Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Deep insight into Zr/Fe combination for successful Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 WGS catalyst doping
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Ioannides, T; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Science & Technology, 7 (2017) 1556-1564
Show abstract ▽
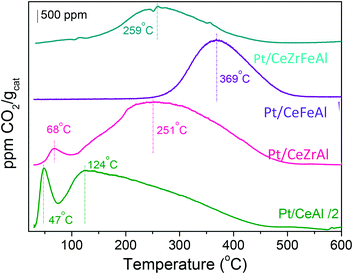
Efficient promotion of the Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 catalytic system was achieved by the addition of two different ceria promoters, Zr and Fe. From the exhaustive data analysis, the key features for enhanced catalytic performance and the roles of each doping metal are established. The combination of both doping agents manifests a synergistic effect reflected in noteworthy improvements in H2 reducibility. In addition, the catalyst's doping influences its chemisorptive properties, which is reflected in an increase of the easiness of carbonaceous species desorption, thus leading to superior catalyst resistance toward deactivation.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1039/c6cy02551j
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical Solvent-Free Synthesis of Quaternary Semiconductor Cu-Fe-Sn-S Nanocrystals
Balaz, Peter; Balaz, Matej; Sayagues, Maria J.; Skorvanek, Ivan; Zorkovska, Anna; Dutkova, Erika; Briancin, Jaroslav; Kovac, Jaroslav; Kovac, Jaroslav, Jr.; Shpotyuk, YaroslavNanoscale Research Letters, 12 (2017) art. 256
Show abstract ▽
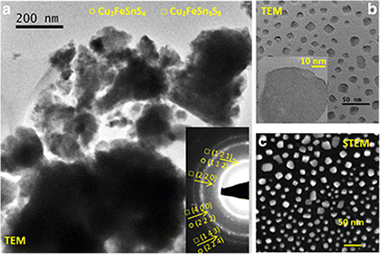
In this study, we demonstrate a one-pot mechanochemical synthesis of the nanocomposite composed of stannite Cu2FeSnS4 and rhodostannite Cu2FeSn3S8 nanocrystals using a planetary ball mill and elemental precursors (Cu, Fe, Sn, S). By this approach, unique nanostructures with interesting properties can be obtained. Methods of XRD, Raman spectroscopy, UV-Vis, nitrogen adsorption, SEM, EDX, HRTEM, STEM, and SQUID magnetometry were applied. Quaternary tetragonal phases of stannite and rhodostannite with crystallite sizes 18-19 nm were obtained. The dominant Raman peaks corresponding to the tetragonal stannite structure corresponding to A-symmetry optical modes were identified in the spectra. The bandgap 1.25 eV calculated from UV-Vis absorption spectrum is very well-acceptable value for the application of the synthesized material. The SEM micrographs illustrate the clusters of particles in micron and submicron range. The formation of agglomerates is also illustrated on the TEM micrographs. Weak ferromagnetic properties of the synthesized nanocrystals were documented.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1186/s11671-017-2029-5
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically Synthesized CuFeSe2 Nanoparticles and Their Properties
Dutkova, E; Skorvanek, I; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Kovac, J; Balaz, PActa Physica Polonica A, 131 (2017) 1156-1158
Show abstract ▽
The mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline CuFeSe2 particles prepared by high-energy milling in a planetary mill in an argon atmosphere from copper, iron, and selenium for 60 min is reported for the first time. The CuFeSe2 nanoparticles crystallize in tetragonal structure with mean crystallite size of about 32 +/- 1 nm. High resolution transmission electron microscopy measurements confirmed the presence of agglomerates which are formed by small nanocrystalline domains (5-40 nm). The magnetic data revealed that paramagnetic CuFeSe2 nanoparticles coexist with a small amount of ferromagnetic impurities at room temperature. The magnetic transition towards a weak ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic behavior occurs in CuFeSe2 at approximately 79 K. The band gap of the CuFeSe2 particles is 0.95 eV which is wider than the band gap in bulk materials (0.16 eV), which could be in many aspects of application more beneficial.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.131.1156
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
High UV-photocatalytic activity of ZnO and Ag/ZnO synthesized by a facile method
C. Jaramillo-Páez; J.A. Navío; M.C. Hidalgo; M. MacíasCatalysis Today, 284 (2017) 121-128
Show abstract ▽
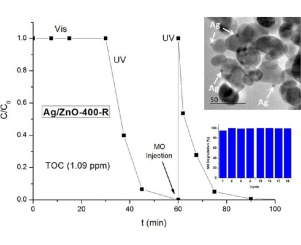
ZnO nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized by a facile precipitation procedure by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn(II) acetate and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7.0 without template addition. We have investigated the effect of annealing temperature in the final surface and structural properties. Photocatalytic studies were performed using two selected substrates, Methyl Orange and Phenol, both as single model substrates and in mixtures of them.
It has been stated that calcination treatments lead to a significant improvement in the photocatalytic properties of the studied samples, even better than TiO2(P25). As expected, the addition of Ag+ during the photocatalytic degradation of MO increases the reaction rate of the degradation of MO, giving a resultant Ag/ZnO photocatalyst which, after recovery, can be reused at least 18 times for the MO degradation tests, being even more photoactive than ZnO.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.11.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Thermal Pretreatment and Nanosilica Addition on Limestone Performance at Calcium-Looping Conditions for Thermochemical Energy Storage of Concentrated Solar Power
Valverde, Jose Manuel; Barea-Lopez, Manuel; Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.Enery & Fuels, 31 (2017) 4226-4236
Show abstract ▽
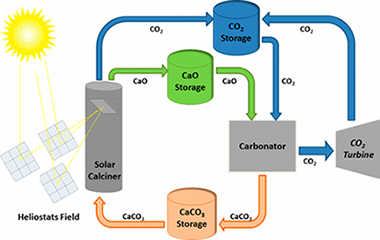
The share of renewable energies is growing rapidly, partly in response to the urgent need for mitigating CO2 emissions from fossil fuel power plants. However, cheap and efficient large-scale energy storage technologies are not yet available to allow for a significant penetration of renewable energies into the grid. Recently, a potentially low-cost and efficient thermochemical energy storage (TCES) system has been proposed, based on the integration of the calcium-looping (CaL) process into concentrated solar power plants (CSPs). The CaL process relies on the multicycle carbonation/calcination of CaO, which can be derived from calcination of widely available, cheap, and nontoxic natural limestone (CaCO3). This work explores the effect on the multicycle activity of limestone-derived CaO of thermal pretreatment under diverse atmospheres and the addition of nanosilica, which would be expected to hinder CaO grain sintering. Importantly, optimum CaL conditions for CSP energy storage differ radically from those used in the application of the CaL process for CO2 capture. Thus, calcination should be ideally carried out under low CO2 partial pressure at moderate temperature (below 750 degrees C), whereas CO2 concentration and temperature should be high for carbonation in order to maximize thermoelectric efficiency. When limestone is subjected to carbonation/calcination cycles at these conditions, its performance is critically dependent on the type of pretreatment. Our results indicate that the multicycle CaO activity is correlated with the size of the particles and the CaO pore size distribution. Thus, CaO activity is impaired as particle size is increased and/or CaO pore size is decreased. These observations suggest that pore plugging poses a main limitation to the multicycle performance of limestone-derived CaO at the optimum CaL conditions for TCES in CSPs, which is supported by scanning electron microscopy analysis. Strategies to enhance the performance of natural limestone at these conditions should be therefore oriented toward minimizing pore plugging rather than CaO grain sintering, which stands as the main limitation at CaL conditions for CO2 capture.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03364
- ‹ anterior
- 196 of 420
- siguiente ›














