Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
NO photooxidation with TiO2 photocatalysts modified with gold and platinum
Rodriguez, MJH; Melian, EP; Santiago, DG; Diaz, OG; Navio, JA; Rodriguez, JMDApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 205 (2017) 148-157
Show abstract ▽
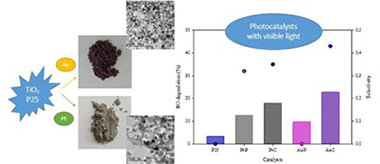
In this study, a comparative analysis is made of TiO2 modified with Pt or Au in NO photoxidation under different radiation and humidity conditions. The metals were deposited on the TiO2 surface using two methods, photodeposition and chemical reduction. All catalysts were supported on borosilicate 3.3 plates using a dip-coating technique. These modified photocatalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller measurements (BET), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectrum analysis (XPS). It was found from the XPS results that Pt and oxidized Pt species coexist on the samples obtained by photodeposition and chemical reduction. In the case of Au, though other oxidation states were also detected the dominant oxidation state for both catalysts is Au. TEM results showed most Au-C particles are below 5 nm, whereas for Au-P the nanoparticles are slightly bigger. With UV irradiation, the Pt modified catalysts do not show any significant improvement in NO photocatalytic oxidation in comparison with the unmodified P25. For Au, both modified photocatalysts (Au-P and Au-C) exceed the photocatalytic efficiency of the unmodified P25, with Au-C giving slightly better results. The incorporation of metals on the TiO2 increases its activity in the visible region.
Mayo, 2017 | DOI: 10.10161/j.apcatb.2016.12.006
Reactividad de Sólidos
New findings on thermal degradation properties of fluoropolymers
Liu, SE; Zhou, WL; Yan, QL; Qi, XF; An, T; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Zhao, FQJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 128 (2017) 675-685
Show abstract ▽
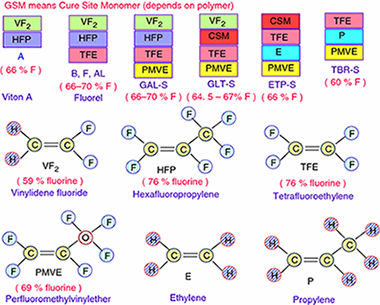
In this paper, the thermal degradation properties of Viton A and Fluorel are investigated by both isoconversional and combined kinetic analysis methods using non-isothermal thermogravimetry technique. It has been found that the heating rate has little affect on the degradation residue of Fluorel and Viton A, where around 1.3% char was formed for Fluorel and 3.5% for Viton A. Different from the literature, the decomposition of Viton A should be considered as an overlapped dehydrofluorination and carbon chain scission process, with activation energy of 214 +/- 11 and 268 +/- 13 kJ mol(-1), respectively. The effect of dehydrofluorination on degradation of Fluorel is not so significant due to low content of H, and hence, it could be considered as a single-step mechanism with average activation energy of 264 +/- 14 kJ mol(-1). The thermal stability of Fluorel is much better than that of Viton A, and the predicted half-life is around 218 min for Fluorel and 49 min for Viton A at 420 A degrees C, which are consistent with experimental values. If using a single-step model as in the literature for Viton A, its half-life at 420 A degrees C would be underestimated for > 20%.
Mayo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-016-5963-z
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
High UV-photocatalytic activity of ZnO and Ag/ZnO synthesized by a facile method
C. Jaramillo-Páez; J.A. Navío; M.C. Hidalgo; M. MacíasCatalysis Today, 284 (2017) 121-128
Show abstract ▽
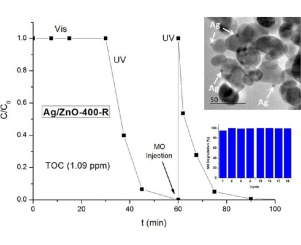
ZnO nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized by a facile precipitation procedure by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn(II) acetate and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7.0 without template addition. We have investigated the effect of annealing temperature in the final surface and structural properties. Photocatalytic studies were performed using two selected substrates, Methyl Orange and Phenol, both as single model substrates and in mixtures of them.
It has been stated that calcination treatments lead to a significant improvement in the photocatalytic properties of the studied samples, even better than TiO2(P25). As expected, the addition of Ag+ during the photocatalytic degradation of MO increases the reaction rate of the degradation of MO, giving a resultant Ag/ZnO photocatalyst which, after recovery, can be reused at least 18 times for the MO degradation tests, being even more photoactive than ZnO.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.11.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Thermal Pretreatment and Nanosilica Addition on Limestone Performance at Calcium-Looping Conditions for Thermochemical Energy Storage of Concentrated Solar Power
Valverde, Jose Manuel; Barea-Lopez, Manuel; Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.Enery & Fuels, 31 (2017) 4226-4236
Show abstract ▽
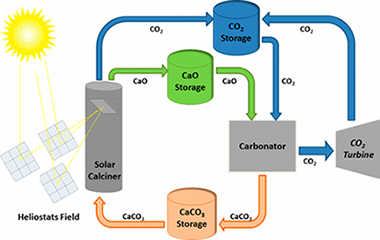
The share of renewable energies is growing rapidly, partly in response to the urgent need for mitigating CO2 emissions from fossil fuel power plants. However, cheap and efficient large-scale energy storage technologies are not yet available to allow for a significant penetration of renewable energies into the grid. Recently, a potentially low-cost and efficient thermochemical energy storage (TCES) system has been proposed, based on the integration of the calcium-looping (CaL) process into concentrated solar power plants (CSPs). The CaL process relies on the multicycle carbonation/calcination of CaO, which can be derived from calcination of widely available, cheap, and nontoxic natural limestone (CaCO3). This work explores the effect on the multicycle activity of limestone-derived CaO of thermal pretreatment under diverse atmospheres and the addition of nanosilica, which would be expected to hinder CaO grain sintering. Importantly, optimum CaL conditions for CSP energy storage differ radically from those used in the application of the CaL process for CO2 capture. Thus, calcination should be ideally carried out under low CO2 partial pressure at moderate temperature (below 750 degrees C), whereas CO2 concentration and temperature should be high for carbonation in order to maximize thermoelectric efficiency. When limestone is subjected to carbonation/calcination cycles at these conditions, its performance is critically dependent on the type of pretreatment. Our results indicate that the multicycle CaO activity is correlated with the size of the particles and the CaO pore size distribution. Thus, CaO activity is impaired as particle size is increased and/or CaO pore size is decreased. These observations suggest that pore plugging poses a main limitation to the multicycle performance of limestone-derived CaO at the optimum CaL conditions for TCES in CSPs, which is supported by scanning electron microscopy analysis. Strategies to enhance the performance of natural limestone at these conditions should be therefore oriented toward minimizing pore plugging rather than CaO grain sintering, which stands as the main limitation at CaL conditions for CO2 capture.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03364
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Features of electrical properties of BE-C(Fe) biocarbons carbonized in the presence of an Fe-containing catalyst
Popov, VV; Orlova, TS; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 59 (2017) 703-709
Show abstract ▽
The effect of partial graphitization on electrical and galvanomagnetic properties of BE-C(Fe) biomorphic carbons produced by beech wood carbonization at temperatures of 850-1600A degrees C in the presence of an iron-containing catalyst is studied. The use of an Fe catalyst at D cent (carb) ae<yen> 1000A degrees C leads to the formation of nanoscale graphite-phase inclusions; its total volume and nanocrystallite sizes increase with D cent (carb). The data on the carrier concentration and mobility are obtained. It was shown that partially graphitized BE-C(Fe) carbons with D cent (carb) ae<yen> 1000A degrees C in the conductivity type and magnetoresistance features relate to highly disordered metal systems whose conductivity can be described taking into account the contribution of quantum corrections, mainly the correction caused by the electron-electron interaction. It is shown that nonmonotonic dependences of the Hall constant R on the magnetic field are characteristic of BE-C(Fe) samples with 1000 ae<currency> D cent (carb) < 1600A degrees C, which is most probably caused by the contribution of various carrier groups, i.e., electrons and holes. In BE-C(Fe) samples with D cent (carb) = 1600A degrees C, the Hall coefficient corresponds to the metal state, which is associated with conducting medium homogenization resulting from the formation of a significant graphite phase volume.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783417040205
- ‹ anterior
- 195 of 420
- siguiente ›














