Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetics of high-temperature oxidation of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets
Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Gotor, FJCorrosion Science, 102 (2016) 168-177
Show abstract ▽
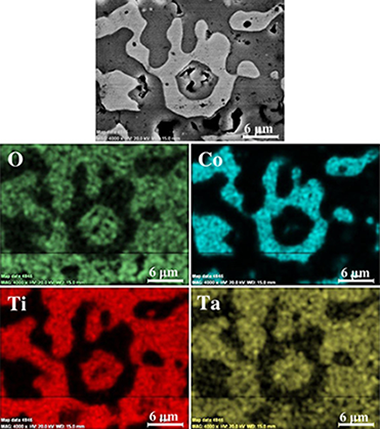
The kinetics of the high-temperature oxidation of titanium–tantalum carbonitride-based cermets with different Ti/Ta ratios was studied. Isothermal oxidation tests were conducted under static air for 48 h at temperatures between 700 °C and 1200 °C. The oxidation satisfied the parabolic kinetics, characteristic of the existence of a protective oxide layer. The apparent activation energy suggests the rate-controlling process during oxidation is the simultaneous inward and outward diffusion of oxygen and titanium, respectively, through the formed protective layer, consisting mainly of a rutile phase. A higher Ta(V) content in the rutile decreased the oxygen diffusivity due to the reduction of oxygen vacancy concentration.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.10.006
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity of partially graphitized biocarbon obtained by carbonization of medium-density fiberboard in the presence of a Ni-based catalyst
Orlova, TS; Parfen'eva, LS; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 58 (2016) 208-214
Show abstract ▽
The thermal conductivity k and resistivity rho of biocarbon matrices, prepared by carbonizing medium-density fiberboard at T (carb) = 850 and 1500A degrees C in the presence of a Ni-based catalyst (samples MDF-C( Ni)) and without a catalyst (samples MDF-C), have been measured for the first time in the temperature range of 5-300 K. X-ray diffraction analysis has revealed that the bulk graphite phase arises only at T (carb) = 1500A degrees C. It has been shown that the temperature dependences of the thermal conductivity of samples MDFC- 850 and MDF-C-850(Ni) in the range of 80-300 K are to each other and follow the law of k(T) similar to T (1.65), but the use of the Ni-catalyst leads to an increase in the thermal conductivity by a factor of approximately 1.5, due to the formation of a greater fraction of the nanocrystalline phase in the presence of the Ni-catalyst at T (carb) = 850A degrees C. In biocarbon MDF-C-1500 prepared without a catalyst, the dependence is k(T) similar to T (1.65), and it is controlled by the nanocrystalline phase. In MDF-C-1500(Ni), the bulk graphite phase formed increases the thermal conductivity by a factor of 1.5-2 compared to the thermal conductivity of MDF-C-1500 in the entire temperature range of 5-300 K; k(T = 300 K) reaches the values of similar to 10 W m(-1) K-1, characteristic of biocarbon obtained without a catalyst only at high temperatures of T (carb) = 2400A degrees C. It has been shown that MDF-C-1500(Ni) in the temperature range of 40aEuro'300 K is characterized by the dependence, k(T) similar to T (1.3), which can be described in terms of the model of partially graphitized biocarbon as a composite of an amorphous matrix with spherical inclusions of the graphite phase.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783416010236
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quantitative analysis of Ni 2p photoemission in NiO and Ni diluted in a SiO2 matrix
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Tougaard, SSurface Science, 644 (2016) 46-52
Show abstract ▽
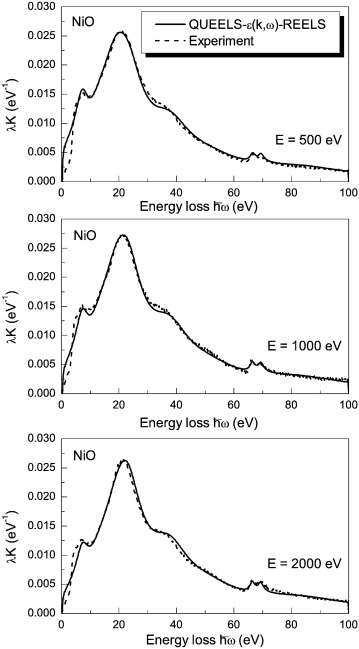
In X-ray excited photoelectron emission (XPS), besides the initial excitation process, the shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface (including bulk and surface effects) and to intrinsic excitations due to the sudden creation of the static core hole. To make an accurate quantitative interpretation of features observed in XPS, these effects must be included in the theoretical description of the emitted photoelectron spectra. It was previously shown [N. Pauly, S. Tougaard, F. Yubero, Surf. Sci. 620 (2014) 17] that these three effects can be calculated by means of the QUEELS-XPS software (Quantitative analysis of Electron Energy Losses at Surfaces for XPS) in terms of effective energy-differential inelastic electron scattering cross-sections. The only input needed to calculate these cross-sections is the energy loss function of the media which is determined from analysis of Reflection Electron Energy Loss Spectra (REELS). The full XPS spectrum is then modeled by convoluting this energy loss cross-section with the primary excitation spectrum that accounts for all effects which are part of the initial photo-excitation process, i.e. lifetime broadening, spin-orbit coupling, and multiplet splitting. In this paper we apply the previously presented procedure to the study of Ni 2p photoemission in NiO and Ni diluted in a SiO2 matrix (Ni:SiO2), samples being prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at room temperature. We observe a significant difference between the corresponding Ni 2p primary excitation spectra. The procedure allows quantifying the relative intensity of the c3d(9)L, c3d(10)L(2), and c3d(8) final states contributing to the Ni 2p photoemission spectra of the Ni2+ species in the oxide matrices. Especially, the intensity ratio in NiO between the non-local and local contributions to the 3d(9)L configuration is determined to be 2.5. Moreover the relative intensity ratio of the c3d(9)L/c3d(10)L(2)/c3d(8) configurations is found to be 1.0/0.83/0.11 for both the NiO and Ni:SiO2 samples.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2015.09.012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Influence of temperature and time on the Eu3+ reaction with synthetic Na-Mica-n (n=2 and 4)
Garcia-Jimenez, MJ; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDChemical Engineering Journal, 284 (2016) 1174-1183
Show abstract ▽
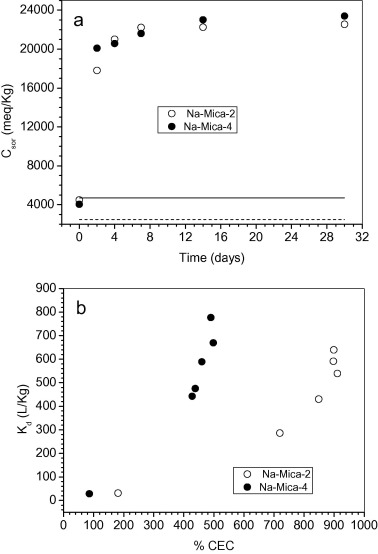
Bentonite is accepted as the best clay material for the engineered barrier of Deep Geological Repositories (DGRs). The performance of clay as the main component of the engineered barrier in the DGR has been intensively studied and the structure of the selected clay mineral play a crucial role. In this sense, a new family of synthetic swelling silicates, Na-Mica-n, with tuned layer charge (n) values between 2.0 and 4.0 per unit cell has recently been synthesized and a general synthetic method has been reported. These swelling high-charge micas could be highly valuable for the decontamination of harmful cations. The ability of these micas to immobilize Eu3+ under subcritical conditions has been probed. The adsorption was in both non-specific sites (cation exchange mechanism) and specific sites (chemical reaction or surface defects adsorption). Moreover, its adsorption capacity, under the same conditions is higher than in saponite and far superior to the bentonites.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.077
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Highly Porous ZnO Thin Films and 1D Nanostructures by Remote Plasma Processing of Zn-Phthalocyanine
Alcaire, M; Filippin, AN; Macias-Montero, M; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Rojas, TC; Mora-Boza, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Barranco, A; Borras, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 13 (2016) 287-297
Show abstract ▽
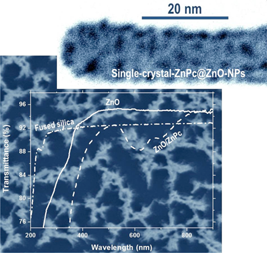
In this paper the fabrication of highly porous 1D nanostructures by a vacuum and plasma etching combined protocol is presented. Zn-phthalocyanine (ZnPc) is utilized as a solid precursor to form the ZnO. First the ZnPc is sublimated in low argon pressure. Depending on the substrate temperature and microstructure, polycrystalline films or single crystal ZnPc nanowires are grown. These starting materials are then subjected to a remote plasma oxidizing treatment. Experimental parameters such as substrate position, plasma power, treatment duration, and substrate temperature determine the microstructure and properties of the final ZnO nanostructures. The article gathers an in depth study of the obtained porous nanostructured films following scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), UV-Vis transmittance, and fluorescence spectroscopies.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201500133
- ‹ anterior
- 234 of 420
- siguiente ›














