Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Targeted multifunctional tannic acid nanoparticles
Aguilera, J. R.; Venegas, V.; Oliva, J. M.; Sayagues, M. J.; de Miguel, M.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J. A.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, M.; Zaderenko, A. P.RSC Advances, 9 (2016) 108611-108620
Show abstract ▽
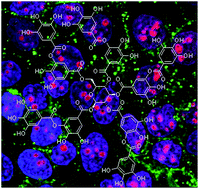
Tannic acid (TA) has multiple effects against cancer, being especially promising in those types that overexpress the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), as TA modulates its activation and downstream signaling pathways, triggering apoptosis. Nonetheless, despite the important role of this receptor in the pathogenesis and progression of a wide variety of tumors, no TA systems targeted to this receptor have been described yet. In this work, we synthesize, characterize by physico-chemical techniques and study the cytotoxic effect and cell uptake of TA nanoparticles targeted to EGFR in both tumoral and normal human skin cells. Our nanoparticles exhibited an extremely high entrapment efficiency, and were only toxic for the tumoral cells. The uptake assay demonstrated that nanoparticles are able to enter the cells through a receptor-mediated mechanism. Furthermore, we have included fluorescent markers in these nanoparticles to combine imaging and therapeutic applications, thus building effectively a multifunctional tool for biomedicine.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c5ra19405a
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Stress measurement using area detectors: a theoretical and experimental comparison of different methods in ferritic steel using a portable X-ray apparatus
Ramirez-Rico, J; Lee, SY; Ling, JJ; Noyan, ICJournal of Materials Science, 51 (2016) 5343-5355
Show abstract ▽
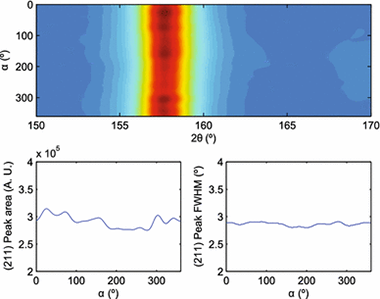
Using area detectors for stress determination by diffraction methods in a single exposure greatly simplifies the measurement process and permits the design of portable systems without complex sample cradles or moving parts. An additional advantage is the ability to see the entire or a large fraction of the Debye ring and thus determine texture and grain size effects before analysis. The two methods most commonly used to obtain stress from a single Debye ring are the so-called cosαcosαand full-ring fitting methods, which employ least-squares procedures to determine the stress from the distortion of a Debye ring by probing a set of scattering vector simultaneously. The widely applied sin2ψsin2ψ method, in contrast, requires sample rotations to probe a different subset of scattering vector orientations. In this paper, we first present a description of the different methods under the same formalism and using a unified set of coordinates that are suited to area detectors normal to the incident beam, highlighting the similarities and differences between them. We further characterize these methods by means of in situ measurements in carbon steel tube samples, using a portable detector in reflection geometry. We show that, in the absence of plastic flow, the different methods yield basically the same results and are equivalent. An analysis of possible sources of errors and their impact in the final stress values is also presented.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-016-9837-3
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity of Fe graphitized wood derived carbon
Ramirez-Rico, J; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Popov, VV; Orlova, TSMaterials & Design, 99 (2016) 528-534
Show abstract ▽
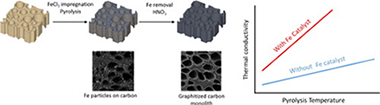
Graphitic porous carbon materials from pyrolysis of wood precursors were obtained by means of a nanosized Fe catalyst, and their microstructure and electrical and thermal transport properties investigated. Thermal and electrical conductivity of graphitized carbon materials increase with the pyrolysis temperature, indicating a relationship between the degree of graphitization and thus in crystallite size with transport properties in the resulting carbon scaffolds. Evaluation of the experimental results indicate that thermal conductivity is mainly through phonons and increases with the temperature in Fe-catalyzed carbons suggesting that the mean free path of phonons in the material is small and defect scattering dominates over phonon-phonon interactions in the range from room temperature to 800 °C.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.03.070
Reactividad de Sólidos
Template-Assisted Hydrothermal Growth of Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanowires for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Applications
Ou, C; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Datta, A; Boughey, FL; Whiter, RA; Sahonta, SL; Kar-Narayan, SACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8 (2016) 13678-13683
Show abstract ▽
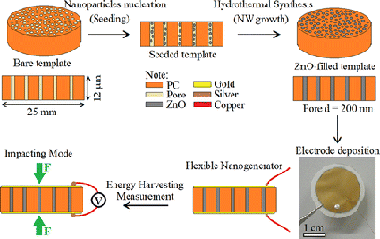
A flexible and robust piezoelectric nanogenerator (NG) based on a polymer-ceramic nanocomposite structure has been successfully fabricated via a cost-effective and scalable template assisted hydrothermal synthesis method. Vertically aligned arrays of dense and uniform zinc oxide (ZnO) nanowires (NWs) with high aspect ratio (diameter similar to 250 nm, length similar to 12 mu m) were grown within nanoporous polycarbonate (PC) templates. The energy conversion efficiency was found to be similar to 4.2%, which is comparable to previously reported values for ZnO NWs. The resulting NG is found to have excellent fatigue performance, being relatively immune to detrimental environmental factors and mechanical failure, as the constituent ZnO NWs remain embedded and protected inside the polymer matrix.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b04041
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
The role of Au, Cu & CeO2 and their interactions for an enhanced WGS performance
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 187 (2016) 98-107
Show abstract ▽
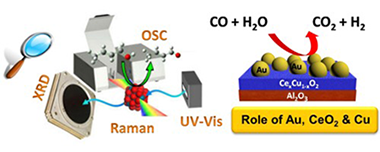
The WGS reaction over multicomponent Au/Ce1-xCuxO2/Al2O3 catalysts is studied in this work. The systems are carefully designed aiming to take advantage of every active phase included in the formulation: gold, ceria and copper. Special emphasis is given to the CeO2-CuO synergy and its influence on the displayed catalytic performance with and without gold. To this aim a meaningful correlation between the physicochemical properties of the mixed materials and their activity/stability is proposed. In general terms the developed catalysts present high activity under realistic WGS reaction conditions, with fairly good long term stability. In addition, the systems successfully withstand start-up/shut-downs situations, indispensable requisite for real applications in the field of pure hydrogen production for fuel cell goals.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.031
- ‹ anterior
- 219 of 420
- siguiente ›














