Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Hot-pressing of (Ti,Mt)(C,N)-Co-Mo2C (Mt = Ta,Nb) powdered cermets synthesized by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Medri, V; Guicciardi, S; Lascano, S; Cordoba, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 292 (2016) 51-61
Show abstract ▽
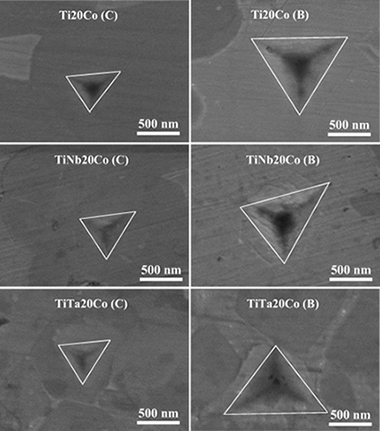
A mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) has been successfully employed for manufacturing powdered cermets based on Ti, Ti–Ta and Ti–Nb carbonitrides using Co as the binder phase and Mo2C as the sintering additive. The powders were sintered by hot-pressing, and complete chemical, microstructural and mechanical characterizations were performed on the densified cermets. When elemental Ta, Nb and/or Mo2C were added to the initial raw mixture submitted to the MSR process, smaller ceramic grains were observed after sintering, which suggested that ceramic particle growth was hindered by the presence of Ta, Nb and/or Mo in the host titanium carbonitride structure. Nanoindentation measurements enabled the determination of the hardness of the ceramic and binder phases, and values in the range of 26–29 GPa and 14–16 GPa were found, respectively. The high hardness values of the binder were related to the formation of intermetallic phases.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b00232
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Non-enzymatic Glucose electrochemical sensor made of porous NiO thin films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Salazar, P; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 201 (2016) 38-44
Show abstract ▽
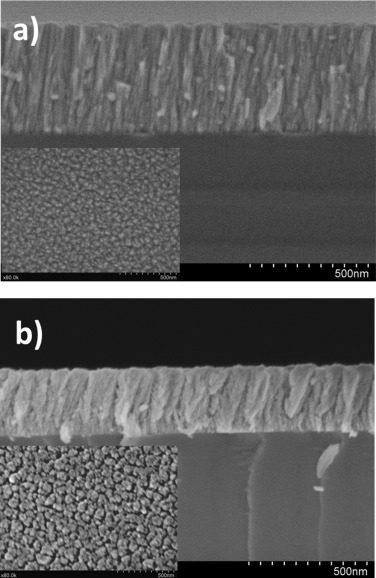
Porous nanostructured NiO thin films have been prepared in one step by magnetron sputtering in an oblique angle configuration (MS-OAD) and used as electrodes for the non-enzymatic detection of glucose. The films have been thoroughly characterized by different complementary techniques and their performance for the analysis of glucose in basic solutions determined by electrochemical methods. These electrodes presented four times higher sensitivity that equivalent compact thin films prepared by MS in a normal configuration and were superior in terms of sensitivity than majority of nickel based electrodes prepared by other methods. Finally, a high sensitivity towards detection of glucose in blood, insensitivity to common interferences, a long term stability and high reproducibility confirmed the good performance and reliability of these electrodes for practical analytical purposes.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.193
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
A panchromatic modification of the light absorption spectra of metal-organic frameworks
Otal, E. H.; Kim, M. L.; Calvo, M. E.; Karvonen, L.; Fabregas, I. O.; Sierra, C. A.; Hinestroza, J. P.Chemical Communications, 52 (2016) 6665-6668
Show abstract ▽
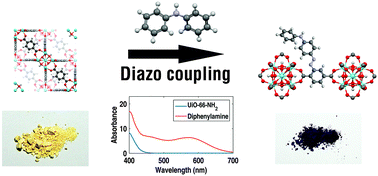
The optical absorption of UiO-66–NH2 MOF was red-shifted using a diazo-coupling reaction. The modifications performed with naphthols and aniline yielded reddish samples, and the modifications with diphenylaniline yielded dark violet ones. The photocatalytic activity of these modified MOFs was assessed for methylene blue degradation, showing a good performance relative to traditional TiO2. The degradation performance was found to correlate with the red shift of the absorption edge. These findings suggest potential applications of these materials in photocatalysis and in dye sensitized solar cells.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c6cc02319c
Reactividad de Sólidos
Electrical properties of reduced 3YTZP ceramics consolidated by spark plasma sintering
Poyato, R; Macias-Delgado, J; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Gonzalez-Romero, RL; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 42 (2016) 6713-6719
Show abstract ▽
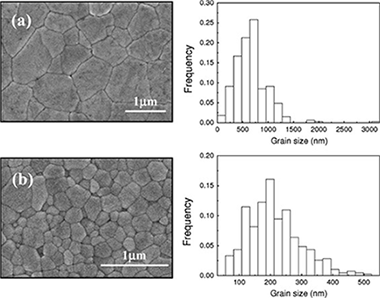
3 mol% Yttria doped zirconia ceramics were consolidated by spark plasma sintering (SPS) at two sintering temperatures with the aim of achieving two different reduction levels. Microstructural characterization of the ceramics was performed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Electrical properties were investigated by means of impedance spectroscopy from room temperature up to 500 degrees C. The two ceramics presented a remarkably different electrical behavior. The effect of the extra electrons introduced by reduction during SPS on both the bulk and the grain boundary conductivity was analyzed and discussed.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.040
Reactividad de Sólidos
Obtention of Li3xLa2/3−xTiO3 ceramics from amorphous nanopowders by spark plasma sintering
Leyet, Y.; Guerrero, F.; Anglada-Rivera, J.; Martinez, I.; Amorin, H.; Romaguera-Barcelay, Y.; Poyato, R.; Gallardo-Lopez, A.Ferroelectrics, 498 (2016) 62-66
Show abstract ▽
In this work, Li3xLa2/3-xTiO3 powder with nominal lithium content (x = 0.08) was synthesized by mechano synthesis method. Spark plasma sintering (SPS) was employed to prepare lithium lanthanum titanium oxide solid-state ceramic. The techniques of X-ray diffraction, high resolution scanning electron microscopy, and Raman spectroscopy were used to characterize the composition and microstructure of samples. The results showed that fine-grained ceramics with relative density of 95.5% were obtained by sintering the oxide powders at 1100 degrees C for only 5min.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1080/00150193.2016.1167538
- ‹ anterior
- 223 of 420
- siguiente ›














