Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline ternary CuInSe2 chalcogenide semiconductor
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Kovac, J; Kovac, J; Bujnakova, Z; Briancin, J; Zorkovska, A; Balaz, P; Ficeriova, JMaterials Letters, 173 (2016) 182-186
Show abstract ▽

The synthesis of nanocrystalline ternary CuInSe2 particles prepared by high-energy milling in a planetary mill in an argon atmosphere from copper, indium and selenium was reported. CuInSe2 particles crystallize in the tetragonal structure with the crystallite size of about 30.5 nm. The Raman spectrum of CuInSe2 nanoparticles shows a strong peak at 176 cm−1 corresponds to the A1 phonon mode of tetragonal CuInSe2 chalcopyrite. HRTEM measurements also revealed the presence of nanocrystals with the size of 10–20 nm with the tendency to form agglomerates. The optical absorption study shows that nanoparticles have direct optical band gap energy of 1.8 eV. The quantum size effect of the particles was confirmed also by PL measurement.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.03.051
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Metallic nanostructures for efficient LED lighting
Lozano, G; Rodriguez, SRK; Verschuuren, MA; Rivas, JGLight: Science and Applications, 5 (2016) e16080
Show abstract ▽
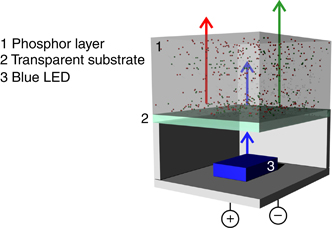
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are driving a shift toward energy-efficient illumination. Nonetheless, modifying the emission intensities, colors and directionalities of LEDs in specific ways remains a challenge often tackled by incorporating secondary optical components. Metallic nanostructures supporting plasmonic resonances are an interesting alternative to this approach due to their strong light-matter interaction, which facilitates control over light emission without requiring external secondary optical components. This review discusses new methods that enhance the efficiencies of LEDs using nanostructured metals. This is an emerging field that incorporates physics, materials science, device technology and industry. First, we provide a general overview of state-of-the-art LED lighting, discussing the main characteristics required of both quantum wells and color converters to efficiently generate white light. Then, we discuss the main challenges in this field as well as the potential of metallic nanostructures to circumvent them. We review several of the most relevant demonstrations of LEDs in combination with metallic nanostructures, which have resulted in light-emitting devices with improved performance. We also highlight a few recent studies in applied plasmonics that, although exploratory and eminently fundamental, may lead to new solutions in illumination.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1038/lsa.2016.80
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Promoting effect of Sn on supported Ni catalyst during steam reforming of glycerol
Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41 (2016) 9234-9244
Show abstract ▽
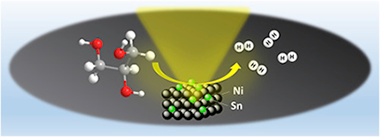
The promoting effect of Sn on the catalytic performance of supported Ni catalyst in the reaction of glycerol steam reforming was studied. The physico-chemical properties of the prepared samples were investigated by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), BET surface area, in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD), laser Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and temperature-programmed oxidation (TPO) techniques. The characterization results of the samples after reduction treatment (in the same conditions than the activation before catalytic activity measurements) revealed the formation of NiSn alloy. The Sn-doped catalyst exhibited a high activity and it was demonstrated that the Sn addition increase the catalyst stability and durability by decreasing the coke deposition.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.119
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and functionalization of monodisperse near-ultraviolet and visible excitable multifunctional Eu3+, Bi3+:REVO4 nanophosphors for bioimaging and biosensing applications
Escudero, Alberto; Carrillo-Carrion, Carolina; Zyuzin, Mikhail V.; Ashraf, Sumaira; Hartmann, Raimo; Nunez, Nuria O.; Ocana, Manuel; Parak, Wolfgang J.Nanoscale, 8 (2016) 12221-12236
Show abstract ▽
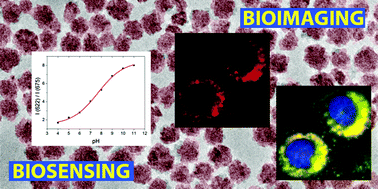
Near-ultraviolet and visible excitable Eu- and Bi-doped NPs based on rare earth vanadates (REVO4, RE = Y, Gd) have been synthesized by a facile route from appropriate RE precursors, europium and bismuth nitrate, and sodium orthovanadate, by homogeneous precipitation in an ethylene glycol/water mixture at 120 °C. The NPs can be functionalized either by a one-pot synthesis with polyacrylic acid (PAA) or by a Layer-by-Layer approach with poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH) and PAA. In the first case, the particle size can also be tuned by adjusting the amount of PAA. The Eu- Bi-doped REVO4 based nanophosphors show the typical red luminescence of Eu(III), which can be excited through an energy transfer process from the vanadate anions, resulting in a much higher luminescence intensity in comparison to the direct excitation of the europium cations. The incorporation of Bi into the REVO4 structure shifts the original absorption band of the vanadate anions towards longer wavelengths, giving rise to nanophosphors with an excitation maximum at 342 nm, which can also be excited in the visible range. The suitability of such nanophosphors for bioimaging and biosensing applications, as well as their colloidal stability in different buffer media of biological interest, their cytotoxicity, their degradability at low pH, and their uptake by HeLa cells have been evaluated. Their suitability for bioimaging and biosensing applications is also demonstrated.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C6NR03369E
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
The role of carbon overlayers on Pt-based catalysts for H-2-cleanup by CO-PROX
Romero-Sarria, F; Garcia-Dali, S; Palma, S; Jimenez-Barrera, EM; Oliviero, L; Bazin, P; Odriozola, JASurface Science, 648 (2016) 84-91
Show abstract ▽
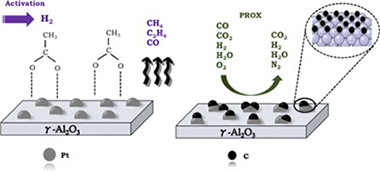
In this work, we analyze the effect of the activation method on the catalytic activity of Pt-based catalysts supported on alumina in the PROX reaction. For this, model Pt/Al2O3 catalysts with variable amounts of acetic acid were prepared and their thermal evolution studied by FTIR spectroscopy. From the analysis of the nature of the platinum surface upon acetic acid decomposition and the gas phase evolved products, we have demonstrated the formation of partially hydrogenated carbon overlayers that tailor the activity of Pt-based catalysts in the PROX reaction.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2015.12.017
- ‹ anterior
- 220 of 420
- siguiente ›














