Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quantitative analysis of Ni 2p photoemission in NiO and Ni diluted in a SiO2 matrix
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Tougaard, SSurface Science, 644 (2016) 46-52
Show abstract ▽
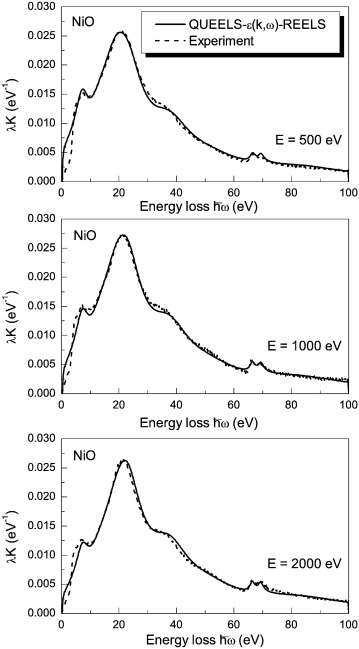
In X-ray excited photoelectron emission (XPS), besides the initial excitation process, the shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface (including bulk and surface effects) and to intrinsic excitations due to the sudden creation of the static core hole. To make an accurate quantitative interpretation of features observed in XPS, these effects must be included in the theoretical description of the emitted photoelectron spectra. It was previously shown [N. Pauly, S. Tougaard, F. Yubero, Surf. Sci. 620 (2014) 17] that these three effects can be calculated by means of the QUEELS-XPS software (Quantitative analysis of Electron Energy Losses at Surfaces for XPS) in terms of effective energy-differential inelastic electron scattering cross-sections. The only input needed to calculate these cross-sections is the energy loss function of the media which is determined from analysis of Reflection Electron Energy Loss Spectra (REELS). The full XPS spectrum is then modeled by convoluting this energy loss cross-section with the primary excitation spectrum that accounts for all effects which are part of the initial photo-excitation process, i.e. lifetime broadening, spin-orbit coupling, and multiplet splitting. In this paper we apply the previously presented procedure to the study of Ni 2p photoemission in NiO and Ni diluted in a SiO2 matrix (Ni:SiO2), samples being prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at room temperature. We observe a significant difference between the corresponding Ni 2p primary excitation spectra. The procedure allows quantifying the relative intensity of the c3d(9)L, c3d(10)L(2), and c3d(8) final states contributing to the Ni 2p photoemission spectra of the Ni2+ species in the oxide matrices. Especially, the intensity ratio in NiO between the non-local and local contributions to the 3d(9)L configuration is determined to be 2.5. Moreover the relative intensity ratio of the c3d(9)L/c3d(10)L(2)/c3d(8) configurations is found to be 1.0/0.83/0.11 for both the NiO and Ni:SiO2 samples.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2015.09.012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Influence of temperature and time on the Eu3+ reaction with synthetic Na-Mica-n (n=2 and 4)
Garcia-Jimenez, MJ; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDChemical Engineering Journal, 284 (2016) 1174-1183
Show abstract ▽
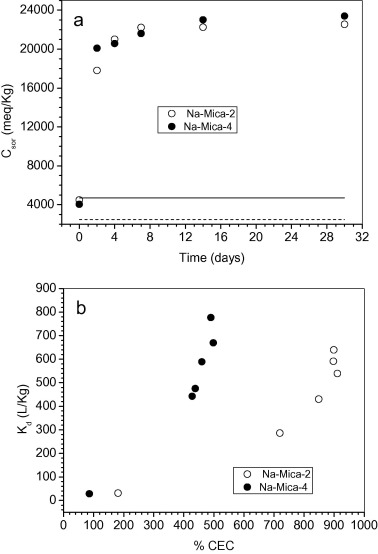
Bentonite is accepted as the best clay material for the engineered barrier of Deep Geological Repositories (DGRs). The performance of clay as the main component of the engineered barrier in the DGR has been intensively studied and the structure of the selected clay mineral play a crucial role. In this sense, a new family of synthetic swelling silicates, Na-Mica-n, with tuned layer charge (n) values between 2.0 and 4.0 per unit cell has recently been synthesized and a general synthetic method has been reported. These swelling high-charge micas could be highly valuable for the decontamination of harmful cations. The ability of these micas to immobilize Eu3+ under subcritical conditions has been probed. The adsorption was in both non-specific sites (cation exchange mechanism) and specific sites (chemical reaction or surface defects adsorption). Moreover, its adsorption capacity, under the same conditions is higher than in saponite and far superior to the bentonites.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.077
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Highly Porous ZnO Thin Films and 1D Nanostructures by Remote Plasma Processing of Zn-Phthalocyanine
Alcaire, M; Filippin, AN; Macias-Montero, M; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Rojas, TC; Mora-Boza, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Barranco, A; Borras, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 13 (2016) 287-297
Show abstract ▽
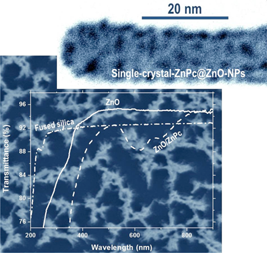
In this paper the fabrication of highly porous 1D nanostructures by a vacuum and plasma etching combined protocol is presented. Zn-phthalocyanine (ZnPc) is utilized as a solid precursor to form the ZnO. First the ZnPc is sublimated in low argon pressure. Depending on the substrate temperature and microstructure, polycrystalline films or single crystal ZnPc nanowires are grown. These starting materials are then subjected to a remote plasma oxidizing treatment. Experimental parameters such as substrate position, plasma power, treatment duration, and substrate temperature determine the microstructure and properties of the final ZnO nanostructures. The article gathers an in depth study of the obtained porous nanostructured films following scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), UV-Vis transmittance, and fluorescence spectroscopies.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201500133
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Application of Prussian Blue electrodes for amperometric detection of free chlorine in water samples using Flow Injection Analysis
Salazar, P; Martin, M; Gonzalez-Mora, JL; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARTalanta, 146 (2016) 410-416
Show abstract ▽
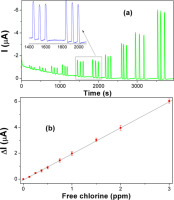
The performance for free chlorine detection of surfactant-modified Prussian Blue screen printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs/PB-BZT) have been assessed by cyclic voltammetry and constant potential amperometry. The characterization of SPCEs/PB-BZT by X-ray photoemission, Raman and infrared spectroscopies confirmed the correct electrodeposition of the surfactant-modified PB film. These electrodes were incorporated in a Flow Injection device and the optimal working conditions determined as a function of experimental variables such as detection potential, electrolyte concentration or flow-rate. The sensor presented a linear response in the range 0–3 ppm free chlorine, with a sensitivity of 16.2 μA ppm−1 cm−2. The limit of detection (LOD) (S/N=3.3) and the limit of quantification (S/N=10) amounted to 8.25 and 24.6 ppb, respectively, adequate for controlling tap and drinking waters. To demonstrate the feasibility of using this free chlorine sensor for real applications possible interferences such as nitrate, nitrite and sulfate ions were successfully tested and discarded. Real free chlorine analysis was carried out in spiked tap water samples and commercial bleaches.
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.08.072
Materiales Coloidales
Ligand-Free Synthesis of Tunable Size Ln:BaGdF5 (Ln = Eu3+ and Nd3+) Nanoparticles: Luminescence, Magnetic Properties, and Biocompatibility
Becerro, AI; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Cantelar, E; Cusso, F; Stepien, G; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MLangmuir, 32 (2016) 411-420
Show abstract ▽
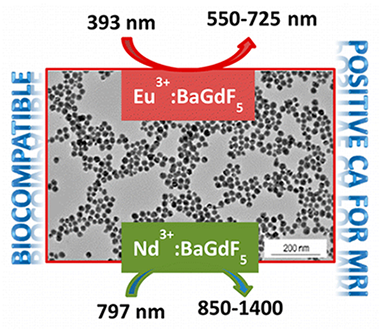
Bifunctional and highly uniform Ln:BaGdF5 (Ln = Eu3+ and Nd3+) nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized using a solvothermal method consisting of the aging at 120 degrees C of a glycerol solution containing the corresponding Lanthanide acetylacetonates and butylmethylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate. The absence of any surfactant in the synthesis process rendered hydrophilic nanospheres (with tunable diameter from 45 nm 85 nm, depending on the cations concentration of the starting solution) which are suitable for bioapplications. The particles are bifunctional because they showed both optical and magnetic properties due to the presence of the optically active lanthanides (Eu3+ in the visible and Nd3+ in the NIR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum) and the paramagnetic gadolinium ion, respectively. The luminescence decay curves of the nanospheres doped with different amounts of Eu3+ and Nd3+ have been recorded in order to determine the optimum dopant concentration in each case, which turned out to be 5% Eu3+ and 0.5% Nd3+. Likewise, proton relaxation times were measured at 1.5 T in water suspensions of the optimum particles found in the luminescence study. The values obtained suggested that both kinds of particles could be used as positive contrast agents for MRI. Finally, it was demonstrated that both the 5% Eu3+ and 0.5% Nd3+-doped BaGdF5 nanospheres showed negligible cytotoxicity for VERO cells for concentrations up to 0.25 mg mL(-1).
Enero, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03837
- ‹ anterior
- 233 of 420
- siguiente ›














