Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Failure mode and effect analysis of a large scale thin-film CIGS photovoltaic module
Delgado-Sanchez, JM; Sanchez-Cortezon, E; Lopez-Lopez, C; Aninat, R; Alba, MDEngireering failure analysis, 76 (2017) 55-60
Show abstract ▽
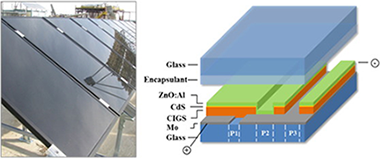
The efficiency of thin-film CIGS based cells at the laboratory scale is now getting closer to conventional Silicon technologies. As a consequence, the long-term stability of CIGS is now one of the main challenges left to address in order to assess its potential as an alternative for photovoltaic plants. This paper reports an overview of the critical risks for the commercial viability of the CIGS thin-film technology. The key causes of the potential failures of this technology are determined through the Failure Mode Analysis and Effects (FMEA) methodology. To validate the results obtained from the FMEA, aging tests and outdoor monitoring were also carried out. Based on the results obtained, we argue that the encapsulation material is the main cause of degradation in CIGS modules.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.02.004
Reactividad de Sólidos
A novel, simple and rapid route to the synthesis of boron cabonitride nanosheets: combustive gaseous unfolding
Jalaly, Maisam; Jose Gotor, Francisco; Semnan, Masih; Jesus Sayagues, MariaScientific Reports, 7 (2017) art. 3453
Show abstract ▽
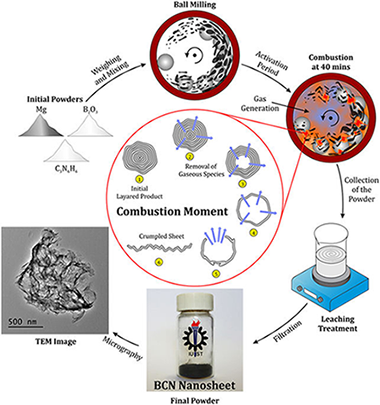
The ternary compound boron carbonitride (BCN) was synthesized in the form of few-layer nanosheets through a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). Magnesium was used to reduce boron trioxide in the presence of melamine in a combustive manner. The process to form the nanostructured material was very rapid (less than 40 min). The prepared powder was investigated by various techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform infrared (FTIR), Micro-Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). The thermal stability and the optical behavior of the BCN nanosheets were also studied by thermal analysis and UV-vis spectroscopy, respectively. The formation mechanism of the nanosheet morphology was described in detail.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03794-7
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A compact and portable optofluidic device for detection of liquid properties and label-free sensing
Lahoz, F; Martin, IR; Walo, D; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 50 (2017) 21
Show abstract ▽
Optofluidic lasers have been widely investigated over the last few years mainly because they can be easily integrated in sensor devices. However, high power pulse lasers arc required as excitation sources, which, in practice, limit the portability of the system. Trying to overcome some of these limitations, in this paper we propose the combined use of a small CW laser with a Fabry-Perot optofluidic planar microcavity showing high sensitivity and versatility for detection of liquid properties and label-free sensing. Firstly, a fluorescein solution in ethanol is used to demonstrate the high performances of the FP microcavity as a temperature sensor both in the laser (high pump power above laser threshold) and in the fluorescence (low pump power) regimes. A shift in the wavelength of the resonant cavity modes is used to detect changes in the temperature and our results show that high sensitivities could be already obtained using cheap and portable CW diode lasers. In the second part of the paper, the demonstration of this portable device for label-free sensing is illustrated under low CW pumping. The wavelength positions of the optolluidic resonant modes are used to detect glucose concentrations in water solutions using a protein labelled with a fluorescent dye as the active medium.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa6cdd
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Analysis of Ni species formed on zeolites, mesoporous silica and alumina supports and their catalytic behavior in the dry reforming of methane
Drobna, Helena; Kout, Martin; Soltysek, Agnieszka; Gonzalez-Delacruz, Victor M.; Caballero, Alfonso; Capek, LiborReaction Kinetics Mechanisms and Catalysis, 121 (2017) 255-274
Show abstract ▽
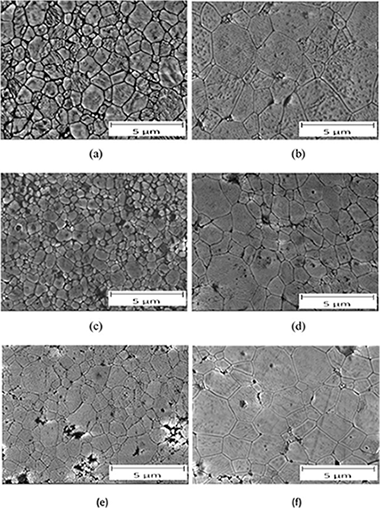
The presented investigation is focused on the analysis of Ni species formed on microporous (zeolites MFI and FAU) and mesoporous materials (Al-MCM- 41 and SBA-15) and alumina supports and their catalytic behavior in the dry reforming of methane. The paper lays emphasis on the relationship between the catalytic behavior of Ni-based catalysts and their textural/structural properties. Ni-based catalysts were prepared by wet impregnation (11 wt% of Ni) followed by calcination in air and reduction in hydrogen. The properties of Ni-based catalysts were also compared prior and after the catalytic tests. The critical role was played by the high value of the specific surface area and the high strength of the interaction between the Ni species and the support, which both determined the high dispersion and stability of metal Ni-0 particles. Ni-Al-MCM-41 and Ni-SBA-15 showed the values of the conversion of CO2 and CH4 above 90% (stable during 12 h). Slightly lower values of the conversion of CO2 and CH4 were observed over Ni-Al2O3 (also stable during 12 h). In contrast to these materials, Ni-MFI and Ni-FAU exhibited the worse metallic Ni-0 particles dispersion and very bad catalytic behavior.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1007/s11144-017-1149-3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Impact of moisture on efficiency-determining electronic processes in perovskite solar cells
Salado, Manuel; Contreras-Bernal, Lidia; Calio, Laura; Todinova, Anna; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Ahmad, Shahzada; Borras, Ana; Idigoras, Jesus; Anta, Juan A.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5 (2017) 10917-10927
Show abstract ▽
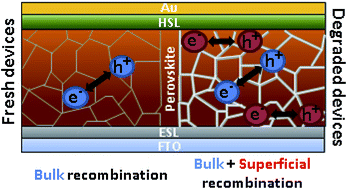
Moisture-induced degradation in perovskite solar cells was thoroughly investigated by structural (SEM, EDS, XRD and XPS) and device characterization (impedance and intensity modulated photocurrent spectroscopy) techniques. Both the influence of the perovskite composition and the nature of the hole selective material were analyzed. The degradation rate was found to be significantly slower for mixed perovskites and P3HT-based devices. However, for a fixed degradation degree (defined as a 50% drop from the initial photocurrent), all configurations show similar features in small-perturbation analysis. Thus, a new mid-frequency signal appears in the impedance response, which seems to be related to charge accumulation at the interfaces. In addition, faster recombination, with a more important surface contribution, and slower transport were clearly inferred from our results. Both features can be associated with the deterioration of the contacts and the formation of a higher number of grain boundaries.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1039/c7ta02264f
- ‹ anterior
- 191 of 420
- siguiente ›














