Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
In vitro stimulation of MC3T3-E1cells and sustained drug delivery by a hierarchical nanostructured SiO2-CaO-P2O5 scaffold
Ramiro-Gutierrez, ML; Santos-Ruiz, L; Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Becerra, J; Diaz-Cuenca, AMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 229 (2016) 31-43
Show abstract ▽
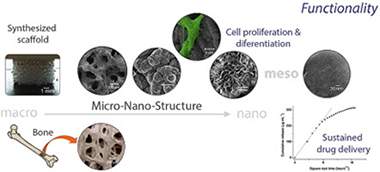
A hierarchical scaffold, SP1_h_HA, consisting of a biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite surface coating growth onto a reticulated structure having a nano-organized porous texture was fabricated and functionally studied in vitro using osteoprogenitor cells. Three scaffold materials (designated as SP0_l, SP0_h and SP1_h) were also prepared through modifications of the processing variables as control materials. The scaffolds were characterized showing well-interconnected micron-sized voids and a nano (4–6 nm)-organized porosity. In order to evaluate potential local risks and performance over mammalian cells the scaffolds were studied in comparison with a commercial clinical grade scaffold material, ProOsteon® 500R. MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblast viability was evaluated using the resazurin assay and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), showing in all cases good proliferative response. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) production and analysis of the differentiation marker osteocalcin (OC), both in non-osteoinductive and osteoinductive media, were assessed using colorimetric and RT-PCR methods. The implementation of the new scaffold processing variables enhanced ALP activity with respect to the SP0_l control material. The cell proliferation, ALP activity, and mRNA OC expression response to SP1_h_HA scaffold were higher than those observed after the use of ProOsteon® 500R. In addition, SP1_h_HA scaffold showed a two stage sustained release of gentamicin sulfate (GS) instead of the quick release shown by ProOsteon® 500R. These results suggest that our synthesized scaffold could be effective for antibiotic delivery and bone regeneration and a better option than ProOsteon® 500R.
Julio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.04.018
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Synthesis, characterization and performance of robust poison resistant ultrathin film yttria stabilized zirconia nickel anodes for application in solid electrolyte fuel cells
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMJournal of Power Sources, 324 (2016) 679-686
Show abstract ▽
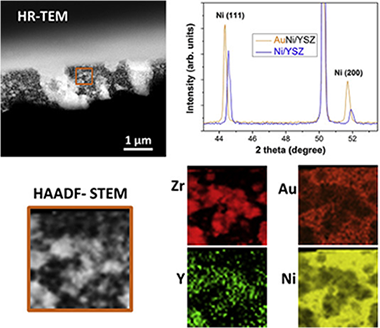
We report on the synthesis of undoped ∼5 μm YSZ-Ni porous thin films prepared by reactive pulsed DC magnetron sputtering at an oblique angle of incidence. Pre-calcination of the amorphous unmodified precursor layers followed by reduction produces a film consisting of uniformly distributed tilted columnar aggregates having extensive three-phase boundaries and favorable gas diffusion characteristics. Similarly prepared films doped with 1.2 at.% Au are also porous and contain highly dispersed gold present as Ni-Au alloy particles whose surfaces are strongly enriched with Au. With hydrogen as fuel, the performance of the undoped thin film anodes is comparable to that of 10–20 times thicker typical commercial anodes. With a 1:1 steam/carbon feed, the un-doped anode cell current rapidly falls to zero after 60 h. In striking contrast, the initial performance of the Au-doped anode is much higher and remains unaffected after 170 h. Under deliberately harsh conditions the performance of the Au-doped anodes decreases progressively, almost certainly due to carbon deposition. Even so, the cell maintains some activity after 3 days operation in dramatic contrast with the un-doped anode, which stops working after only three hours of use. The implications and possible practical application of these findings are discussed.
Julio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.05.124
Reactividad de Sólidos
Constant rate thermal analysis of a dehydrogenation reaction
Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Murafa, N; Subrt, JRSC Advances, 6 (2016) 81454-81460
Show abstract ▽
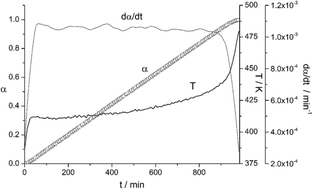
The Constant Rate Thermal Analysis (CRTA) procedure has been employed for the first time to study the kinetics of MgH2 dehydrogenation by thermogravimetry under high vacuum. CRTA implies controlling the temperature in such a way that the decomposition rate is maintained constant all over the process, employing the mass change as the experimental signal proportional to the reaction rate. The CRTA curves present a higher resolution power to discriminate the kinetic model obeyed by the reaction in comparison with conventional heating rate curves. The combined kinetic analysis has been applied to obtain the kinetic parameters, which show that MgH2 decomposition under high vacuum obeys first-order kinetics (F1). It has been proposed that the dehydrogenation of MgH2 under high vacuum takes place by instantaneous nucleation in the border line of the bidimensional crystallites followed by the growth of the nuclei.
Julio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C6RA10157G
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Unbroken Perovskite: Interplay of Morphology, Electro-optical Properties, and Ionic Movement
Correa-Baena, JP; Anaya, M; Lozano, G; Tress, W; Domanski, K; Saliba, M; Matsui, T; Jacobsson, TJ; Calvo, ME; Abate, A; Gratzel, M; Miguez, H; Hagfeldt, AAdvanced Materials, 28 (2016) 5031-5037
Show abstract ▽
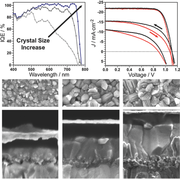
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite materials have risen up as leading components for light-harvesting applications. However, to date many questions are still open concerning the operation of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). A systematic analysis of the interplay among structural features, optoelectronic performance, and ionic movement behavior for FA(0.83)MA(0.17)Pb(I0.83Br0.17)(3) PSCs is presented, which yield high power conversion efficiencies up to 20.8%.
Julio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201600624
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic removal of patent blue V dye on Au-TiO2 and Pt-TiO2 catalysts
Vaiano, V; Iervolino, G; Sannino, D; Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Ciambelli, P; Navio, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 188 (2016) 134-146
Show abstract ▽
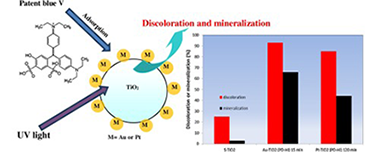
In this work it was studied the efficiency of a photocatalytic process for the removal of patent blue V. This dye is very difficult to remove by conventional treatments such as adsorption or coagulation therefore the photocatalytic process is a very interesting alternative for the removal this dye mainly because it does not require expensive oxidants and it can be carried out at mild temperatures and pressures. In this work it was tested the efficiency of Au-TiO2 and Pt-TiO2 photocatalysts in the Patent blue V removal. The Au-TiO2 catalysts were prepared by two different methods: chemical reduction and photochemical deposition; Pt-TiO2 catalysts were obtained only by photochemical deposition. In the synthesis of the catalysts prepared by photochemical deposition, it was evaluated the influence of some parameters, such as deposition time and the intensity of the light source over the physicochemical properties and photocatalytic activity of the materials obtained. An analysis of the effect of the catalyst dosage and initial patent blue V concentration over the dye degradation efficiency was also attempted.
In general, it was observed that the presence of Au or Pt on TiO2 enhances the patent blue V photodegradation; it was found that noble metal particle size and distribution on TiO2 surface are important factors influencing the dye removal. The highest dye degradation was obtained over the Au-TiO2 catalyst prepared by photochemical deposition, using high light intensity and 15 min of deposition time during the synthesis. A discoloration and a total organic carbon (TOC) removal of 93 and 67% respectively, were obtained over this material after 180 min of UV irradiation. These values are higher than that the obtained on S-TiO2 (discoloration and TOC removal of about 25% and 3%, respectively).
Julio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.001
- ‹ anterior
- 218 of 420
- siguiente ›














