Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Cu–TiO2 systems for the photocatalytic H2 production: Influence of structural and surface support features
Obregon, S; Munoz-Batista, MJ; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Kubacka, A; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 179 (2015) 468-478
Show abstract ▽
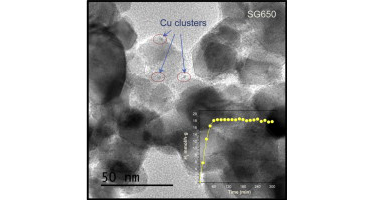
The influence of different TiO2 supports on the Cu active species has been studied. It was found that the photocatalytic H2 evolution is highly affected by the structural and electronic features of surface Cu species. Thus, metal dispersion and oxidation state appears strongly conditioned by the structural and surface properties of the TiO2 support. We have examined three TiO2 supports prepared by different synthetic methods; sol–gel, hydrothermal and microemulsion. In addition, we have induced structural and surface modifications by sulfate pretreatment over freshly prepared TiO2 precursors and subsequent calcination. Notably different copper dispersion and oxidation state is obtained by using these different TiO2 supports. From the wide structural and surface analysis of the catalysts we are able to propose that the occurrence of highly disperse Cu2+ species, the sample surface area as well as the crystallinity of the TiO2 support are directly related to the photocatalytic activity for H2 production reaction.
Diciembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.043
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Impact of hydrothermal treatment of FEBEX and MX80 bentonites in water, HNO3 and Lu(NO3)(3) media: Implications for radioactive waste control
Osuna, FJ; Chain, P; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 118 (2015) 48-55
Show abstract ▽
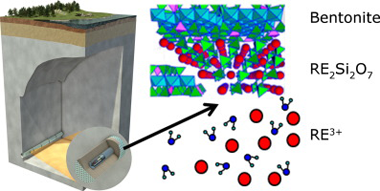
Engineered barriers of deep geological repositories (DGR) are commonly constructed with bentonite. FEBEX and MX80 bentonites have been selected by different countries as reference materials for the sealing of repositories; however, their chemical reactivity with high-level long-lived radioactive wastes (HLRW) under subcritical conditions had not been explored before. The hydrothermal stability in neutral and acid media and chemical reactivity in contact with an actinide analogous compound were both studied. The long-range and short-range structural changes were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance and scanning electron microscopy. Both bentonites have exhibited a good stability in neutral and acid media and have generated a new phase immobilizing the actinide analogous compound. The extent of the chemical reaction is higher in MX80 bentonite than in FEBEX bentonite.
Diciembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.08.036
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Efficient synthesis of ammonia from N-2 and H-2 alone in a ferroelectric packed-bed DBD reactor
Gomez-Ramirez, A; Cotrino, J; Lambert, RM; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Sources Science and Technology, 24 (2015) 065011
Show abstract ▽
A detailed study of ammonia synthesis from hydrogen and nitrogen in a planar dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactor was carried out. Electrical parameters were systematically varied, including applied voltage and frequency, electrode gap, and type of ferroelectric material (BaTiO3 versus PZT). For selected operating conditions, power consumption and plasma electron density were estimated from Lissajous diagrams and by application of the Bolsig + model, respectively. Optical emission spectroscopy was used to follow the evolution of plasma species (NH*, N*, N-2(+) and N-2*) as a function of applied voltage with both types of ferroelectric material. PZT gave both greater energy efficiency and higher ammonia yield than BaTiO3: 0.9 g NH3 kWh(-1) and 2.7% single pass N-2 conversion, respectively. This performance is substantially superior to previously published findings on DBD synthesis of NH3 from N-2 and H-2 alone. The influence of electrical working parameters, the beneficial effect of PZT and the importance of controlling reactant residence time are rationalized in a reaction model that takes account of the principal process variables
Diciembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1088/0963-0252/24/6/065011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructure and impedance spectroscopy of 3YTZP/SWNT ceramic nanocomposites
Poyato, R; Macias-Delgado, J; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 41 (2015) 12861-12868
Show abstract ▽
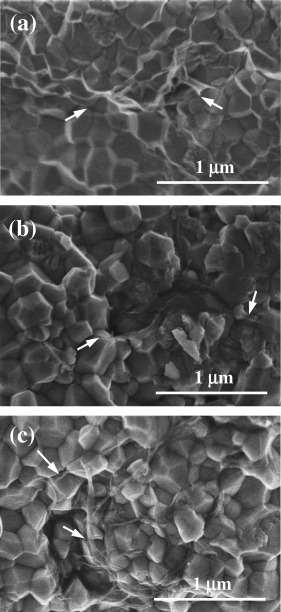
This work provides new insights on microstructure and electrical properties of 3 mol% Y2O3-ZrO2 (3YTZP) composites with 0.5, 1, and 1.5 vol% single walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs). The composites were spark plasma sintered (SPS) in identical conditions at 1250 degrees C from powder prepared by two different processing routines, with the aim of optimizing the SWNTs dispersion throughout the ceramic matrix. High densification and submicrometric grain size were achieved in all the composites. Electrical properties of the composites were characterized in a wide temperature range, and modeling of the impedance properties was approached by means of an equivalent circuit that allows separation of the individual SWNT bundles contribution to resistance from the resistance due to junctions between bundles. Effects of the homogeneous distribution of SWNTs at the ceramic grain boundaries on the crystalline phases, percolation threshold, total conductivity and evolution of junctions' resistivity with temperature were analyzed and discussed.
Diciembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.06.123
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Atomic scale characterization of SiO2/4H-SiC interfaces in MOSFETs devices
Beltran, AM; Duguay, S; Strenger, C; Bauer, AJ; Cristiano, F; Schamm-Chardon, SSolid State Communications, 221 (2015) 28-32
Show abstract ▽
The breakthrough of 4H-SiC MOSFETs is stemmed mainly due to the mobility degradation in their channel in spite of the good physical intrinsic material properties. Here, two different n-channel 4H-SiC MOSFETs are characterized in order to analyze the elemental composition at the SiC/SiO2 interface and its relationship to their electrical properties. Elemental distribution analyses performed by EELS reveal the existence of a transition layer between the SiC and the SiO2 regions of the same width for both MOSFETs despite a factor of nearly two between their electron mobility. Additional 3D compositional mapping by atom probe tomography corroborates these results, particularly the absence of an anomalous carbon distribution around the SiC/SiO2interface.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ssc.2015.08.017
- ‹ anterior
- 237 of 420
- siguiente ›














