Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Deep insight into Zr/Fe combination for successful Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 WGS catalyst doping
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Ioannides, T; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Science & Technology, 7 (2017) 1556-1564
Show abstract ▽
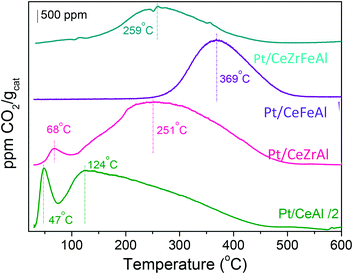
Efficient promotion of the Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 catalytic system was achieved by the addition of two different ceria promoters, Zr and Fe. From the exhaustive data analysis, the key features for enhanced catalytic performance and the roles of each doping metal are established. The combination of both doping agents manifests a synergistic effect reflected in noteworthy improvements in H2 reducibility. In addition, the catalyst's doping influences its chemisorptive properties, which is reflected in an increase of the easiness of carbonaceous species desorption, thus leading to superior catalyst resistance toward deactivation.
Abril, 2017 | DOI: 10.1039/c6cy02551j
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Monitoring the Reaction Mechanism in Model Biogas Reforming by InSitu Transient and Steady-State DRIFTS Measurements
Bobadilla, LF; Garcilaso, V; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemsuschem, 10 (2017) 1193-1201
Show abstract ▽
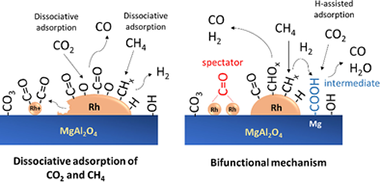
In this work, the reforming of model biogas was investigated on a Rh/MgAl2O4 catalyst. In situ transient and steady-state diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) measurements were used to gain insight into the reaction mechanism involved in the activation of CH4 and CO2. It was found that the reaction proceeds through of an initial pathway in which methane and CO2 are both dissociated on Rh metallic sites and additionally a bifunctional mechanism in which methane is activated on Rh sites and CO2 is activated on the basic sites of the support surface via a formate intermediate by H-assisted CO2 decomposition. Moreover, this plausible mechanism is able to explain why the observed apparent activation energy of CO2 is much lower than that of CH4. Our results suggest that CO2 dissociation facilitates CH4activation, because the oxygen-adsorbed species formed in the decomposition of CO2 are capable of reacting with the CHx species derived from methane decomposition.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201601379
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Reliability of new poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) membranes treated with oxygen plasma plus silicon dioxide layers for pre-prosthetic guided bone regeneration processes
Castillo-Dali, G; Castillo-Oyague, R; Batista-Cruzado, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Rodriguez-Gonzalez-Elipe, A; Saffar, JL; Lynch, CD; Gutierrez-Perez, JL; Torres-Lagares, DMedicina Oral Patología Oral y Cirugia Oral, 22 (2017) E242-E250
Show abstract ▽
Background: The use of cold plasmas may improve the surface roughness of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) membranes, which may stimulate the adhesion of osteogenic mediators and cells, thus accelerating the biodegradation of the barriers. Moreover, the incorporation of metallic-oxide particles to the surface of these membranes may enhance their osteoinductive capacity. Therefore, the aim of this paper was to evaluate the reliability of a new PLGA membrane after being treated with oxygen plasma (PO2) plus silicon dioxide (SiO2) layers for guided bone regeneration (GBR) processes.
Material and Methods: Circumferential bone defects (diameter: 11 mm; depth: 3 mm) were created on the top of eight experimentation rabbits' skulls and were randomly covered with: (1) PLGA membranes (control), or (2) PLGA/ PO2/SiO2 barriers. The animals were euthanized two months afterwards. A micromorphologic study was then performed using ROI (region of interest) colour analysis. Percentage of new bone formation, length of mineralised bone, concentration of osteoclasts, and intensity of ostheosynthetic activity were assessed and compared with those of the original bone tissue. The Kruskal-Wallis test was applied for between-group com asignificance level of a=0.05 was considered.
Results: The PLGA/ PO2/SiO2 membranes achieved the significantly highest new bone formation, length of miner-alised bone, concentration of osteoclasts, and ostheosynthetic activity. The percentage of regenerated bone supplied by the new membranes was similar to that of the original bone tissue. Unlike what happened in the control group, PLGA/PO2/SiO2 membranes predominantly showed bone layers in advanced stages of formation. Conclusions: The addition of SiO2 layers to PLGA membranes pre-treated with PO2 improves their bone-regeneration potential. Although further research is necessary to corroborate these conclusions in humans, this could be a promising strategy to rebuild the bone architecture prior to rehabilitate edentulous areas.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21512
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multicolored Emission and Lasing in DCM-Adamantane Plasma Nanocomposite Optical Films
Alcaire, M; Cerdan, L; Zamarro, FL; Aparicio, FJ; Gonzalez, JC; Ferrer, FJ; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Barranco, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (2017) 8948-8959
Show abstract ▽
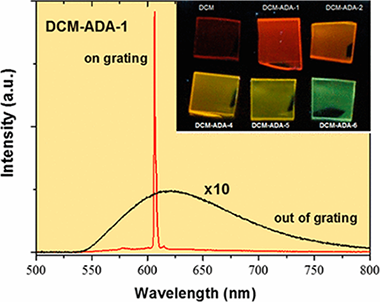
We present a low-temperature versatile protocol for the fabrication of plasma nanocomposite thin films to act as tunable emitters and optical gain media. The films are obtained by the remote plasma-assisted deposition of a 4-(dicyano-methylene)-2-methy1-6-(4-dimethylamino-styry1)-4Hpyran (DCM) laser dye alongside adamantane. The experimental parameters that determine the concentration of the dye in the films and their optical properties, including light absorption, the refractive index, and luminescence, are evaluated. Amplified spontaneous emission experiments in the DCM/adamantane nano composite waveguides show the improvement of the copolymerized nano composites' properties compared to films that were deposited with DCM as the sole precursor. Moreover, one-dimensional distributed feed-back laser emission is demonstrated and characterized in some of the nanocomposite films that are studied. These results open new paths for the optimization of the optical and lasing properties of plasma nanocomposite polymers, which can be straightforwardly integrated as active components in optoelectronic devices.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01534
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Aperiodic Metal-Dielectric Multilayers as Highly Efficient Sunlight Reflectors
Alberto Jiménez-Solano; Miguel Anaya; Mauricio E. Calvo; Mercedes Alcon-Camas; Carlos Alcañiz; Elena Guillén; Noelia Martínez; Manuel Gallas; Thomas Preussner; Ramón Escobar-Galindo; Hernán MíguezAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) 1600833
Show abstract ▽
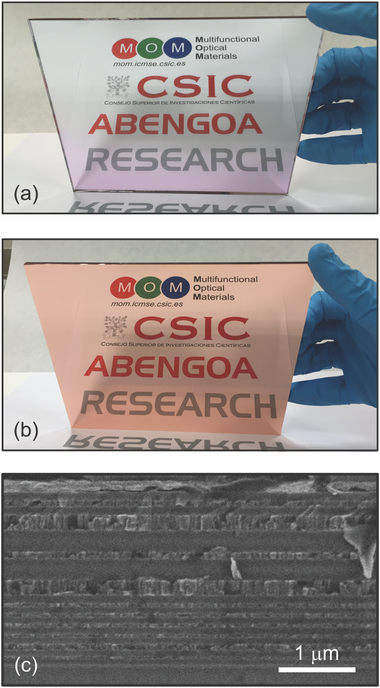
The optimum reflection of the solar spectrum at well-defined incident directions as well as its durability in time are, both, fundamental requirements of the optics of thermosolar and photovoltaic energy conversion systems. The stringent high performance needed for these applications implies that, almost exclusively, second face mirrors based on silver are employed for this purpose. Herein, the possibility to develop solar mirrors using other metals, such as copper and aluminum, is theoretically and experimentally analyzed. It is found that reflectors based on these inexpensive metals are capable of reflecting the full solar spectrum with efficiencies comparable to that of silver-based reflectors. The designs herein proposed are based on aperiodic metal-dielectric multilayers whose optimized configuration is chosen employing a code based on a genetic algorithm that allows selecting the best one among 108 tested reflectors. The use of metals with wider spectral absorption bands is compensated by the use of multilayered designs in which metal absorption is almost suppressed, as the analysis of the electric field intensity distribution demonstrates. The feasibility of the proposed mirrors is demonstrated by their actual fabrication by large area deposition techniques amenable for mass production.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201600833
- ‹ anterior
- 197 of 420
- siguiente ›














