Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of the impact energy on the chemical homogeneity of a (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N) solid solution obtained via a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
de La Obra, AG; Gotor, FJ; Chicardi, EJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 708 (2017) 1008-1017
Show abstract ▽
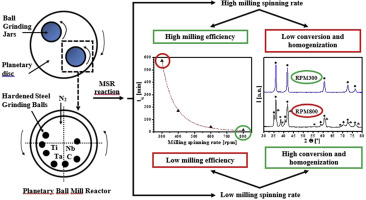
A titanium-tantalum-niobium carbonitride solid solution, (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N), was synthesised in a planetary mill via a mechanochemical process that involves a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) from stoichiometric Ti/Ta/Nb/C mixtures that are milled under a nitrogen atmosphere. The influence of the spinning rate of the planetary mill, which determines the impact energy of the milling process, on the ignition time (t(ig)) of the MSR process as well as the chemical homogeneity of the final product was analysed. The results indicated that the dependence of tig on the spinning rate followed a potential function with a potential factor of 4.85, implying a remarkable reduction in the milling time required to induce the self-sustaining reaction at increasing spinning rates (i.e., from 4200 min at 200 rpm to 15 min at 800 rpm). However, the chemical and structural characterisation of the obtained products at ignition without any extra milling treatment indicated that a single solid solution phase was only obtained at the lowest spinning rates (i.e., less than 300 rpm). At increasing rates, the relative amount of the intended solid solution phase continuously decreased, and new undesirable secondary phases were formed. Despite the long milling times required for the milling experiments that were performed at the slowest spinning rates, iron contamination from the milling media was negligible due to the low intensity milling regime.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.109
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High-temperature creep of carbon nanofiber-reinforced and graphene oxide-reinforced alumina composites sintered by spark plasma sintering
Cano-Crespo, Rafael; Malmal Moshtaghioun, Bibi; Gomez-Garcia, Diego; Dominguez-Rodriguez, Arturo; Moreno, RodrigoCeramics International, 43 (2017) 7136-7141
Show abstract ▽
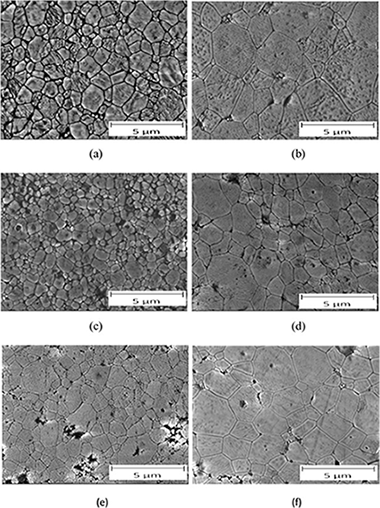
Alumina (Al2O3) ceramic composites reinforced with either graphene oxide (GO) or carbon nanofibers (CNFs) were prepared using Spark Plasma Sintering. The effects of GO and CNFs on the microstructure and in consequence on their mechanical properties were investigated. The microstructure of the sintered materials have been characterized quantitatively prior to and after the creep experiments in order to discover the deformation mechanism. Graphene-oxide reinforced alumina composites were found to be more creep resistant than carbon nanofibers-reinforced alumina ones or monolithic alumina with the same grain size distribution. In all the cases, grain boundary sliding was identified as the deformation mechanism
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.146
Reactividad de Sólidos
Non-isothermal Characterization of the Precipitation Hardening of a Cu-11Ni-19Zn-1Sn Alloy
Donoso, E; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JM; Espinoza, R; Mosquera, EMetallurgical and Materials Transactions A-Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 48A (2017) 3090-3095
Show abstract ▽
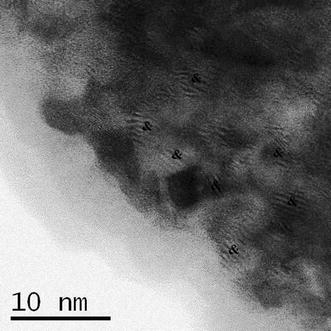
The precipitation hardening of a Cu-11Ni-19Zn-1Sn alloy has been studied by means of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM), and hardness measurements. The calorimetric curves, in the range of temperatures analyzed, show the presence of one exothermic reaction followed by an endothermic one. The exothermic DSC peak is due to the segregation of Cu2NiZn precipitates and it is associated to a noticeable improvement of the mechanical properties of the alloy. The endothermic effect is associated to the dissolution of the Cu2NiZn precipitates into the copper matrix for restoring the starting Cu-11Ni-19Zn-1Sn homogeneous solid solution. The reaction mechanisms of these processes have been proposed from the kinetic analysis of the exothermic and endothermic DSC signals. The results obtained point out that tin plays a decisive role on the precipitation hardening of the alloy, because age hardening is not observed in the case of a Cu-Ni-Zn ternary alloy of similar composition.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1007/s11661-017-4063-4
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In Situ Determination of the Water Condensation Mechanisms on Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes
Macias-Montero, Manuel; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Nicolas Filippin, A.; Rico, Victor J.; Espinos, Juan P.; Fraxedas, Jordi; Perez-Dieste, Virginia; Escudero, Carlos; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Borras, AnaLangmuir, 33 (2017) 6449-6456
Show abstract ▽
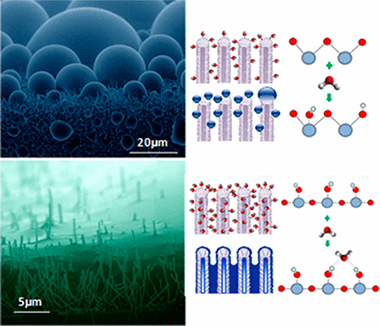
One-dimensional (1D) nanostructured surfaces based on high-density arrays of nanowires and nanotubes of photoactive titanium dioxide (TiO2) present a tunable wetting behavior from superhydrophobic to superhydrophilic states. These situations are depicted in a reversible way by simply irradiating with ultraviolet light (superhydrophobic to superhydrophilic) and storage in dark. In this article, we combine in situ environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) and near ambient pressure photoemission analysis (NAPP) to understand this transition. These experiments reveal complementary information at microscopic and atomic level reflecting the surface wettability and chemical state modifications experienced by these 1D surfaces upon irradiation. We pay special attention to the role of the water condensation mechanisms and try to elucidate the relationship between apparent water contact angles of sessile drops under ambient conditions at the macroscale with the formation of droplets by water condensation at low temperature and increasing humidity on the nanotubes surfaces. Thus, for the as-grown nanotubes, we reveal a metastable and superhydrophobic Cassie state for sessile drops that tunes toward water dropwise condensation at the microscale compatible with a partial hydrophobic Wenzel state. For the UV-irradiated surfaces, a filmwise wetting behavior is observed for both condensed water and sessile droplets. NAPP analyses show a hydroxyl accumulation on the as-grown nanotubes surfaces during the exposure to water condensation conditions, whereas the water filmwise condensation on a previously hydroxyl enriched surface is proved for the superhydrophilic counterpart.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00156
Reactividad de Sólidos
The Oxy-CaL process: A novel CO2 capture system by integrating partial oxy-combustion with the Calcium-Looping process
Ortiz, C; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Benitez-Guerrero, M; Perejon, A; Romeo, LMApplied Energy, 196 (2017) 1-17
Show abstract ▽
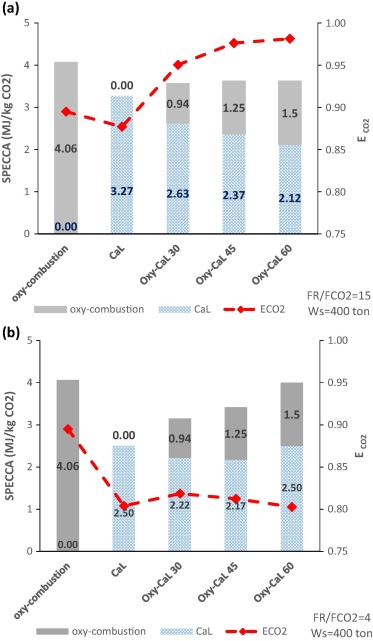
This paper proposes a novel CO2 capture technology from the integration of partial oxy-combustion and the Calcium -Looping capture process based on the multicycle carbonation/calcination of limestone derived CaO. The concentration of CO2 in the carbonator reactor is increased by means of partial oxycombustion, which enhances the multicycle CaO conversion according to thermogravimetric analysis results carried out in our work, thus improving the CO2 capture efficiency. On the other hand, energy consumption for partial oxy-combustion is substantially reduced as compared to total oxy-combustion. All in all, process simulations indicate that the integration of both processes has potential advantages mainly regarding power plant flexibility whereas the overall energy penalty is not increased. Thus, the resulting energy consumption per kilogram of CO2 avoided is kept smaller than 4 MI/kg CO2, which remains below the typical values reported for total oxy-combustion and amine based CO2 capture systems whereas CO2 capture efficiency is enhanced in comparison with the Calcium -Looping process.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.120
- ‹ anterior
- 192 of 420
- siguiente ›














