Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recycling of construction and demolition waste generated by building infrastructure for the production of glassy materials
Dominguez, A; Dominguez, MI; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACeramics International, 42 (2016) 17217-175223
Show abstract ▽
The use of waste materials generated by construction and demolition industry to yield valuable glassy materials, i.e. enamel for glazed ceramic tiles and cellular glasses is presented in this study. Both types of materials are produced by one-step treatment at moderate temperatures after simple waste chemical composition adjust. The enamels are manufactured directly from the initial waste powder by melting, while the expanded materials result from mixing of the vitreous material obtained after waste vitrification with an adequate foaming agent and posterior thermal treatment. Through the manuscript the feasibility of one step production of second generation profit materials is discussed in order to help achieving sustainable development and environmental protection.
Noviembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.157
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Forced deactivation and postmortem characterization of a metallic microchannel reactor employed for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX)
Laguna, OH; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 302 (2016) 650-662
Show abstract ▽
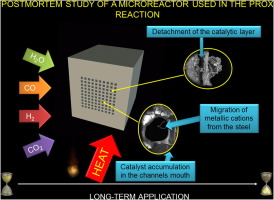
This manuscript is one of the few works presenting evidences of the effect of prolonged use of a microreactor. Our reactor has been designed for the PROX reaction. Near to 550 h of operation under different feed-streams, including CO2 and H2O, in the 100-300 degrees C temperature range, and several regeneration cycles, and a final forced deactivation during similar to 360 h resulted in the permanent loss of activity of the microreactor. This could be attributed to some phenomena whose have compromised the chemical nature of the catalyst and that of the reactor including: displacement of the coating to the mouth of the channels, detachments and cracks of the catalytic layer, migration of some elements of the metallic substrate to the surface (Fe, Cr, Y), and deposition of carbonaceous species from the reaction over the catalytic layer and/or the metallic substrate. Furthermore, sulfur compounds were detected in both inlet and outlet zones of the microreactor, coming probably from a lubricant applied over the screws that sealed the assembling of the microreactor.
This is a first approach for understanding possible effects of deactivation during long-term applications of a microreactor in the PROX reaction that could be considered as a case study useful for future designs of this kind of devices. The presented information could be extrapolated to similar reactions where thermal treatments along with highly corrosive atmospheres would be applied, in order to carry out a more appropriate design of future generations" of microreactors, with a longer useful life. For that purpose not only the adequate selection of the catalysts must be done, but also the adequate choice of the fabrication material of the reactors is needed.
Octubre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.104
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced carbon nanotube dispersion in 3YTZP/SWNTs composites and its effect on room temperature mechanical and electrical properties
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Vega-Padillo, J; Poyato, R; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 682 (2016) 70-79
Show abstract ▽
In this work, several modifications of the colloidal processing technique and spark plasma sintering (SPS) to prepare yttria tetragonal zirconia composites (YTZP) with single walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) have been tested with the aim of eliminating SWNT agglomerates. These modifications include high versus low energy ultrasonic agitation during colloidal processing, lyophilization of the 3YTZP/SWNT slurry and electrical insulation during sintering of the composites. Semi-quantitative microstructural characterization of the carbon nanotube distribution in the sintered composites showed that high energy ultrasonic agitation reduces drastically agglomerate size. Lyophilization of the mixed suspensions avoids SWNT bundle size growth. Combination of both produces an enhanced carbon nanotube network distribution along the grain boundaries (GB) due to the absence of carbon nanotube agglomerates and to a limited SWNT bundle size. This results in an increase of the real SWNT content in the GBs up to nominal SWNT content and therefore an enhanced SWNT efficiency in the composites. The agglomerate-free highly-dispersed composites exhibit a decrease in density together with grain size refinement, a decrease in room temperature hardness, an increase in flexural strength and a most significant increase in room temperature electrical conductivity. Improved SWNT distribution also lowers electrical percolation threshold to a very low level in SWNT ceramic composites, <1 vol% SWNT.
Octubre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.262
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Liquid-phase oxidation with hydrogen peroxide of benzyl alcohol and xylenes on Ca-10(PO4)(6)(OH)(2) - CaWO4
Dominguez, MI; Cojocaru, B; Tudorache, M; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MA; Parvulescu, VIComptes Rendus Chimie, 19 (2016) 1156-1165
Show abstract ▽
A W-containing apatite (W/HAp) catalyst was prepared following a hydrothermal synthesis route and served as a model catalyst. Crystallographic analysis indicated that the resulting material contained hydroxyapatite, Ca10-3xWx(PO4)(6)(OH)(2), W-hydroxyapatite, calcium tungstate, CaWO4, and tricalcium phosphate, Ca-3(PO4)(2). The catalyst was investigated in liquid phase oxidation of benzyl alcohol and xylenes using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant. For comparison, commercial calcium phosphate, hydroxyapatite and CaWO4 were tested in the same reaction. Calcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite appeared as inactive and decomposed hydrogen peroxide non-selectively. A moderate activity but low hydrogen peroxide efficiency was observed for the CaWO4 phase. In contrast, the W/HAp catalyst showed a reasonable activity and a better hydrogen peroxide efficiency in the oxidation of benzyl alcohol and xylenes. This new W/HAp catalyst showed, after six cycles, losses of the activity below 15% compared to the fresh catalyst with no effect on the selectivity. It is noteworthy that ICP-OES analyses showed no tungsten leaching that is the main advantage of this catalyst.
Octubre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2015.10.013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Permeability and mechanical integrity of porous biomorphic SiC ceramics for application as hot-gas filters
Gomez-Martin, A.; Orihuela, M. P.; Becerra, J. A.; Martinez-Fernandez, J.; Ramirez-Rico, J.Materials & Design, 107 (2016) 450-460
Show abstract ▽
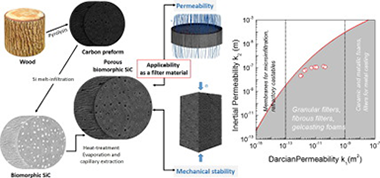
Biomorphic SiC is a biotemplated material fabricated by Si melt-infiltration of carbon preforms from wood pyrolysis. In this work, porous bioSiC ceramics from five different wood precursors, with porosities between 45 and 72% were studied for their feasibility in filtering applications.
Gas permeability and mechanical stability were investigated as a function of the microstructure of the starting wood precursor. Air-permeation performance at room temperature was measured for a range of flow rates, and the permeability constants were assessed by fitting of Forchheimer's equation to the experimental data. Darcian permeabilities were achieved in the range 10− 11–10− 12 m2, while inertial terms were in the range 10− 7–10− 8 m, showing a correlation with the average pore size and orientation of the larger channels. Regarding the mechanical stability, maximum compressive strength values were reached in the range of 3–115 MPa.
These results improve our understanding of the ways in which the microstructure influences permeability and mechanical robustness, enabling the device requirements to be tailored by selecting the wood precursor. It was also shown that these materials are promising for hot-gas filtering applications.
Octubre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.06.060
- ‹ anterior
- 210 of 420
- siguiente ›














