Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biological strategy for the fabrication of highly ordered aragonite helices: the microstructure of the cavolinioidean gastropods
Checa, AG; Macias-Sanchez, E; Ramirez-Rico, JScientific Reports, 6 (2016) article number 25989
Show abstract ▽
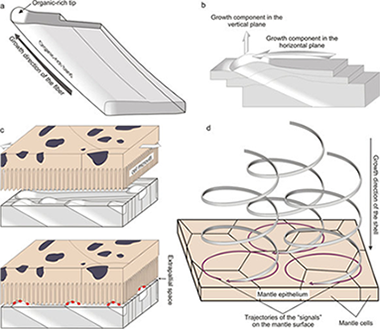
The Cavolinioidea are planktonic gastropods which construct their shells with the so-called aragonitic helical fibrous microstructure, consisting of a highly ordered arrangement of helically coiled interlocking continuous crystalline aragonite fibres. Our study reveals that, despite the high and continuous degree of interlocking between fibres, every fibre has a differentiated organic-rich thin external band, which is never invaded by neighbouring fibres. In this way, fibres avoid extinction. These intra-fibre organic-rich bands appear on the growth surface of the shell as minuscule elevations, which have to be secreted differentially by the outer mantle cells. We propose that, as the shell thickens during mineralization, fibre secretion proceeds by a mechanism of contact recognition and displacement of the tips along circular trajectories by the cells of the outer mantle surface. Given the sizes of the tips, this mechanism has to operate at the subcellular level. Accordingly, the fabrication of the helical microstructure is under strict biological control. This mechanism of fibre-by-fibre fabrication by the mantle cells is unlike that any other shell microstructure.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1038/srep25989
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The interaction between hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskite and selective contacts in perovskite solar cells: an infrared spectroscopy study
Idigoras, J; Todinova, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, A; Anta, JAPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18 (2016) 13583-13590
Show abstract ▽
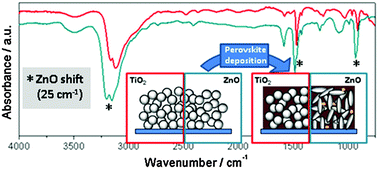
The interaction of hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskite and selective contacts is crucial to get efficient, stable and hysteresis-free perovskite-based solar cells. In this report, we analyze the vibrational properties of methylammonium lead halide perovskites deposited on different substrates by infrared absorption (IR) measurements (4000-500 cm(-1)). The materials employed as substrates are not only characterized by different chemical natures (TiO2, ZnO and Al2O3), but also by different morphologies. For all of them, we have investigated the influence of these substrate properties on perovskite formation and its degradation by humidity. The effect of selective-hole contact (Spiro-OmeTad and P3HT) layers on the degradation rate by moisture has also been studied. Our IR results reveal the existence of a strong interaction between perovskite and all ZnO materials considered, evidenced by a shift of the peaks related to the N-H vibrational modes. The interaction even induces a morphological change in ZnO nanoparticles after perovskite deposition, pointing to an acid-base reaction that takes place through the NH3+ groups of the methylammonium cation. Our IR and X-ray diffraction results also indicate that this specific interaction favors perovskite decomposition and PbI2 formation for ZnO/perovskite films subjected to humid conditions. Although no interaction is observed for TiO2, Al2O3, and the hole selective contact, the morphology and chemical nature of both contacts appear to play an important role in the rate of degradation upon exposure to moisture.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c6cp01265e
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Solution processed high refractive index contrast distributed Bragg reflectors
Anaya, M; Rubino, A; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 4 (2016) 4532-4537
Show abstract ▽
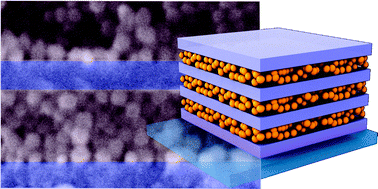
We have developed a method to alternate porous and dense dielectric films in order to build high refractive index contrast distributed Bragg reflectors (DBRs) capable of reflecting very efficiently in a targeted spectral range employing a small number of layers in the stack. Porous layers made of SiO2 nanoparticles and compact sol–gel processed TiO2 layers are sequentially deposited. The key to the preservation of porosity of every other layer during the deposition process is the use of a sacrificial layer of polystyrene that prevents the infiltration of the interstitial voids between nanoparticles with the homogeneous solution of TiO2 precursors. Our approach allows preparing a series of DBRs operating along the whole visible spectral range. Reflectance values as high as 90% are achieved from only seven layers. The particular distribution of porosity along one direction gives rise to an interesting interplay between the optical properties of the system and the vapor pressure in the surrounding atmosphere, which we foresee could be put into practice in gas sensing devices.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C6TC00663A
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biodegradable polyester films from renewable aleuritic acid: surface modifications induced by melt-polycondensation in air
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; de Vargas-Parody, MI; Cruz-Carrillo, MA; Morales-Florez, V; de la Rosa-Fox, N; Heredia, AJournal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 49 (2016) 175601
Show abstract ▽
Good water barrier properties and biocompatibility of long-chain biopolyesters like cutin and suberin have inspired the design of synthetic mimetic materials. Most of these biopolymers are made from esterified mid-chain functionalized.-long chain hydroxyacids. Aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxypalmitic) acid is such a polyhydroxylated fatty acid and is also the major constituent of natural lac resin, a relatively abundant and renewable resource. Insoluble and thermostable films have been prepared from aleuritic acid by melt-condensation polymerization in air without catalysts, an easy and attractive procedure for large scale production. Intended to be used as a protective coating, the barrier's performance is expected to be conditioned by physical and chemical modifications induced by oxygen on the air-exposed side. Hence, the chemical composition, texture, mechanical behavior, hydrophobicity, chemical resistance and biodegradation of the film surface have been studied by attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), atomic force microscopy (AFM), nanoindentation and water contact angle (WCA). It has been demonstrated that the occurrence of side oxidation reactions conditions the surface physical and chemical properties of these polyhydroxyester films. Additionally, the addition of palmitic acid to reduce the presence of hydrophilic free hydroxyl groups was found to have a strong influence on these parameters.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/49/17/175601
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
A panchromatic modification of the light absorption spectra of metal-organic frameworks
Otal, E. H.; Kim, M. L.; Calvo, M. E.; Karvonen, L.; Fabregas, I. O.; Sierra, C. A.; Hinestroza, J. P.Chemical Communications, 52 (2016) 6665-6668
Show abstract ▽
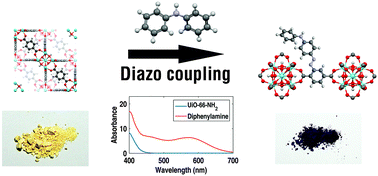
The optical absorption of UiO-66–NH2 MOF was red-shifted using a diazo-coupling reaction. The modifications performed with naphthols and aniline yielded reddish samples, and the modifications with diphenylaniline yielded dark violet ones. The photocatalytic activity of these modified MOFs was assessed for methylene blue degradation, showing a good performance relative to traditional TiO2. The degradation performance was found to correlate with the red shift of the absorption edge. These findings suggest potential applications of these materials in photocatalysis and in dye sensitized solar cells.
Mayo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c6cc02319c
- ‹ anterior
- 224 of 420
- siguiente ›














