Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Ru-Ni Catalyst in the Combined Dry-Steam Reforming of Methane: The Importance in the Metal Order Addition
Alvarez, MA; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JATopics in Catalysis, 59 (2016) 303-313
Show abstract ▽
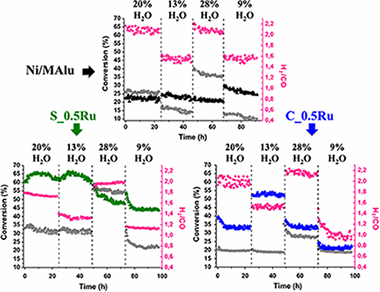
Biogas is one of the main biomass-energy resources. Its use for syngas production with a H-2/CO ratio close to two would have huge environmental, social and economic impact in the actual energetic scenario. However, the use of dry reforming, where the two main components are transformed into syngas, does not allow the desired H-2/CO ratio. For this reason, the addition of water is proposed. The process was performed with two Ru-Ni catalysts where the metal order in the impregnation process was varied. The catalysts were prepared either by simultaneous or consecutive impregnation of the active phases and its catalytic performance in the combined dry-steam reforming of methane was tested. The catalysts were characterized by XRF, XRD, S-BET, TPR-H-2 and Raman spectroscopy. The existence of a strong Ni-Ru interaction is evidenced by Raman spectroscopy and TPR-H-2 in the sample synthesized by the simultaneous impregnation. Concerning the catalytic activity, this sample presents the highest CH4 and CO2 conversion values in the entire composition rate and the lowest amount of carbon deposits after reaction. After pulse, and reactivity tests it was concluded that the higher Ni-Ru interaction displayed by the catalyst synthesized by the simultaneous impregnation, enhances the carbon gasification.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1007/s11244-015-0426-5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Vacuum template synthesis of multifunctional nanotubes with tailored nanostructured walls
Filippin, AN; Macias-Montero, M; Saghi, Z; Idigoras, J; Burdet, P; Barranco, A; Midgley, P; Anta, JA; Borras, AScientific Reports, 5 (2016) 20637
Show abstract ▽
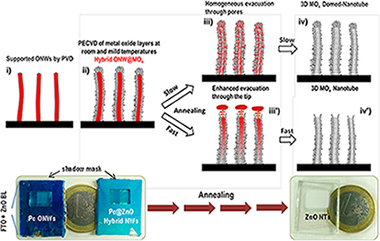
A three-step vacuum procedure for the fabrication of vertical TiO2 and ZnO nanotubes with three dimensional walls is presented. The method combines physical vapor deposition of small-molecules, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition of inorganic functional thin films and layers and a post-annealing process in vacuum in order to remove the organic template. As a result, an ample variety of inorganic nanotubes are made with tunable length, hole dimensions and shapes and tailored wall composition, microstructure, porosity and structure. The fabrication of multishell nanotubes combining different semiconducting oxides and metal nanoparticles is as well explored. This method provides a feasible and reproducible route for the fabrication of high density arrays of vertically alligned nanotubes on processable substrates. The emptying mechanism and microstructure of the nanotubes have been elucidated through SEM, STEM, HAADF-STEM tomography and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. In this article, as a proof of concept, it is presented the straightforward integration of ZnO nanotubes as photoanode in a photovoltaic cell and as a photonic oxygen gas sensor.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1038/srep20637
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanostructured Ti thin films by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Martin, JM; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Macias-Montero, M; Ferrer, FJ; Santiso, J; Rico, V; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AJournal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 49 (2016) 045303
Show abstract ▽
The growth of Ti thin films by the magnetron sputtering technique at oblique angles and at room temperature is analysed from both experimental and theoretical points of view. Unlike other materials deposited in similar conditions, the nanostructure development of the Ti layers exhibits an anomalous behaviour when varying both the angle of incidence of the deposition flux and the deposition pressure. At low pressures, a sharp transition from compact to isolated, vertically aligned, nanocolumns is obtained when the angle of incidence surpasses a critical threshold. Remarkably, this transition also occurs when solely increasing the deposition pressure under certain conditions. By the characterization of the Ti layers, the realization of fundamental experiments and the use of a simple growth model, we demonstrate that surface mobilization processes associated to a highly directed momentum distribution and the relatively high kinetic energy of sputtered atoms are responsible for this behaviour.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/49/4/045303
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Maximized performance of dye solar cells on plastic: a combined theoretical and experimental optimization approach
Li, Yuelong; Carretero-Palacios, Sol; Yoo, Kicheon; Kim, Jong Hak; Jimenez-Solano, Alberto; Lee, Chul-Ho; Miguez, Hernan; Ko, Min JaeEnergy & Environmental Science, 9 (2016) 2061-2071
Show abstract ▽
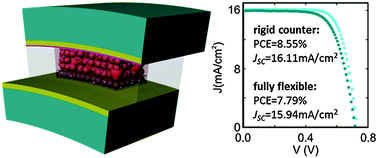
We demonstrate that a combined optimization approach based on the sequential alternation of theoretical analysis and experimental realization gives rise to plastic supported dye solar cells for which both light harvesting efficiency and electron collection are maximized. Rationalized configurations with optimized light trapping and charge extraction are realized to achieve photoanodes on plastic prepared at low temperature, showing a power conversion efficiency of 8.55% and a short circuit photocurrent of 16.11 mA cm−2, unprecedented for plastic based dye solar cell devices. Furthermore, the corresponding fully flexible designs present stable mechanical properties after several bending cycles, displaying 7.79% power conversion efficiency, an average broadband internal quantum efficiency above 90%, and a short circuit photocurrent of 15.94 mA cm−2, which is the largest reported value for bendable cells of this sort to date.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C6EE00424E
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanoindentation and scratch resistance of multilayered TiO2-SiO2 coatings with different nanocolumnar structures deposited by PV-OAD
Roa, JJ; Rico, V; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Jimenez-Pique, EJournal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 49 (2016) 13
Show abstract ▽
This paper presents a study of the mechanical properties and an evaluation of damage mechanisms of nanocolumnar TiO2-SiO2 multilayer coatings prepared by physical vapour oblique angle deposition at different configurations (slanted, zigzag or chiral) and two zenithal evaporation angles (70 degrees or 85 degrees). The characterization at micro-and nanometric length scales of the mechanical properties of the multilayers has been carried out by nanoindentation and nanoscratch tests, while the morphological evaluation of the surface and sub-surface damages produced with a sharp indenter and the adhesive and/or cohesive failures between coating and substrate have been investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy and focused ion beam, respectively. The obtained results have shown that the main processing parameters controlling the mechanical response of the different multilayers is the zenithal angle of deposition and the number of layers in the multilayer stack, while the coating architecture had only a minor effect on the mechanical response. This analysis also revealed a higher resistance to scratch testing and a brittle failure behaviour for the low zenithal angle coatings as compared with the high angle ones.
Febrero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/49/13/135104
- ‹ anterior
- 231 of 420
- siguiente ›














