Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Single-step fabrication process of 1-D photonic crystals coupled to nanocolumnar TiO2 layers to improve DSC efficiency
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Colodrero, S; Miguez, H; Gonzalez-Elipe, AROptics Express, 23 (2015) A1642-A1650
Show abstract ▽
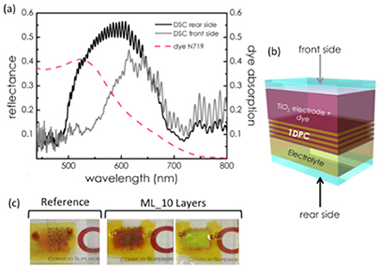
The present work proposes the use of a TiO2 electrode coupled to a one-dimensional photonic crystal (1DPC), all formed by the sequential deposition of nanocolumnar thin films by physical vapor oblique angle deposition (PV-OAD), to enhance the optical and electrical performance of DSCs while transparency is preserved. We demonstrate that this approach allows building an architecture combining a non-dispersive 3 µm of TiO2 electrode and 1 µm TiO2-SiO2 1DPC, both columnar, in a single-step process. The incorporation of the photonic structure is responsible for a rise of 30% in photovoltaic efficiency, as compared with a transparent cell with a single TiO2 electrode. Detailed analysis of the spectral dependence of the photocurrent demonstrates that the 1DPC improves light harvesting efficiency by both back reflection and optical cavity modes confinement within the TiO2 films, thus increasing the overall performance of the cell.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1364/OE.23.0A1642
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Adaptable Ultraviolet Reflecting Polymeric Multilayer Coatings of High Refractive Index Contrast
Smirnov, JRC; Ito, M; Calvo, ME; Lopez-Lopez, C; Jimenez-Solano, A; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Zavala-Rivera, P; Tanaka, K; Sivaniah, E; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 3 (2015) 1633-1639
Show abstract ▽
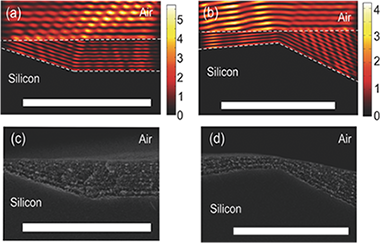
A synthetic route is demonstrated to build purely polymeric nanostructured multilayer coatings, adaptable to arbitrary surfaces, and capable of efficiently blocking by reflection a targeted and tunable ultraviolet (UV) range. Reflection properties are determined by optical interference between UV light beams reflected at the interfaces between polystyrene layers of different porosity and hence refractive index. As no dopant absorber intervenes in the shielding effect, polymer degradation effects are prevented. Alternated porosity results from the modulation of photochemical effects at the few tens of nanometers length scale, combined with the collective osmotic shock induced during the processing of the precursor diblock copolymer film. Experimental evidence of the application of this method to coat rough surfaces with smooth and conformal UV protecting films is provided.
Noviembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201500209
Materiales Avanzados
An improved method for determining the external specific surface area and the plasticity index of clayey samples based on a simplified method for non-swelling fine-grained soils
Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 115 (2015) 97-107
Show abstract ▽
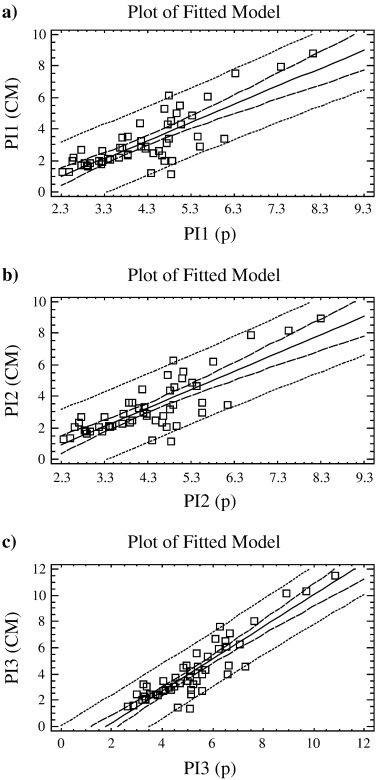
Previous studies have used the clay content of soils for estimating the specific surface areas and different correlations have been found, including plasticity-value correlations. Based on several assumptions, Dolinar (2012) proposed a simplified method for determining the external specific surface area of non-swelling fine-grained soils. An equation relates the external specific surface area (BET-nitrogen) with percentage of clay fraction (< 2 μm), determined by hydrometer method, and plasticity index (Atterberg).
In this work, based on that simplified method, the authors have developed an improved method for determining the external specific surface area of fine-grained clay samples. Instead of percentage of clay fraction, it was proposed to use the clay mineral content estimated by XRD methods. From an analysis of previous Dolinars results, the calculated and measured values of external specific surface area were studied for a group of non-swelling and fine-grained soil samples (Dolinar's samples), five non-swelling clayey samples and data samples from the literature. Additionally, an estimation of the plasticity index (Atterberg) has been also considered in this improved method. Both these methods, simplified and improved, were tested and compared using all these samples. It demonstrated the practical application of both these methods for an estimation of external specific surface area and plasticity index. However, in the present research two models were considered to determine the specific surface areas (BET and Langmuir) and the influence of several sources of errors in these predictions was discussed. The predictions were found more accurate when specific surface area from Langmuir's model is considered. It is concluded that the present research will be useful for the prediction of external specific surface area and plasticity index of non-swelling clayey materials and to dispose of theoretical practical relationships between clay mineralogy and geotechnical properties of valuable interest.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.07.015
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Full solution processed mesostructured optical resonators integrating colloidal semiconductor quantum dots
Calvo, ME; Hidalgo, N; Schierholz, R; Kovacs, A; Fernandez, A; Bellino, MG; Soler-Illia, GJAA; Miguez, HNanoscale, 7 (2015) 16583-16589
Show abstract ▽
Herein we show a solution based synthetic pathway to obtain a resonant optical cavity with embedded colloidal semiconductor quantum dots (CSQDs). The optical cavity pore network, surrounded by two dense Bragg mirrors, was designed ad hoc to selectively host the quantum dots, while uncontrolled infiltration of those in the rest of the layered structure was prevented. Coupling between the optical resonant modes of the host and the natural emission of the embedded nanoparticles gives rise to the fine tuning of the luminescence spectrum extracted from the ensemble. Our approach overcomes, without the need for an encapsulating agent and exclusively by solution processing, the difficulties that arise from the low thermal and chemical stability of the CSQDs. It opens the route to achieving precise control over their location and hence over the spectral properties of light emitted by these widely employed nanomaterials. Furthermore, as the porosity of the cavity is preserved after infiltration, the system remains responsive to environmental changes, which provides an added value to the proposed structure.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1039/C5NR03977K
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synergy between gold and oxygen vacancies in gold supported on Zr-doped ceria catalysts for the CO oxidation
Laguna, OH; Perez, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 176 (2015) 385-395
Show abstract ▽
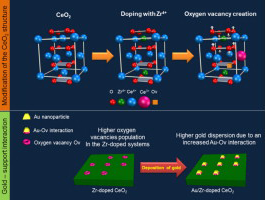
The CO oxidation activity of 1 wt.% gold catalysts prepared by deposition-precipitation on a series of ceria doped with Zr supports was studied. The supports (10, 25 and 50 Zr at.%) were synthesized by a pseudo sol-gel method through the thermal decomposition of the corresponding metallic propionates. All the prepared solids were characterized by means of XRF, BET, XRD, Raman spectroscopy, SEM, and H-2-TPR. Solid solution was obtained in all mixed systems, while the segregation of different Ce-Zr oxides was observed for the solid with the 50 Zr at.%. The oxygen vacancies population and the amount of easier reducible Ce4+ species in the solids increase with the Zr content. No major textural or structural modifications were detected after gold deposition, although a strong Au-support interaction was generated. Such interaction is strongly influenced by the nucleation of gold deposits on the oxygen vacancies and consequently the amount of Zr inserted in the ceria network also determines the dispersion of gold. The presence of gold eases the surface reduction at lower temperatures, and as higher the amount of Zr in the gold catalysts, higher the CO conversion at low temperatures, probably due to the enhancement of the electronic transfer at the surface of the catalysts.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.019
- ‹ anterior
- 239 of 420
- siguiente ›














