Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
A novel, simple and rapid route to the synthesis of boron cabonitride nanosheets: combustive gaseous unfolding
Jalaly, Maisam; Jose Gotor, Francisco; Semnan, Masih; Jesus Sayagues, MariaScientific Reports, 7 (2017) art. 3453
Show abstract ▽
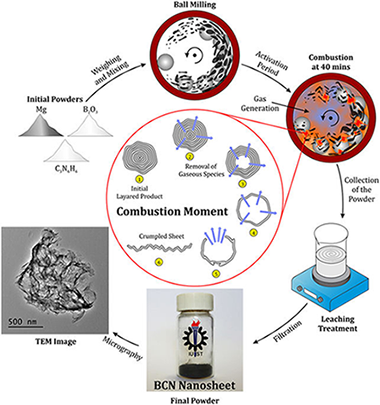
The ternary compound boron carbonitride (BCN) was synthesized in the form of few-layer nanosheets through a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). Magnesium was used to reduce boron trioxide in the presence of melamine in a combustive manner. The process to form the nanostructured material was very rapid (less than 40 min). The prepared powder was investigated by various techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform infrared (FTIR), Micro-Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). The thermal stability and the optical behavior of the BCN nanosheets were also studied by thermal analysis and UV-vis spectroscopy, respectively. The formation mechanism of the nanosheet morphology was described in detail.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03794-7
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A compact and portable optofluidic device for detection of liquid properties and label-free sensing
Lahoz, F; Martin, IR; Walo, D; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 50 (2017) 21
Show abstract ▽
Optofluidic lasers have been widely investigated over the last few years mainly because they can be easily integrated in sensor devices. However, high power pulse lasers arc required as excitation sources, which, in practice, limit the portability of the system. Trying to overcome some of these limitations, in this paper we propose the combined use of a small CW laser with a Fabry-Perot optofluidic planar microcavity showing high sensitivity and versatility for detection of liquid properties and label-free sensing. Firstly, a fluorescein solution in ethanol is used to demonstrate the high performances of the FP microcavity as a temperature sensor both in the laser (high pump power above laser threshold) and in the fluorescence (low pump power) regimes. A shift in the wavelength of the resonant cavity modes is used to detect changes in the temperature and our results show that high sensitivities could be already obtained using cheap and portable CW diode lasers. In the second part of the paper, the demonstration of this portable device for label-free sensing is illustrated under low CW pumping. The wavelength positions of the optolluidic resonant modes are used to detect glucose concentrations in water solutions using a protein labelled with a fluorescent dye as the active medium.
Junio, 2017 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa6cdd
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Critical Role of Oxygen in Silver-Catalyzed Glaser-Hay Coupling on Ag(100) under Vacuum and in Solution on Ag Particles
Orozco, N; Kyriakou, G; Beaumont, SK; Sanz, JF; Holgado, JP; Taylor, MJ; Espinos, JP; Marquez, AM; Watson, DJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMACS Catalysis, 7 (2017) 3113-3120
Show abstract ▽
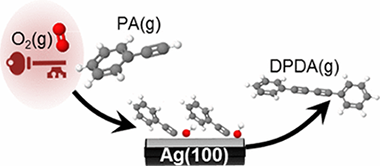
The essential role of oxygen in enabling heterogeneously catalyzed Glaser–Hay coupling of phenylacetylene on Ag(100) was elucidated by STM, laboratory and synchrotron photoemission, and DFT calculations. In the absence of coadsorbed oxygen, phenylacetylene formed well-ordered dense overlayers which, with increasing temperature, desorbed without reaction. In striking contrast, even at 120 K, the presence of oxygen led to immediate and complete disruption of the organic layer due to abstraction of acetylenic hydrogen with formation of a disordered mixed layer containing immobile adsorbed phenylacetylide. At higher temperatures phenylacetylide underwent Glaser–Hay coupling to form highly ordered domains of diphenyldiacetylene that eventually desorbed without decomposition, leaving the bare metal surface. DFT calculations showed that, while acetylenic H abstraction was otherwise an endothermic process, oxygen adatoms triggered a reaction-initiating exothermic pathway leading to OH(a) + phenylacetylide, consistent with the experimental observations. Moreover, it was found that, with a solution of phenylacetylene in nonane and in the presence of O2, Ag particles catalyzed Glaser–Hay coupling with high selectivity. Rigorous exclusion of oxygen from the reactor strongly suppressed the catalytic reaction. Interestingly, too much oxygen lowers the selectivity toward diphenyldiacetylene. Thus, vacuum studies and theoretical calculations revealed the key role of oxygen in the reaction mechanism, subsequently borne out by catalytic studies with Ag particles that confirmed the presence of oxygen as a necessary and sufficient condition for the coupling reaction to occur. The direct relevance of model studies to a mechanistic understanding of coupling reactions under conditions of practical catalysis was reaffirmed.
Mayo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00431
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis, Characterisation, and Photocatalytic Behaviour of Mesoporous ZnS Nanoparticles Prepared Using By-Product Templating
Emrooz, HBM; Rahmani, AR; Gotor, FJAustralian Journal of Chemistry, 70 (2017) 1099-1105
Show abstract ▽
High surface area mesoporous ZnS nanoparticles (MZN) were obtained with the aid of the by-product of the synthesising reaction. This by-product, namely NaNO3, can be considered as a soft template responsible for the formation of pores. Ethanol and water were chosen as the synthesis media. Ultrasonic waves were used as an accelerator for the synthesis of MZNs. Photocatalytic activities of the synthesised samples for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) were investigated under ultraviolet irradiation. Synthesised specimens were characterised using field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction, diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, N-2-physisorption, and FT-IR spectroscopy. Results indicated that the synthesis media has a pronounced effect on the surface properties of the final porous particles by several mechanisms. The specific surface area of the MZN samples synthesised in water and ethanol were determined to be 53 and 201m(2)g(-1), respectively. The difference in the specific surface area was attributed to the weak solvation of S2- ions (Na(2)S5H(2)O in ethanol) and also to the by-product of the synthesis reaction. The photocatalytic behaviour of the mesoporous ZnS nanoparticles synthesised in these two media were investigated and the results have been interpreted with the aid of effective surface area, pore volume, and bandgap energy of the specimens.
Mayo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1071/CH17192
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Design and Realization of a Novel Optically Disordered Material: A Demonstration of a Mie Glass
Miranda-Munoz, Jose M.; Lozano, Gabriel; Miguez, HernanAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) art. 1700025
Show abstract ▽
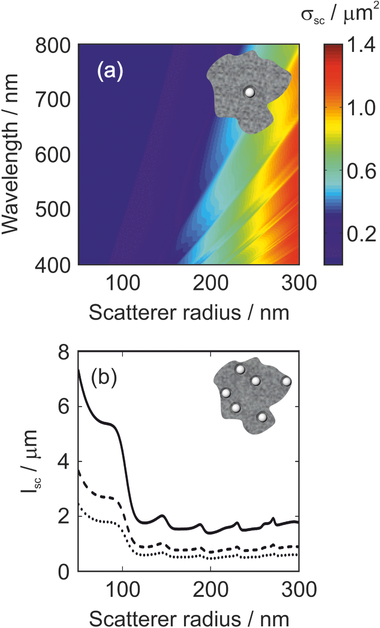
Herein, a diffusive material presenting optical disorder is introduced, which represents an example of a Mie glass. Comprising spherical crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles randomly dispersed in a mesoporous TiO2 matrix, it is proved that the scattering of light in this inhomogeneous solid can be predicted in an unprecedented manner from single-particle considerations employing Mie theory. To that aim, a study of the dependence of the key parameters employed is performed to describe light propagation in random media, i.e., the scattering mean free path and the transport mean free path, as a function of the size and concentration of the spherical inclusions based on a comparison between experimental results and analytical calculations. It is also demonstrated that Mie glasses enable enhanced fluorescence intensity due to a combined absorptance enhancement of the excitation light combined with an improved outcoupling of the emitted light. The method offers the possibility to perform a deterministic design for the realization of a light diffuser with tailor-made scattering properties.
Mayo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700025
- ‹ anterior
- 193 of 420
- siguiente ›














