Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Three-Dimensional Optical Tomography and Correlated Elemental Analysis of Hybrid Perovskite Microstructures: An Insight into Defect-Related Lattice Distortion and Photoinduced Ion Migration
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Li, YL; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 7 (2016) 5227-5234
Show abstract ▽
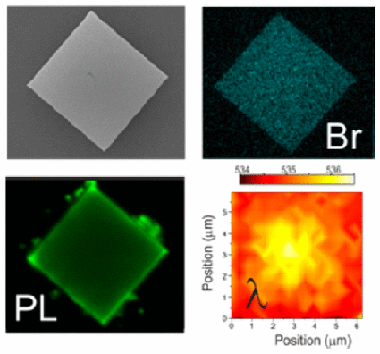
Organic lead halide perovskites have recently been proposed for applications in light-emitting devices of different sorts. More specifically, regular crystalline microstructures constitute an efficient light source and fulfill the geometrical requirements to act as resonators, giving rise to waveguiding and optical amplification. Herein we show three-dimensional laser scanning confocal tomography studies of different types of methylammonium lead bromide microstructures which have allowed us to dissect their photoemission properties with a precision of 0.036 mu m(3). This analysis shows that their spectral emission presents strong spatial variations which can be attributed to defect-related lattice distortions. It is also largely enhanced under light exposure, which triggers the migration of halide ions away from illuminated regions, eventually leading to a strongly anisotropic degradation. Our work points to the need for performing an optical quality test of individual crystallites prior to their use in optoelectronics devices and provides a means to do so.
Diciembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acsjpclett.6b02456
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of Ball Milling on CaO Crystal Growth During Limestone and Dolomite Calcination: Effect on CO2 Capture at Calcium Looping Conditions
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; de la Calle, A; Medina, S; Perez-Maqueda, LACryst. Growth Des., 16 (2016) 7025–7036
Show abstract ▽
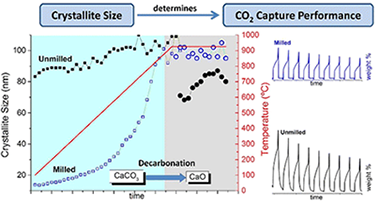
Under Calcium-Looping “realistic” operation conditions (high CO2 concentration and temperature), the multicycle CO2 capture capacity performance of CaO derived from limestone and dolomite is inversely related to its crystallite size. Ball-milling the raw sorbents results in the formation of larger nascent CaO nanocrystals during the calcination. Constraint sintering effect due to inert compounds such as dolomitic MgO mitigates the inactivation.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01228
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recycling of construction and demolition waste generated by building infrastructure for the production of glassy materials
Dominguez, A; Dominguez, MI; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACeramics International, 42 (2016) 17217-175223
Show abstract ▽
The use of waste materials generated by construction and demolition industry to yield valuable glassy materials, i.e. enamel for glazed ceramic tiles and cellular glasses is presented in this study. Both types of materials are produced by one-step treatment at moderate temperatures after simple waste chemical composition adjust. The enamels are manufactured directly from the initial waste powder by melting, while the expanded materials result from mixing of the vitreous material obtained after waste vitrification with an adequate foaming agent and posterior thermal treatment. Through the manuscript the feasibility of one step production of second generation profit materials is discussed in order to help achieving sustainable development and environmental protection.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.157
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
WGS and CO-PrOx reactions using gold promoted copper-ceria catalysts: "Bulk CuO-CeO2 vs. CuO-CeO2/Al2O3 with low mixed oxide content"
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 197 (2016) 62-72
Show abstract ▽
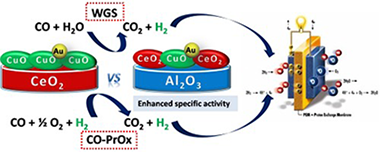
A copper-ceria bulk catalyst has been compared to a series of catalysts designed according to the as called "supported approach", corresponding to the dispersion of low content mixed copper-ceria oxide on alumina matrix. The principal characteristics of both types of catalysts are contemplated and the differences in their electronic and redox properties discussed in details. As a plus, the gold metal promotion of the catalysts is also envisaged. The advantages of the systems in the CO clean up reactions, WGS and CO-PrOx are commented. While the WGS activity appears to be ruled especially by the Cu/Ce surface to volume ratio, the CO-PrOx reaction is governed by the CuO loading. Gold addition provides benefits only at the low temperature WGS regime. Very importantly, the supported systems are always superior to the bulk configuration in terms of specific activity, a key factor from the catalyst's design perspective.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.022
Materiales Avanzados
Surface functionalizing of a lipid nanosystem to promote brain targeting: step-by-step design and physico-chemical characterization
Cozar-Bernal, MJ; Garcia-Esteban, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Rabasco, AM; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, MLPharmaceutical Development and Technology, 21 (2016) 823-831
Show abstract ▽
The use of lipid nanosystems as drug delivery to the central nervous system may be advantageous over the current strategies. The aim of this study was to develop and characterize functionalized liposomes for treatment of brain diseases. The covalent method of coupling IgG to liposomes via the derivatized lipid 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[4-(p-maleimidophenyl)butyramide](MPB-PE) was investigated. Optimized coupling conditions are shown to result in the efficient conjugation of IgG to liposomes containing low concentrations of MPB-PE (3/1 SH:IgG). The qualitative analysis has shown that after the extrusion process, more homogeneous populations of vesicles have been obtained with a nanometric size suitable to be effective to further anchor the protein. Negative values of zeta potential demonstrate that they are stable systems. Lyophilization was used to maintain the stability of the formulation. These very interesting results encourage further investigations to formulate peptide- and protein-loaded immunoliposomes, making targeting of liposomes as an attractive approach for brain drug delivery.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.3109/10837450.2015.1063651
- ‹ anterior
- 207 of 420
- siguiente ›














