MA; Criado, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 711 (2017) 541-551
Show abstract ▽
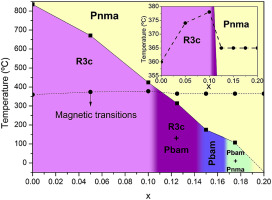
High-quality samples, in terms of phase purity and dielectric properties, of composition Bi1-xSmxFeO3 (0.05 <= x <= 0.20) have for the first time been prepared by mechanosynthesis. Close inspection of the powder diffraction data, analysis via Rietveld refinement and TEM microscopy demonstrates that the Bi1-xSmxFeO3 samples contain only perovskite phases. Additionally, by a combination of Rietveld analysis, TEM, DSC, temperature-dependent XRD and permittivity data a tentative phase diagram has been proposed where the high temperature paraelectric phase Pnma has been confirmed for samarium substituted BiFeO3. Regarding the physical properties, the samples resulted to be electrically homogenous and highly insulating at room temperature, suggesting that other sources of conductivity, such as mixed valence of Fe associated with possible oxygen non-stoichiometry, have been avoided during the samples synthesis. In spite of the high quality of the samples, the dielectric and magnetic behaviour of the Bi1-xSmxFeO3 samples change only modestly on Sm substitution, with neither a great change in the resistivity or remnant magnetisation of Sm substituted samples in comparison with BiFeO3.
Julio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.289
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Formation of Subsurface W5+ Species in Gasochromic Pt/WO3 Thin Films Exposed to Hydrogen
Castillero, Pedro; Rico-Gavira, Victor; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Barranco, Angel; Perez-Dieste, Virginia; Escudero, Carlos; Espinos, Juan P.; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 121 (2017) 15719-15727
Show abstract ▽
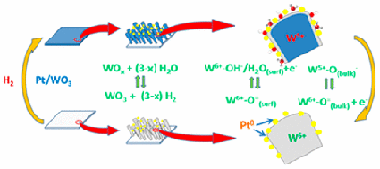
M/WO3 (M = Pt, Pd) systems formed by a porous WO3 thin film decorated by metal nanoparticles are known for their reversible coloring upon exposure to H2 at room temperature. In this work, this gasochromic behavior is investigated in situ by means of near-ambient photoemission (NAPP). Pt/WO3 systems formed by very small Pt nanoparticles (10 ± 1 nm average size) incorporated in the pores of nanocolumnar WO3 thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at an oblique angle have been exposed to a small pressure of hydrogen at ambient temperature. The recorded UV–vis transmission spectra showed the reversible appearance of a very intense absorption band responsible for the blue coloration of these gasochromic films. In an equivalent experiment carried out in the NAPP spectrometer, W 4f, O 1s, Pt 4f, and valence band photoemission spectra have been recorded at various photon energies to follow the evolution of the reduced tungsten species and hydroxyl groups formed upon film exposure to hydrogen. The obtained results are compared with those of a conventional X-ray photoemission study after hydrogen exposure between 298 and 573 K. As investigated by NAPP, the gasochromic behavior at 298 K is accounted for by a reaction scheme in which hydrogen atoms resulting from the dissociation of H2 onto the Pt nanoparticles are spilt over to the WO3 substrate where they form surface OH–/H2O species and subsurface W5+ cations preferentially located in buried layers of the oxide network.
Julio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03385
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Cobalt Carbide Identified as Catalytic Site for the Dehydrogenation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde
A. Rodríguez-Gómez; J.P. Holgado; A. CaballeroACS Catalysis, 7 (2017) 5243-5247
Show abstract ▽
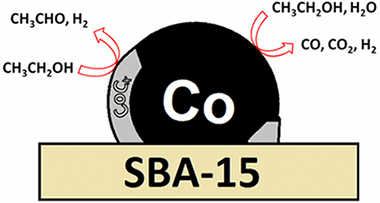
Two cobalt catalysts, Co/SBA-15 and Co/SiO2, have been studied in steam reforming of ethanol (SRE). Besides the steam reforming products, ethoxide dehydrogenation to acetaldehyde is observed as one of the main reactions. Although by hydrogen treatment cobalt is reduced to the metallic state, under SRE conditions, a phase appears that has been identified as cobalt carbide and correlates with acetaldehyde production. These findings provide insights about the catalytic sites, for SRE, in cobalt catalysts. Comparison with previous results shows that these conclusions are not translatable to other cobalt catalysts, stressing the importance of the support on the catalytic behavior of cobalt.
Julio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01348
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cs+ immobilization by designed micaceous adsorbent under subcritical conditions
Osuna, FJ; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 143 (2017) 293-299
Show abstract ▽
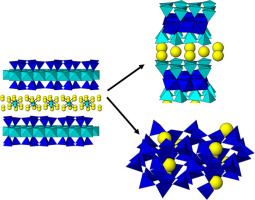
The adsorption of Cs+ by clay minerals is a complicate process, being cation exchange and frayed-edge sites the major mechanisms that govern it. However, environmental variables have a significant impact on the process. In this work, the influence of the temperature and time in the cesium adsorption capacity of Na-Mica-n (n = 2 and 4) have been explored under subcritical conditions. Those synthetic micas were able to immobilize cations Cs+ combining adsorption at nonspecific sites, at specific sites and chemical reaction. The distribution constant of Cs+ was larger in the Na-Mica-2 denoting a higher concentration of specific adsorption sites when layer charge decreased.
Julio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.03.041
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Plasma assisted deposition of single and multistacked TiO2 hierarchical nanotube photoanodes
Filippin, AN; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Idigoras, J; Rojas, TC; Barranco, A; Anta, JA; Borras, ANanoscale, 9 (2017) 8133-8141
Show abstract ▽
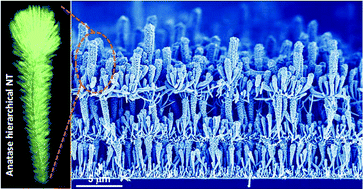
We present herein an evolved methodology for the growth of nanocrystalline hierarchical nanotubes combining physical vapor deposition of organic nanowires (ONWs) and plasma enhanced chemical vacuum deposition of anatase TiO2 layers. The ONWs act as vacuum removable 1D and 3D templates, with the whole process occurring at temperatures ranging from RT to 250 degrees C. As a result, a high density of hierarchical nanotubes with tunable diameter, length and tailored wall microstructures are formed on a variety of processable substrates as metal and metal oxide films or nanoparticles including transparent conductive oxides. The reiteration of the process leads to the development of an unprecedented 3D nanoarchitecture formed by stacking the layers of hierarchical TiO2 nanotubes. As a proof of concept, we present the superior performance of the 3D nanoarchitecture as a photoanode within an excitonic solar cell with efficiencies as high as 4.69% for a nominal thickness of the anatase layer below 2.75 mu m. Mechanical stability and straightforward implementation in devices are demonstrated at the same time. The process is extendable to other functional oxides fabricated by plasma-assisted methods with readily available applications in energy harvesting and storage, catalysis and nanosensing.
Julio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1039/c7nr00923b
- ‹ anterior
- 190 of 420
- siguiente ›














