Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Simultaneous Production of CH4 and H-2 from Photocatalytic Reforming of Glucose Aqueous Solution on Sulfated Pd-TiO2 Catalysts
Vaiano, V; Iervolino, G; Sarno, G; Sannino, D; Rizzo, L; Mesa, JJM; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JAOil & Gas Science and Technology-Revue D IFP Energies Nouvelles, 70 (2015) 891-902
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the simultaneous production of CH4 and H-2 from photocatalytic reforming of glucose aqueous solution on Pd-TiO2 catalysts under UV light irradiation by Light-Emitting Diodes (LED) was investigated. The Pd-TiO2 catalysts were prepared by the photodeposition method. The Pd content was in the range 0.5-2 wt% and a photodeposition time in the range 15-120 min was used. Pd-TiO2 powders were extensively characterized by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), SBET, X-Ray Fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), UV-Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectra (UV-Vis DRS), TEM and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). It was found that the lower Pd loading (0.5 wt%) and 120 min of photodeposition time allowed us to obtain homogeneously distributed metal nanoparticles of small size; it was also observed that the increase in the metal loading and deposition time led to increasing the Pd-0 species effectively deposited on the sulfated TiO2 surface. Particle size and the oxidation state of the palladium were the main factors influencing the photocatalytic activity and selectivity. The presence of palladium on the sulfated titania surface enhanced the H-2 and CH4 production. In fact, on the catalyst with 0.5 wt% Pd loading and 120 min of photodeposition time, H-2 production of about 26 lmol was obtained after 3 h of irradiation time, higher than that obtained with titania without Pd (about 8.5 lmol). The same result was obtained for the methane production. The initial pH of the solution strongly affected the selectivity of the system. In more acidic conditions, the production of H-2 was enhanced, while the CH4 formation was higher under alkaline conditions.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.2516/ogst/2014062
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Atomic scale characterization of SiO2/4H-SiC interfaces in MOSFETs devices
Beltran, AM; Duguay, S; Strenger, C; Bauer, AJ; Cristiano, F; Schamm-Chardon, SSolid State Communications, 221 (2015) 28-32
Show abstract ▽
The breakthrough of 4H-SiC MOSFETs is stemmed mainly due to the mobility degradation in their channel in spite of the good physical intrinsic material properties. Here, two different n-channel 4H-SiC MOSFETs are characterized in order to analyze the elemental composition at the SiC/SiO2 interface and its relationship to their electrical properties. Elemental distribution analyses performed by EELS reveal the existence of a transition layer between the SiC and the SiO2 regions of the same width for both MOSFETs despite a factor of nearly two between their electron mobility. Additional 3D compositional mapping by atom probe tomography corroborates these results, particularly the absence of an anomalous carbon distribution around the SiC/SiO2interface.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ssc.2015.08.017
Green pigments of Roman mural paintings from Seville Alcazar
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; de Haro, MDJ; Siguenza, B; Martinez-Blanes, JMApplied Clay Science, 116 (2015) 211-219
Show abstract ▽
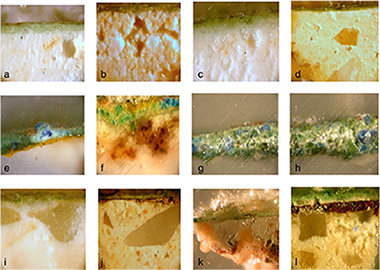
We report here a study of 30 fragments of green wall paintings from Roman times found in the Patio de Banderas excavation in Seville Alcazar. The sample characterisation was realised using optical microscopy, colourimetry, infrared and micro-Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The study of these pigments is important because it can help determine the source or the pictorial technique used. The samples studied in this work have been divided into two groups, according to the composition of their green pigments. In the first group, celadonite has been characterised as the primary component of the green colour; chlorite was also detected. Particles constituted by chromium accompanied by aluminium, iron and zinc were found in all studied samples of this group. Chlorite and chromium oxide could also be responsible for the green colour. The presence of chromium suggested the presence of green colour pigment from Verona. In the second group, a mixture of celadonite and glauconite was detected and could be responsible for the green colour observed. The addition of refracting material such as Egyptian blue was also used. A mixture of Egyptian green and Egyptian blue together with celadonite and glauconite was also found. Four classes of intonaco were recognised and classified based upon the composition of the aggregates.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.03.016
Reactividad de Sólidos
A new model of the carbonator reactor in the calcium looping technology for post-combustion CO2 capture
Ortiz, C; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Becerra, JA; Perez-Maqueda, LAFuel, 160 (2015) 328-338
Show abstract ▽
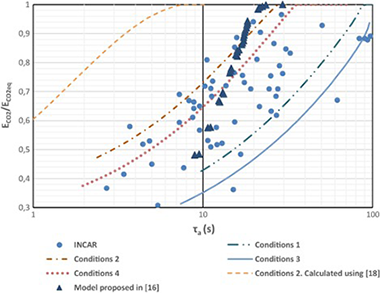
The Ca-Looping (CaL) process is considered as a promising technology for CO2 post-combustion capture in power generation plants yielding a minor penalty on plant performance as compared with other capture technologies such as conventional amine-based capture systems. This manuscript presents a new carbonator reactor model based on lab-scale multicyclic CaO conversion results, which take into account realistic CaO regeneration conditions that necessarily involve calcination under high CO2 partial pressure and high temperature. Under these conditions, CaO conversion in the diffusion controlled stage is a relevant contribution to the carbonation degree during typical residence times. The main novelty of the model proposed in the present work is the consideration of the capture efficiency in the diffusion controlled phase of carbonation. It is demonstrated that increasing the residence time by a few minutes in the carbonator yields a significant improvement of the capture efficiency. Model predictions are shown to agree with experimental results retrieved from pilot-scale tests. The new model allows a more accurate evaluation and prediction of carbonator’s performance over a wider range of residence times. The results obtained may be relevant for the optimization of CaL operation parameters to be used in real power plants.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.07.095
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Enhancement of stability and photoactivity of TiO2 coatings on annular glass reactors to remove emerging pollutants from waters
Espino-Estevez, MR; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C; Gonzalez-Diaz, OM; Navio, JA; Fernandez-Hevia, D; Dona-Rodriguez, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 279 (2015) 488-497
Show abstract ▽
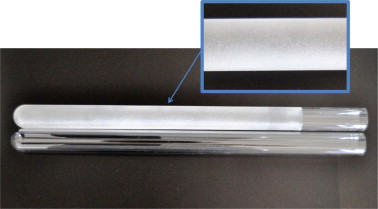
TiO2 coatings of highly photoactive lab-made titania were prepared on the outer wall of the inner tube of a glass tubular reactor by dip-coating method. The effect of decreasing the size of the aggregates to improve adhesion and photoactivity of the coatings to degrade phenol, diclofenac and isoproturon was also investigated. Chemical disaggregation of the TiO2 particles resulted in a lower aggregate size, between 0.1 and 1 μm, than mechanical disaggregation, between 1 and 10 μm. The results of the adhesion tape test showed that either milling of aggregate material with a planetary mill or chemical stabilization of the particles were necessary to obtain TiO2 coatings on glass tube with acceptable quality to be used in water treatment applications. SEM images showed that coatings prepared after milling the TiO2 suspension were more homogeneous without surface aggregates. The degree of adhesion of the coatings after increasing the roughness of the support by abrasive blasting was also evaluated. Adhesion to the substrate was slightly lower when using the modified support. The photoactivity results showed that the coatings prepared after wet milling of catalyst during 30 min and after chemical disaggregation were more efficient in terms of degradation and mineralization when using phenol as model molecule. Subsequent studies with two emerging pollutants, diclofenac and isoproturon, also showed enhanced efficiency of these coatings. The reusability of the TiO2 coatings was also evaluated and a promising photocatalytic performance was observed with a very low variation of the decay rate after five consecutive usages.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.038
- ‹ anterior
- 238 of 420
- siguiente ›














