Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Selectivity control in oxidation of 1-tetradecanol on supported nano Au catalysts
Martinez-Gonzalez, S; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Corberan, VCCatalysis Today, 278 (2016) 113-119
Show abstract ▽
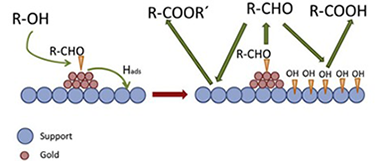
Selective oxidation of tetradecanol, a model higher fatty alcohol, on Au/CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst has been investigated to assess the factors that control selectivity. The analysis of the effect of operation conditions (temperature, run time and alcohol/metal (AIM) ratio) on catalytic performance revealed a quite complex reaction network, in which acid formation starts only after a certain level of conversion is reached. This level depends linearly on the total support surface available, indicating that it must be saturated by species generated by the reaction itself to allow acid formation to start. Addition of water to reaction medium did not modify this level, indicating that such species is not adsorbed water, as previously hypothesized, but probably spilled over hydrogen species. The resulting drastic change in the selectivity trends makes the ratio A/M a critical factor to control selectivity to aldehyde and to acid. Selectivity to ester is less sensible to operation parameters. It is noteworthy that aldehyde yields up to 27% with 90% selectivity, and acid yields up to 40% with 81% selectivity can be reached by proper selection of operation parameters.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.019
Reactividad de Sólidos
The calorimetric analysis as a tool for studying the aging hardening mechanism of a Cu-10wt%Ni-5.5wt%Sn alloy
Dianez, MJ; Donoso, E; Sayagues, MJ; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JMJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 688 (2016) 288-294
Show abstract ▽
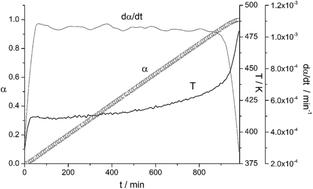
The transformations of a Cu-10wt%Ni-5.5wt%Sn alloy as a function of the aging time in the range from room temperature up to 600 degrees C have been followed by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). The results obtained have shown that this alloy undergone two overlapping exothermic phase transitions with DSC peaks at 208 degrees C and 305 degrees C, respectively, followed by an endothermic phase transformation with a DSC peak at 526 degrees C. The structural analysis by TEM, ED, EDX and XRD of the intermediates phases previously discriminated by DSC suggests that the first exothermic peak is associated to the spinodal decomposition of the sample, while the second one is associated to the segregation of a DO22 (Cu-x-Ni1-x)(3)Sn tetragonal phase coherent with the alpha-Cu structure of the starting alloy. The endothermic peak has been associated to the precipitation of cubic DO3 nanocrystals from the DO22 phase previously formed. The microhardness measurements carried out in combination with the structural characterization demonstrate that the aging hardening of the alloy under study is exclusively due to the formation of the coherent DO22 phase. The DO22/DO3 transition leads to a dramatic drop of the hardness of the alloy.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Stoichiometric Control of SiOx Thin Films Grown by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alvarez, R; Lopez-Santos, C; Ferrer, FJ; Rico, V; Guillen, E; Alcon-Camas, M; Escobar-Galindo, R; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 13 (2016) 1242-1248
Show abstract ▽
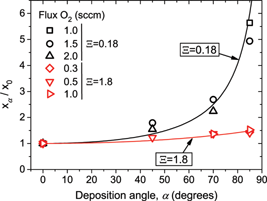
The deposition of SiOx (x <= 2) compound thin films by the reactive magnetron sputtering technique at oblique angles is studied from both theoretical and experimental points of view. A simple mathematical formula that links the film stoichiometry and the deposition conditions is deduced. Numerous experiments have been carried out to test this formula at different deposition pressures and oblique angle geometries obtaining a fairly good agreement in all studied conditions. It is found that, at low deposition pressures, the proportion of oxygen with respect to silicon in the film increases a factor of similar to 5 when solely tilting the film substrate with respect to the target, whereas at high pressures the film stoichiometry depends very weakly on the tilt angle. This behavior is explained by considering the fundamental processes mediating the growth of the film by this technique.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201600077
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the ionic liquid presence on the selective oxidation of glucose over molybdenum based catalysts
Megias-Sayago, C; Carrasco, CJ; Ivanova, S; Montilla, FJ; Galindo, A; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 278 (2016) 82-90
Show abstract ▽
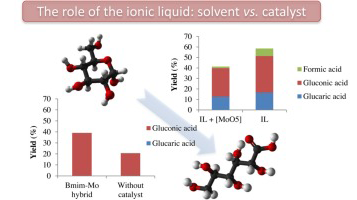
Two different approaches are proposed in this work in order to study the influence of the ionic liquid presence in the reaction of glucose oxidation by H2O2 in mild conditions. The ionic liquids are applied either as a solvent by using homogeneous Mo based catalyst, [Mo(O)(O2)2(H2O)n] complex, or by using it as an integral part of a heterogeneous catalyst, organic inorganic hybrids based on Mo Keggin structure. Both catalytic strategies resulted in acceptable glucose transformation degrees but lead to different oxidation products depending on the role of the ionic liquid. The hybrid approach restrains the number of the received products being the most selective one. A detailed study of the effect of the hybrid nature and reaction conditions is proposed in the second part of this study.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.040
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Three-Dimensional Optical Tomography and Correlated Elemental Analysis of Hybrid Perovskite Microstructures: An Insight into Defect-Related Lattice Distortion and Photoinduced Ion Migration
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Li, YL; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 7 (2016) 5227-5234
Show abstract ▽
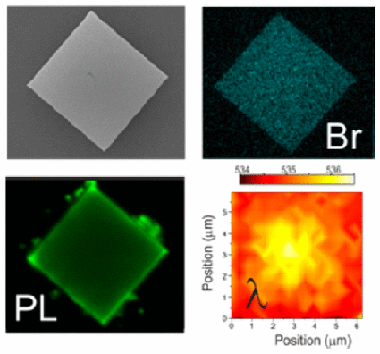
Organic lead halide perovskites have recently been proposed for applications in light-emitting devices of different sorts. More specifically, regular crystalline microstructures constitute an efficient light source and fulfill the geometrical requirements to act as resonators, giving rise to waveguiding and optical amplification. Herein we show three-dimensional laser scanning confocal tomography studies of different types of methylammonium lead bromide microstructures which have allowed us to dissect their photoemission properties with a precision of 0.036 mu m(3). This analysis shows that their spectral emission presents strong spatial variations which can be attributed to defect-related lattice distortions. It is also largely enhanced under light exposure, which triggers the migration of halide ions away from illuminated regions, eventually leading to a strongly anisotropic degradation. Our work points to the need for performing an optical quality test of individual crystallites prior to their use in optoelectronics devices and provides a means to do so.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acsjpclett.6b02456
- ‹ anterior
- 206 of 420
- siguiente ›














