Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Reactividad de Sólidos
Outstanding visible photocatalytic activity of a new mixed bismuth titanatate material
Zambrano, P; Sayagues, MJ; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCApplied Surface Science, 394 (2017) 16-24
Show abstract ▽
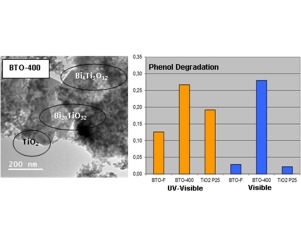
In this work, a new photocatalyst based on bismuth titanates with outstanding visible photocatalytic activity was prepared by a facile hydrothermal method. The synthesised material showed visible activity as high as UV activity of commercial TiO2 P25 under the same experimental conditions for phenol degradation. A wide characterisation of the photocatalyst was performed. The material was composed of three phases; majority of Bi20TiO32 closely interconnected to Bi4Ti3O12 and amorphous TiO2. The high visible activity showed by this material could be ascribed to a combination of several features; i.e. low band gap energy value (2.1 eV), a structure allowing a good separation path for visible photogenerated electron-holes pairs and a relatively high surface area. This photocatalyst appeared as a promising material for solar and visible applications of photocatalysis.
Enero, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.042
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Front contact optimization of industrial scale CIGS solar cells for low solar concentration using 2D physical modeling
Delgado-Sanchez, JM; Lopez-Gonzalez, JM; Orpella, A; Sanchez-Cortezon, E; Alba, MD; Lopez-Lopez, C; Alcubilla, RRenewable Energy, 101 (2017) 90-95
Show abstract ▽
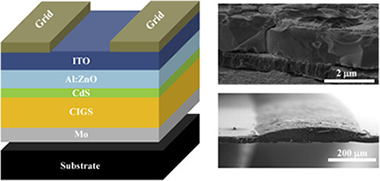
Cu(In,Ga)Se-2 (CIGS) technology is one of the best absorber materials with record efficiencies among photovoltaic thin-film technologies (22.3% at lab scale and 16% at large commercial module). Although research on this material was originally motivated by low-cost, glass-glass applications focusing to fixed photovoltaic structures, the high efficiency values make CIGS an interesting alternative for low concentration systems. In this paper a 2D model for Cu(In,Ga)Se-2 (CIGS) solar cells under low solar concentration is described and contrasted with experimental data. Using simulation, the effect of front electric contact design parameters: finger width, finger separation, and number of buses are analyzed for solar concentrations from 1 up to 10 suns. Efficiency maps allowing front contact grid optimization are shown and analyzed for each concentration factor (Cx), assessing the viability of CIGS solar cells for low concentration applications, where commercial CIGS solar cells may exhibit 35% of electrical power increases with proper front grid optimization under low concentration respect to conventional grid design.
Enero, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.08.046
Materiales Coloidales
Luminescent Eu-doped GdVO4 nanocrystals as optical markers for anti-counterfeiting purposes
Moretti, E; Pizzol, G; Fantin, M; Enrichi, F; Scopece, P; Ocana, M; Polizzi, SChemical Papers, 71 (2017) 149-159
Show abstract ▽
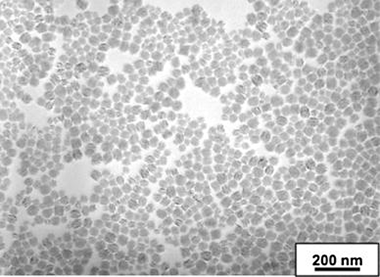
Luminescent Eu: GdVO4 nanoparticles, with an average size of 60 nm, were deposited first on monocrystalline silicon wafers, then on four different natural stone materials, by a spray-coating technique and a silica layer was subsequently deposited by atmospheric pressure plasma jet to protect the luminescent layer and improve its adhesion to the substrate. The luminescent films were characterized by photoluminescence excitation and emission, while the surface morphology was examined by FEGSEM microscopy and spectroscopic ellipsometry to determine the coating thickness. The optical appearance of the coatings was also evaluated by colorimetric measurements and the efficacy of the fixing action of the silica layer was estimated by PL measurements performed before and after a Scotch TM tape peeling test. The proposed methodology, easily applied on the surface of stone supports, has led to the realization of a luminescent film displaying good mechanical properties, transparent and undetectable in the presence of visible light, but easily activated by UV light source, indicating that the Eu: GdVO4 nanophosphors could be used as luminescent nanotags for a reliable anti-counterfeiting technology.
Enero, 2017 | DOI: 10.1007/s11696-016-0081-8
2016
2016
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Based on Nickel Nanoporous Thin Films Prepared by Physical Vapor Deposition at Oblique Angles for Beverage Industry Applications
Salazar, P; Rico, V; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of the Electrochemical Society, 163 (14) (2016) B704-B709
Show abstract ▽
Nickel nanoporous thin films deposited on Indium tin oxide conductive plates have been prepared by physical vapor deposition in an oblique angle configuration. The scanning electron microscopy characterization of these films revealed a microstructure formed by tilted nanocolumns of ca. 40-60 nm of diameter inclined by ca. 26 degrees with respect to the normal. These highly porous films had ca. 30% of void space and provided a large exposed area and outstanding diffusion properties for sensor applications. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the deposition of metallic nickel, while Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies demonstrated that electrochemically treated films presented an oxi/hydroxide outer layer that is the active phase for glucose sensing. The activated electrodes had a high sensitivity (2.05 A M-1 cm(-2)), an excellent coefficient of determination (R-2: 0.999), an outstanding reproducibility (3.2%) and a detection limit of 0.34 mu M. Their glucose selectivity was excellent with regard to common electroactive interferences and other sugars found in agro-alimentary products. Tests carried out with commercial beverages proved the reliability of these electrodes for glucose analysis in real conditions.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1149/2.1241614jes
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the ionic liquid presence on the selective oxidation of glucose over molybdenum based catalysts
Megias-Sayago, C; Carrasco, CJ; Ivanova, S; Montilla, FJ; Galindo, A; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 278 (2016) 82-90
Show abstract ▽
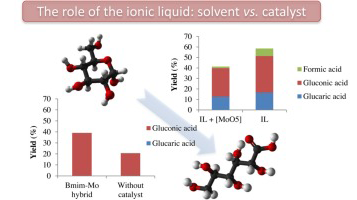
Two different approaches are proposed in this work in order to study the influence of the ionic liquid presence in the reaction of glucose oxidation by H2O2 in mild conditions. The ionic liquids are applied either as a solvent by using homogeneous Mo based catalyst, [Mo(O)(O2)2(H2O)n] complex, or by using it as an integral part of a heterogeneous catalyst, organic inorganic hybrids based on Mo Keggin structure. Both catalytic strategies resulted in acceptable glucose transformation degrees but lead to different oxidation products depending on the role of the ionic liquid. The hybrid approach restrains the number of the received products being the most selective one. A detailed study of the effect of the hybrid nature and reaction conditions is proposed in the second part of this study.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.040
- ‹ anterior
- 205 of 420
- siguiente ›














