Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multicolored Emission and Lasing in DCM-Adamantane Plasma Nanocomposite Optical Films
Alcaire, M; Cerdan, L; Zamarro, FL; Aparicio, FJ; Gonzalez, JC; Ferrer, FJ; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Barranco, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (2017) 8948-8959
Show abstract ▽
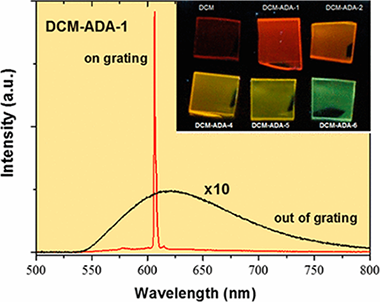
We present a low-temperature versatile protocol for the fabrication of plasma nanocomposite thin films to act as tunable emitters and optical gain media. The films are obtained by the remote plasma-assisted deposition of a 4-(dicyano-methylene)-2-methy1-6-(4-dimethylamino-styry1)-4Hpyran (DCM) laser dye alongside adamantane. The experimental parameters that determine the concentration of the dye in the films and their optical properties, including light absorption, the refractive index, and luminescence, are evaluated. Amplified spontaneous emission experiments in the DCM/adamantane nano composite waveguides show the improvement of the copolymerized nano composites' properties compared to films that were deposited with DCM as the sole precursor. Moreover, one-dimensional distributed feed-back laser emission is demonstrated and characterized in some of the nanocomposite films that are studied. These results open new paths for the optimization of the optical and lasing properties of plasma nanocomposite polymers, which can be straightforwardly integrated as active components in optoelectronic devices.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01534
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Aperiodic Metal-Dielectric Multilayers as Highly Efficient Sunlight Reflectors
Alberto Jiménez-Solano; Miguel Anaya; Mauricio E. Calvo; Mercedes Alcon-Camas; Carlos Alcañiz; Elena Guillén; Noelia Martínez; Manuel Gallas; Thomas Preussner; Ramón Escobar-Galindo; Hernán MíguezAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) 1600833
Show abstract ▽
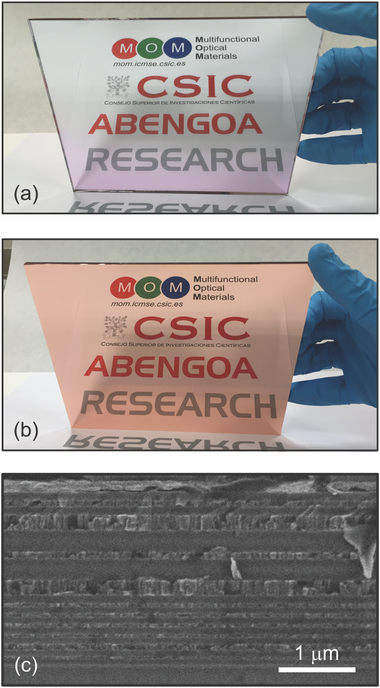
The optimum reflection of the solar spectrum at well-defined incident directions as well as its durability in time are, both, fundamental requirements of the optics of thermosolar and photovoltaic energy conversion systems. The stringent high performance needed for these applications implies that, almost exclusively, second face mirrors based on silver are employed for this purpose. Herein, the possibility to develop solar mirrors using other metals, such as copper and aluminum, is theoretically and experimentally analyzed. It is found that reflectors based on these inexpensive metals are capable of reflecting the full solar spectrum with efficiencies comparable to that of silver-based reflectors. The designs herein proposed are based on aperiodic metal-dielectric multilayers whose optimized configuration is chosen employing a code based on a genetic algorithm that allows selecting the best one among 108 tested reflectors. The use of metals with wider spectral absorption bands is compensated by the use of multilayered designs in which metal absorption is almost suppressed, as the analysis of the electric field intensity distribution demonstrates. The feasibility of the proposed mirrors is demonstrated by their actual fabrication by large area deposition techniques amenable for mass production.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201600833
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Ceramics of Ta-doping stabilized orthorhombic ZrO2 densified by spark plasma sintering and the effect of post-annealing in air
Sponchia, G; Moshtaghioun, BM; Benedetti, A; Riello, P; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Ortiz, ALScripta Materialia, 130 (2017) 128-132
Show abstract ▽
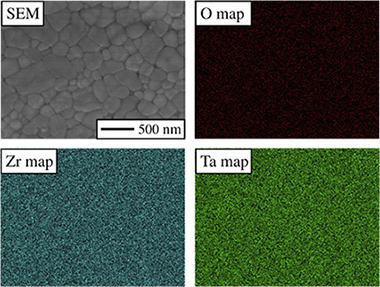
16 mol% Ta-doped ZrO2 powders were synthesized and densified by spark-plasma sintering (SPS) in vacuum, followed by post-SPS annealing in air, thus obtaining two ultrafine-grained ceramics consisting of Ta-doping stabilized orthorhombic ZrO2. The as-SPSed ceramic is black because it is actually a suboxide essentially with reduced cations and abundant oxygen vacancies, whereas the post-annealed ceramic is white because it is an oxide without vacancies and with only partially reduced cations. Both ceramics are relatively hard and brittle, but the as-SPSed ceramic was slightly more so, attributable to crystallographic and microstructural differences. Implications of interest for the ceramics community are discussed.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.11.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Large-Scale Storage of Concentrated Solar Power from Industrial Waste
Perejon, Antonio; Valverde, Jose Manuel; Miranda-Pizarro, Juan; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5 (2017) 2265-2272
Show abstract ▽
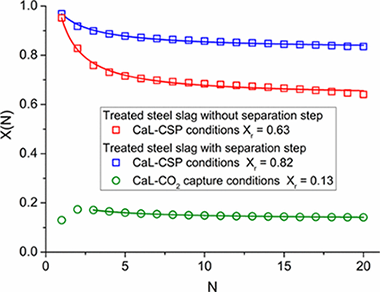
Deep penetration of renewable energies into the grid relies on the development of large-scale energy storage technologies using cheap, abundant, and nontoxic materials. Concentrated solar power (CSP) is particularly suitable to massively store thermal energy for dispatchable electricity generation. This is currently accomplished in a few demonstration plants by using molten salts albeit in a not competitive way yet. Process simulation studies indicate that thermochemical energy storage of CSP by means of the calcium looping (CaL) technology would reduce the cost of storage and increase the flexibility of energy supply provided that widely available and cheap CaO precursors with high and stable multicycle activity are used. In this work, we investigate the behavior of calcium rich steel slag at CaL conditions that would expectedly maximize the efficiency of CSP energy storage and power production. When treated with acetic acid, this nontoxic widely abundant waste yields a CaO rich solid with stable conversion near 0.8 over successive carbonation/calcination cycles at these CaL conditions
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02576
Materiales Coloidales
Diverse Applications of Nanomedicine
Pelaz, Beatriz; Alexiou, Christoph; Alvarez -Puebla, Ramon A.; Alves, Frauke; Andrews, Anne M.; Ashraf, Sumaira; Balogh, Lajos P.; Ballerini, Laura; Bestetti, Alessandra; Brendel, Cornelia; Bosi, Susanna; Carril, Monica; Chan, Warren C. W.; Chen, ChunyingACS Nano, 11 (2017) 2312-2381
Show abstract ▽
The design and use of materials in the nanoscale size range for addressing medical and health-related issues continues to receive increasing interest. Research in nanomedicine spans a multitude of areas, including drug delivery, vaccine development, antibacterial, diagnosis and imaging tools, wearable devices, implants, high-throughput screening platforms, etc. using biological, nonbiological, biomimetic, or hybrid materials. Many of these developments are starting to be translated into viable clinical products. Here, we provide an overview of recent developments in nanomedicine and highlight the current challenges and upcoming opportunities for the field and translation to the clinic.
Marzo, 2017 | DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06040
- ‹ anterior
- 198 of 420
- siguiente ›














