Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Combined TGA-MS kinetic analysis of multistep processes. Thermal decomposition and ceramification of polysilazane and polysiloxane preceramic polymers
Garcia-Garrido, C; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18 (2016) 29348-29360
Show abstract ▽
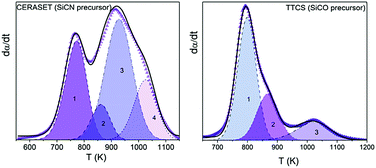
The polymer-to-ceramic transformation kinetics of two widely employed ceramic precursors, 1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetravinylcyclotetrasiloxane (TTCS) and polyureamethylvinylsilazane (CERASET), have been investigated using coupled thermogravimetry and mass spectrometry (TG-MS), Raman, XRD and FTIR. The thermally induced decomposition of the pre-ceramic polymer is the critical step in the synthesis of polymer derived ceramics (PDCs) and accurate kinetic modeling is key to attaining a complete understanding of the underlying process and to attempt any behavior predictions. However, obtaining a precise kinetic description of processes of such complexity, consisting of several largely overlapping physico-chemical processes comprising the cleavage of the starting polymeric network and the release of organic moieties, is extremely difficult. Here, by using the evolved gases detected by MS as a guide it has been possible to determine the number of steps that compose the overall process, which was subsequently resolved using a semiempirical deconvolution method based on the Frasier-Suzuki function. Such a function is more appropriate that the more usual Gaussian or Lorentzian functions since it takes into account the intrinsic asymmetry of kinetic curves. Then, the kinetic parameters of each constituent step were independently determined using both model-free and model-fitting procedures, and it was found that the processes obey mostly diffusion models which can be attributed to the diffusion of the released gases through the solid matrix. The validity of the obtained kinetic parameters was tested not only by the successful reconstruction of the original experimental curves, but also by predicting the kinetic curves of the overall processes yielded by different thermal schedules and by a mixed TTCS-CERASET precursor.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c6cp03677e
Materiales Avanzados
Surface functionalization of a lipid nanosystem to promote brain targeting: step-by-step design and physico-chemical characterization
Cózar-Bernal, MJ; García-Esteban, E; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Rabasco, AM; González-Rodríguez, MLPharmaceutical Development and Technology, 21 (7) (2016) 823-831
Show abstract ▽
The use of lipid nanosystems as drug delivery to the central nervous system may be advantageous over the current strategies. The aim of this study was to develop and characterize functionalized liposomes for treatment of brain diseases. The covalent method of coupling IgG to liposomes via the derivatized lipid 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[4-(p-maleimidophenyl)butyramide](MPB-PE) was investigated. Optimized coupling conditions are shown to result in the efficient conjugation of IgG to liposomes containing low concentrations of MPB-PE (3/1 SH:IgG). The qualitative analysis has shown that after the extrusion process, more homogeneous populations of vesicles have been obtained with a nanometric size suitable to be effective to further anchor the protein. Negative values of zeta potential demonstrate that they are stable systems. Lyophilization was used to maintain the stability of the formulation. These very interesting results encourage further investigations to formulate peptide- and protein-loaded immunoliposomes, making targeting of liposomes as an attractive approach for brain drug delivery.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.3109/10837450.2015.1063651
Glutamate microbiosensors based on Prussian Blue modified carbon fiber electrodes for neuroscience applications: In-vitro characterization
Salazar, P; Martin, M; O'Neill, RD; Gonzalez-Mora, JLSensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 235 (2016) 117-125
Show abstract ▽
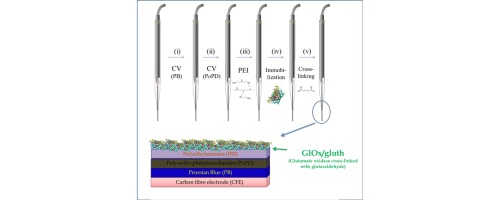
Herein we report a Prussian Blue modified carbon fiber electrode (CFE/PB) to be used in microbiosensors for glutamate monitoring in physiological applications as an alternative to the classical Pt and Pt-Ir transducers. Their low dimensions (∼250 μm CFE length and ∼10 μm diameter) are advantageous for measuring in living tissues. In addition, PB-modified microelectrodes allow the detection of enzyme-generated hydrogen peroxide at a low applied potential (∼0.0 V against SCE), contrasting the high potential used in many previous designs (∼0.7 V), decreasing the endogenous interference contributions. Moreover, the electrosynthesized polymer, poly-o-phenylenediamine (PoPD), was used to improve biosensor stability and selectivity. CFE/PB was conveniently characterized using impedance, Raman and XPS spectroscopies. Optimization of the fabrication procedure and analytical conditions is described, including activation of CFE/PB, enzyme enrichment, cross-linking, stabilization and anti-interference. A range of analytical parameters were also characterized such as sensitivity, limit of detection, linear range, and enzymatic loading. Finally, an optimized biosensor displaying a linear sensitivity of 135 ± 2 nA μM−1 cm−2 (n = 3), LOD of <2 μM, linear range up to 150 μM and effectively free of interference, is proposed as a suitable candidate for in-vivo glutamate monitoring in the central nervous system.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.05.057
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of Ball Milling on CaO Crystal Growth During Limestone and Dolomite Calcination: Effect on CO2 Capture at Calcium Looping Conditions
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; de la Calle, A; Medina, S; Perez-Maqueda, LACryst. Growth Des., 16 (2016) 7025–7036
Show abstract ▽
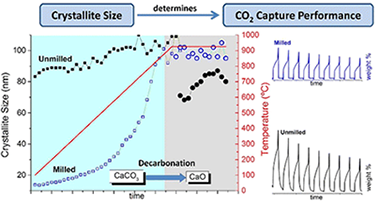
Under Calcium-Looping “realistic” operation conditions (high CO2 concentration and temperature), the multicycle CO2 capture capacity performance of CaO derived from limestone and dolomite is inversely related to its crystallite size. Ball-milling the raw sorbents results in the formation of larger nascent CaO nanocrystals during the calcination. Constraint sintering effect due to inert compounds such as dolomitic MgO mitigates the inactivation.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01228
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recycling of construction and demolition waste generated by building infrastructure for the production of glassy materials
Dominguez, A; Dominguez, MI; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACeramics International, 42 (2016) 17217-175223
Show abstract ▽
The use of waste materials generated by construction and demolition industry to yield valuable glassy materials, i.e. enamel for glazed ceramic tiles and cellular glasses is presented in this study. Both types of materials are produced by one-step treatment at moderate temperatures after simple waste chemical composition adjust. The enamels are manufactured directly from the initial waste powder by melting, while the expanded materials result from mixing of the vitreous material obtained after waste vitrification with an adequate foaming agent and posterior thermal treatment. Through the manuscript the feasibility of one step production of second generation profit materials is discussed in order to help achieving sustainable development and environmental protection.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.157
- ‹ anterior
- 208 of 420
- siguiente ›














