Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Nickel catalyst with outstanding activity in the DRM reaction prepared by high temperature calcination treatment
Smolakova, L; Kout, M; Capek, L; Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Gonzalez-Delacruz, VM; Hromadko, L; Caballero, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41 (2016) 8459-8469
Show abstract ▽
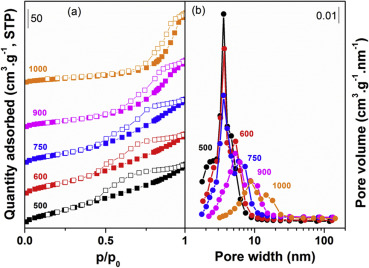
The catalytic performance of some Ni-Ce/Al2O3 catalytic systems (11 wt.% Ni and 3 wt.% Ce) were checked after being submitted to different calcination and reduction treatments. It was found that, the reduced Ni-Ce/Al2O3 catalysts were more active and stable in the dry reforming reaction of methane than thecorresponding not-reduced catalysts. This high activity was initially connected with the smaller size of pre-reduced Ni species, which at the same time leads on to the formation of filamentous carbon. The best overall performance was obtained for the reduced catalyst after being calcined at 1000 degrees C. This catalyst presents a very high stability, a low level of carbon formation, maintaining the nickel particle size constant during reaction. Surprisingly, although its reduction degree is only 12% at 750 degrees C, its catalytic activity is similar to the full reduced catalysts. So, the small number of reduced metallic particles of this catalyst shows a very high activity, much higher than the other catalysts.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.161
Reactividad de Sólidos
Use of steel slag for CO2 capture under realistic calcium-looping conditions
Miranda-Pizarro, J; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LARSC Advances, 6 (2016) 37656-37663
Show abstract ▽

In this study, CaO derived from steel slag pretreated with diluted acetic acid has been tested as a dry sorbent for CO2 capture under realistic Ca-Looping (CaL) conditions, which necessarily implies calcination under high CO2 partial pressure and fast transitions between carbonation and calcination stages. The multicycle capture performance of the sorbent has been investigated by varying the precalcination time, carbonation/calcination residence times and with the introduction of a recarbonation stage. Results show that the sorbent can be regenerated in very short residence times at 900 °C under high CO2 partial pressure, thus reducing the calciner temperature by about 30–50 °C when compared to limestone. Although the introduction of a recarbonation stage to reactivate the sorbent, as suggested in previous studies for limestone, results in a slightly enhanced capture capacity, the sorbent performance can be significantly improved if the main role of the solid-state diffusion-controlled carbonation is not dismissed. Thus, a notable enhancement of the capture capacity is achieved when the carbonation residence time is prolonged beyond just a few minutes, which suggests a critical effect of solids residence time in the carbonator on the CO2 capture efficiency of the CaL process when integrated into a power plant.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C6RA03210A
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Portable IR dye laser optofluidic microresonator as a temperature and chemical sensor
Lahoz, F; Martin, IR; Gil-Rostra, J; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AROptics Express, 24 (2016) 14383-14392
Show abstract ▽
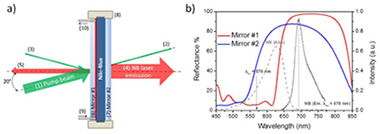
A compact and portable optofluidic microresonator has been fabricated and characterized. It is based on a Fabry-Perot microcavity consisting essentially of two tailored dichroic Bragg mirrors prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering deposition. The microresonator has been filled with an ethanol solution of Nile-Blue dye. Infrared laser emission has been measured with a pump threshold as low as 0.12 MW/cm2 and an external energy conversion efficiency of 41%. The application of the device as a temperature and a chemical sensor is demonstrated. Small temperature variations as well as small amount of water concentrations in the liquid laser medium are detected as a shift of the resonant laser modes.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1364/OE.24.014383
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Plasmonic Nanoparticles as Light-Harvesting Enhancers in Perovskite Solar Cells: A User’s Guide
Carretero-Palacios, S.; Jiménez-Solano, A.; Míguez, H.ACS Energy Letters, 1 (2016) 323-331
Show abstract ▽
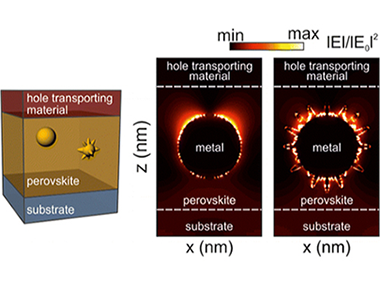
In this Perspective we discuss the implications of employing metal particles of different shape, size, and composition as absorption enhancers in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite solar cells, with the aim of establishing some guidelines for the future development of plasmonic resonance-based photovoltaic devices. Hybrid perovskites present an extraordinarily high absorption coefficient which, as we show here, makes it difficult to extrapolate concepts and designs that are applied to other solution-processed photovoltaic materials. In addition, the variability of the optical constants attained from perovskite films of seemingly similar composition further complicates the analysis. We demonstrate that, by means of rigorous design, it is possible to provide a realistic prediction of the magnitude of the absorption enhancement that can be reached for perovskite films embedding metal particles. On the basis of this, we foresee that localized surface plasmon effects will provide a means to attain highly efficient perovskite solar cells using films that are thinner than those usually employed, hence facilitating collection of photocarriers and significantly reducing the amount of potentially toxic lead present in the device.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00138
Reactividad de Sólidos
Targeted multifunctional tannic acid nanoparticles
Aguilera, J. R.; Venegas, V.; Oliva, J. M.; Sayagues, M. J.; de Miguel, M.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J. A.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, M.; Zaderenko, A. P.RSC Advances, 6 (2016) 7279-7287
Show abstract ▽
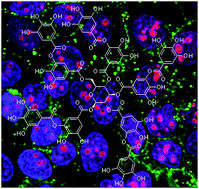
Tannic acid (TA) has multiple effects against cancer, being especially promising in those types that overexpress the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), as TA modulates its activation and downstream signaling pathways, triggering apoptosis. Nonetheless, despite the important role of this receptor in the pathogenesis and progression of a wide variety of tumors, no TA systems targeted to this receptor have been described yet. In this work, we synthesize, characterize by physico-chemical techniques and study the cytotoxic effect and cell uptake of TA nanoparticles targeted to EGFR in both tumoral and normal human skin cells. Our nanoparticles exhibited an extremely high entrapment efficiency, and were only toxic for the tumoral cells. The uptake assay demonstrated that nanoparticles are able to enter the cells through a receptor-mediated mechanism. Furthermore, we have included fluorescent markers in these nanoparticles to combine imaging and therapeutic applications, thus building effectively a multifunctional tool for biomedicine.
Junio, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C5RA19405A
- ‹ anterior
- 222 of 420
- siguiente ›














