Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tailor-made preparation of Co-C, Co-B, and Co catalytic thin films using magnetron sputtering: insights into structure-composition and activation effects for catalyzed NaBH4 hydrolysis
Paladini, M; Godinho, V; Arzac, GM; de Haro, MCJ; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, ARSC Advances, 6 (2016) 108611-108620
Show abstract ▽
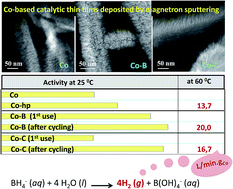
The magnetron sputtering (MS) methodology is a powerful tool for tailor-made fabrication of Co-based thin film catalysts with controlled microstructures and compositions for sodium borohydride (SBH) hydrolysis. In particular, Co-C catalysts were tested in this reaction and compared to Co-B and Co catalyst coatings. The microstructural and chemical analyses by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), Rutherford back scattering (RBS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to characterize a complete library of thin film catalysts. Pure Co materials were characterized by their nanocrystalline microstructure, and grain refinement was achieved via an increase in the deposition pressure. The incorporation of boron or carbon via co-deposition results in amorphization and dispersion of the active metallic Co phase. The composition can be tuned while keeping a controlled microstructure, and a comparison of activity at 25 degrees C was performed on catalysts deposited on Ni foam substrates. A comparison of the initial activities showed that the Co-B samples were more active than the Co-C samples because of electronic effects. However, a strong activation was found for the Co-C catalysts after the first use. This effect was dependent upon the incorporation of cobalt boride (CoxB) species on the catalysts' surface, as shown by XPS. After the first several uses, the activity of the Co-C samples (values up to 2495 mL min(-1) g(catalyst)(-1)) were as high as that of fresh Co-B, and the surface composition of both the catalysts was similar. This activation was not observed for the pure Co and was very weak for the Co-B catalysts. The use of polymeric (PTFE) substrates (flexible membranes) illustrated the versatility of the methodology to obtain catalytic membranes and allowed for a TEM microstructural analysis at the nanoscale. Catalytic activities at 60 degrees C were as high as 16.7 and 20 L min(-1) g(Co)(-1) for the Co-C and Co-B membranes, respectively. We determined the optimized conditions to increase the catalytic activity of Co-based coatings prepared via magnetron sputtering.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c6ra23171c
Materiales Coloidales
Multifunctional Eu-doped NaGd(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles functionalized with poly(L-lysine) for optical and MRI imaging
M. Laguna; N.O. Nuñez; V. Rodríguez; E. Cantelar, G. Stepien, M.L. García, J.M. de la Fuente; M. OcañaDalton Transactions, 45 (2016) 16354-16365
Show abstract ▽
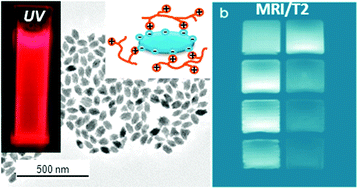
A method for the synthesis of non-aggregated and highly uniform Eu3+ doped NaGd(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles is reported for the first time. The obtained particles present tetragonal structure, ellipsoidal shape and their size can be varied by adjusting the experimental synthesis parameters. These nanoparticles, which were coated with citrate anions and functionalised with PLL, have also been developed in order to improve their colloidal stability in physiological medium (2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid, MES). A study of the luminescent dynamics of the samples as a function of the Eu doping level has been conducted in order to find the optimum nanophosphors, whose magnetic relaxivity and cell viability have also been evaluated for the first time for this system, in order to assess their suitability as multifunctional probes for optical (in vitro) and magnetic bioimaging applications.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c6dt02663j
Materiales Coloidales
Optical sensing by integration of analyte-sensitive fluorophore to particles
Carrillo-Carrion, C; Escudero, A; Parak, WJTrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 84 (2016) 84-85
Show abstract ▽
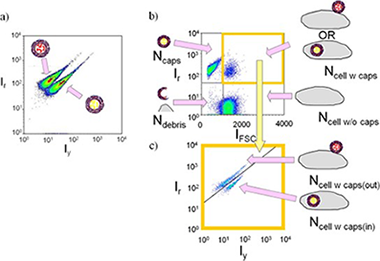
Analyte-sensitive fluorophores are a common tool in analytical chemistry. In case they are conjugated to the surface of colloidal nanoparticles new or improved applications are possible. An overview of the potential of such fluorophore-particle conjugates is given by means of several examples. First, using pH-sensitive fluorophores attached to particles are a helpful tool for investigating particle uptake by cells, as they can indicate whether particles are in the neutral slightly alkaline extracellular medium, or in acidic intracellular vesicles after endocytosis. Second, relating to lifetime-based methodologies, the fluorescence resonance energy transfer between fluorophores attached to quantum dots leads to longer lifetimes, improving their performance and expanding the possibilities of methods, such as lifetime imaging for in vivo applications. It also can be exploited for multiplexing approaches, in which the effective lifetime of the fluorophores can be tuned, allowing thus for the detection of several analytes based on temporal discrimination. Attention is focused to these three areas of application, because they are among the most reported in recent literature, and therefore of particular interest.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2016.05.001
Reactividad de Sólidos
Combined TGA-MS kinetic analysis of multistep processes. Thermal decomposition and ceramification of polysilazane and polysiloxane preceramic polymers
Garcia-Garrido, C; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18 (2016) 29348-29360
Show abstract ▽
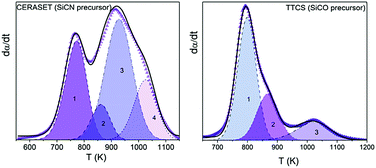
The polymer-to-ceramic transformation kinetics of two widely employed ceramic precursors, 1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetravinylcyclotetrasiloxane (TTCS) and polyureamethylvinylsilazane (CERASET), have been investigated using coupled thermogravimetry and mass spectrometry (TG-MS), Raman, XRD and FTIR. The thermally induced decomposition of the pre-ceramic polymer is the critical step in the synthesis of polymer derived ceramics (PDCs) and accurate kinetic modeling is key to attaining a complete understanding of the underlying process and to attempt any behavior predictions. However, obtaining a precise kinetic description of processes of such complexity, consisting of several largely overlapping physico-chemical processes comprising the cleavage of the starting polymeric network and the release of organic moieties, is extremely difficult. Here, by using the evolved gases detected by MS as a guide it has been possible to determine the number of steps that compose the overall process, which was subsequently resolved using a semiempirical deconvolution method based on the Frasier-Suzuki function. Such a function is more appropriate that the more usual Gaussian or Lorentzian functions since it takes into account the intrinsic asymmetry of kinetic curves. Then, the kinetic parameters of each constituent step were independently determined using both model-free and model-fitting procedures, and it was found that the processes obey mostly diffusion models which can be attributed to the diffusion of the released gases through the solid matrix. The validity of the obtained kinetic parameters was tested not only by the successful reconstruction of the original experimental curves, but also by predicting the kinetic curves of the overall processes yielded by different thermal schedules and by a mixed TTCS-CERASET precursor.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c6cp03677e
Materiales Avanzados
Surface functionalization of a lipid nanosystem to promote brain targeting: step-by-step design and physico-chemical characterization
Cózar-Bernal, MJ; García-Esteban, E; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Rabasco, AM; González-Rodríguez, MLPharmaceutical Development and Technology, 21 (7) (2016) 823-831
Show abstract ▽
The use of lipid nanosystems as drug delivery to the central nervous system may be advantageous over the current strategies. The aim of this study was to develop and characterize functionalized liposomes for treatment of brain diseases. The covalent method of coupling IgG to liposomes via the derivatized lipid 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[4-(p-maleimidophenyl)butyramide](MPB-PE) was investigated. Optimized coupling conditions are shown to result in the efficient conjugation of IgG to liposomes containing low concentrations of MPB-PE (3/1 SH:IgG). The qualitative analysis has shown that after the extrusion process, more homogeneous populations of vesicles have been obtained with a nanometric size suitable to be effective to further anchor the protein. Negative values of zeta potential demonstrate that they are stable systems. Lyophilization was used to maintain the stability of the formulation. These very interesting results encourage further investigations to formulate peptide- and protein-loaded immunoliposomes, making targeting of liposomes as an attractive approach for brain drug delivery.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.3109/10837450.2015.1063651
- ‹ anterior
- 209 of 420
- siguiente ›














