Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
High-Throughput Fabrication of Resonant Metamaterials with Ultrasmall Coaxial Apertures via Atomic Layer Lithography
Yoo, D; Nguyen, NC; Martin-Moreno, L; Mohr, DA; Carretero-Palacios, S; Shaver, J; Peraire, J; Ebbesen, TW; Oh, SHNano Letters, 16 (2016) 2040-2046
Show abstract ▽
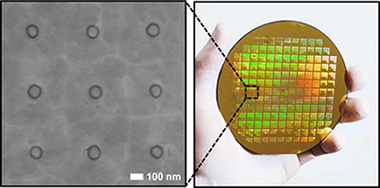
We combine atomic layer lithography and glancing angle ion polishing to create wafer-scale metamaterials composed of dense arrays of ultrasmall coaxial nanocavities in gold films. This new fabrication scheme makes it possible to shrink the diameter and increase the packing density of 2 nm-gap coaxial resonators, an extreme subwavelength structure first manufactured via atomic layer lithography, both by a factor of 100 with respect to previous studies. We demonstrate that the nonpropagating zeroth-order Fabry-Perot mode, which possesses slow light-like properties at the cutoff resonance, traps infrared light inside 2 nm gaps (gap volume similar to lambda(3)/10(6)). Notably, the annular gaps cover only 3% or less of the metal surface, while open-area normalized transmission is as high as 1700% at the epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) condition. The resulting energy accumulation alongside extraordinary optical transmission can benefit applications in nonlinear optics, optical trapping, and surface-enhanced spectroscopies. Furthermore, because the resonance wavelength is independent of the cavity length and dramatically red shifts as the gap size is reduced, large-area arrays can be constructed with lambda(resonance) >> period, making this fabrication method ideal for manufacturing resonant metamaterials.
Marzo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00024
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Photophysical Analysis of the Formation of Organic–Inorganic Trihalide Perovskite Films: Identification and Characterization of Crystal Nucleation and Growth
Anaya, M; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Calvo, ME; Lopez, C; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 120 (2016) 3071-3076
Show abstract ▽
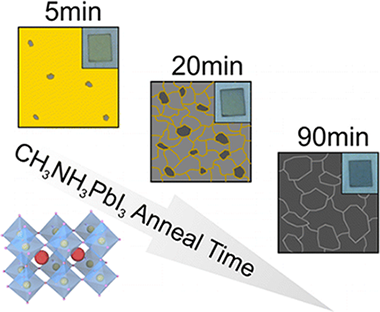
In this work we demonstrate that the different processes occurring during hybrid organic–inorganic lead iodide perovskite film formation can be identified and analyzed by a combined in situ analysis of their photophysical and structural properties. Our observations indicate that this approach permits unambiguously identifying the crystal nucleation and growth regimes that lead to the final material having a cubic crystallographic phase, which stabilizes to the well-known tetragonal phase upon cooling to room temperature. Strong correlation between the dynamic and static photoemission results and the temperature-dependent X-ray diffraction data allows us to provide a description and to establish an approximate time scale for each one of the stages and their evolution. The combined characterization approach herein explored yields key information about the kinetics of the process, such as the link between the evolution of the defect density during film formation, revealed by a fluctuating photoluminescence quantum yield, and the gradual changes observed in the PbI2-related precursor structure.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b00398
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis and characterization of CuInS2 nanocrystalline semiconductor prepared by high-energy milling
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Briancin, J; Zorkovska, A; Bujnakova, Z; Kovac, J; Kovac, J; Balaz, P; Ficeriova, JJournal of Materials Science, 51 (2016) 1978-1984
Show abstract ▽
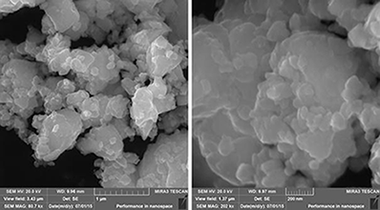
Nanocrystalline CuInS2 particles have been synthesized from copper, indium, and sulfur powders by high-energy milling in a planetary mill in an argon atmosphere. Structural characterization of the prepared nanoparticles, including phase identification, Raman spectroscopy, specific surface area measurement, and particle size analysis were performed. The optical properties were studied using UV-Vis absorption and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy. The production of CuInS2 (JCPDS 027-0159) particles with a crystallite size of about 17.5-23.5 nm was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The crystal structure has a tetragonal body-centered symmetry belonging to the I-42d space group. The Raman spectra also proved the formation of pure CuInS2 nanoparticles. TEM and HRTEM measurements revealed the presence of nanoparticles of different dimensions (10-20 nm) and their tendency to form agglomerates. The nanoparticles tend to agglomerate due to their large specific surface area. The average size of the synthesized particles was determined by photon cross-correlation spectroscopy to be in the range of 330-530 nm (bimodal size distribution). The band gap of the CuInS2 particles is 2 eV which is wider than that in bulk materials. The decrease in size leads to the blue-shift of the PL spectra. Therefore, CuInS2 nanoparticles are promising candidates for optical applications, and they have high potential in solar energy conversion.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-015-9507-x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Ripening and recrystallization of NaCl nanocrystals in humid conditions
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Macias-Montero, M; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARRSC Advances, 6 (2016) 3778-3782
Show abstract ▽
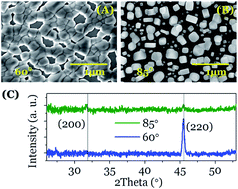
This study shows that Ostwald ripening, a universal mechanism responsible for the increase of crystal size during precipitation from solutions, can be meditated by ion diffusion through condensed monolayers of water that connect separated nanocrystals. In an environmental electron microscope we have observed "in situ" the time evolution of the number, shape, size and crystallographic texture of NaCl nanoparticles deposited by electron beam evaporation at oblique angles. Analysis of NaCl nanoparticles before and after water vapor condensation has evidenced that the size of nanocrystals is not the unique driving force inducing nanoparticle ripening and recrystallization, but the faceting of their crystalline habits and the amorphisation degree of the initially deposited nuclei also play important roles. These findings have implications for other crystallization and nucleation processes and can be of relevance for rock weathering and related phenomena.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C5RA22425J
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Determination of the Anisotropic Elastic Properties of Rocksalt Ge2Sb2Te5 by XRD, Residual Stress, and DFT
Cecchini, R; Kohary, K; Fernandez, A; Cabibbo, M; Marmier, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 120 (2016) 5624-5629
Show abstract ▽
The chalcogenide material Ge2Sb2Te5 is the prototype phase-change material, with widespread applications for optical media and random access memory. However, the full set of its independent elastic properties has not yet been published. In this study, we determine the elastic constants of the rocksalt Ge2Sb2Te5, experimentally by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and residual stress and computationally by density functional theory (DFT). The stiffnesses (XRD-stress/DFT) in GPa are C-11 = 41/58, C-12 = 7/8, and C-44 = 8/12, and the Zener ratio is 0.46/0.48. These values are important to understand the effect of elastic distortions and nonmelting processes on the performances of increasingly small phase change data bits.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b09867
- ‹ anterior
- 230 of 420
- siguiente ›














