Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Full solution processed mesostructured optical resonators integrating colloidal semiconductor quantum dots
Calvo, ME; Hidalgo, N; Schierholz, R; Kovacs, A; Fernandez, A; Bellino, MG; Soler-Illia, GJAA; Miguez, HNanoscale, 7 (2015) 16583-16589
Show abstract ▽
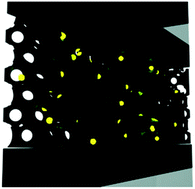
Herein we show a solution based synthetic pathway to obtain a resonant optical cavity with embedded colloidal semiconductor quantum dots (CSQDs). The optical cavity pore network, surrounded by two dense Bragg mirrors, was designed ad hoc to selectively host the quantum dots, while uncontrolled infiltration of those in the rest of the layered structure was prevented. Coupling between the optical resonant modes of the host and the natural emission of the embedded nanoparticles gives rise to the fine tuning of the luminescence spectrum extracted from the ensemble. Our approach overcomes, without the need for an encapsulating agent and exclusively by solution processing, the difficulties that arise from the low thermal and chemical stability of the CSQDs. It opens the route to achieving precise control over their location and hence over the spectral properties of light emitted by these widely employed nanomaterials. Furthermore, as the porosity of the cavity is preserved after infiltration, the system remains responsive to environmental changes, which provides an added value to the proposed structure.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1039/C5NR03977K
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synergy between gold and oxygen vacancies in gold supported on Zr-doped ceria catalysts for the CO oxidation
Laguna, OH; Perez, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 176 (2015) 385-395
Show abstract ▽
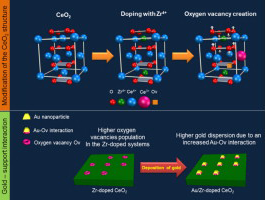
The CO oxidation activity of 1 wt.% gold catalysts prepared by deposition-precipitation on a series of ceria doped with Zr supports was studied. The supports (10, 25 and 50 Zr at.%) were synthesized by a pseudo sol-gel method through the thermal decomposition of the corresponding metallic propionates. All the prepared solids were characterized by means of XRF, BET, XRD, Raman spectroscopy, SEM, and H-2-TPR. Solid solution was obtained in all mixed systems, while the segregation of different Ce-Zr oxides was observed for the solid with the 50 Zr at.%. The oxygen vacancies population and the amount of easier reducible Ce4+ species in the solids increase with the Zr content. No major textural or structural modifications were detected after gold deposition, although a strong Au-support interaction was generated. Such interaction is strongly influenced by the nucleation of gold deposits on the oxygen vacancies and consequently the amount of Zr inserted in the ceria network also determines the dispersion of gold. The presence of gold eases the surface reduction at lower temperatures, and as higher the amount of Zr in the gold catalysts, higher the CO conversion at low temperatures, probably due to the enhancement of the electronic transfer at the surface of the catalysts.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.019
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Role of Y in the oxidation resistance of CrAlYN coatings
Dominguez-Meister, S; El Mrabet, S; Escobar-Galindo, R; Mariscal, A; de Haro, CJ; Justo, A; Brizuela, M; Rojas, TC; Sanchez-Lopez, JCApplied Surface Science, 363 (2015) 504-511
Show abstract ▽
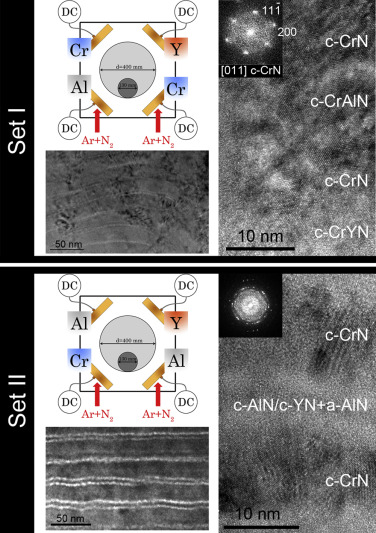
CrAlYN coatings with different aluminum (4–12 at.%) and yttrium (2–5 at.%) contents are deposited by d.c. reactive magnetron sputtering on silicon and M2 steel substrates using metallic targets and Ar/N2 mixtures. The influence of the nanostructure and chemical elemental distribution on the oxidation resistance after heating in air at 1000 °C is studied by means of cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (X-SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GD-OES). The sequential exposure to the metallic targets during the synthesis leads to a multilayer structure where concentration of metallic elements (Cr, Al and Y) is changing periodically. A good oxidation resistance is observed when Al- and Y-rich regions are separated by well-defined CrN layers, maintaining crystalline coherence along the columnar structure. This protective behavior is independent of the type of substrate and corresponds to the formation of a thin mixed (Al, Cr)-oxide scale that protects the film underneath. The GD-OES and XRD analysis have demonstrated that Y acts as a reactive element, blocking the Fe and C atoms diffusion from the steel and favoring higher Al/Cr ratio in the passivation layer after heating. The coating with Y content around 4 at.% exhibited the best performance with a thinner oxide scale, a delay in the CrN decomposition and transformation to Cr2N, and a more effective Fe and C blocking.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.099
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Synergistic strategies for the preparation of highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells on plastic substrates: combination of chemical and physical sintering
Li, Y; Yoo, K; Lee, DK; Kim, JY; Son, HJ; Kim, JH; Lee, CH; Miguez, H; Ko, MJRSC Advances, 5 (2015) 76795-76803
Show abstract ▽
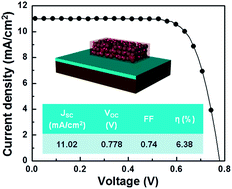
Preparation of well-interconnected TiO2 electrodes at low temperature is critical for the fabrication of highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) on plastic substrates. Herein we explore a synergistic approach using a combination of chemical and physical sintering. We formulate a binder-free TiO2 paste based on “nanoglue” as the chemical sintering agent, and use it to construct a photoelectrode on plastic by low-temperature physical compression to further improve the connectivity of TiO2 films. We systematically investigated the factors affecting the photovoltaic performance and found the conditions to achieve electron diffusion lengths as long as 25 μm and charge collection efficiencies as high as 95%, as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements indicate. We apply this approach to obtain a DSC deposited on plastic displaying 6.4% power conversion efficiency based on commercial P25 titania particles.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1039/C5RA10290A
Reactividad de Sólidos
Structural, Optical, and Electrical Characterization of Yttrium-Substituted BiFeO3 Ceramics Prepared by Mechanical Activation
Perejon, A; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAInorganic Chemistry, 54 (2015) 9876-9884
Show abstract ▽
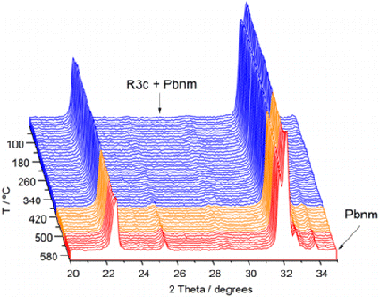
Ceramics of Bi1-xYxFeO3 solid solutions (x = 0.02, 0.07, and 0.10) have been prepared by mechanical activation followed by sintering. The effect of yttrium content on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of the materials has been studied. Thus, single-phase solid solutions with rhombohedral R3c structure have been achieved for x = 0.02 and 0.07, while for x = 0.10 the main R3c phase has been detected together with a small amount of the orthorhombic Pbnm phase. Multiferroic properties of the samples, studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), showed that both T-N and T-C (temperatures of the antiferromagnetic paramagnetic and ferroelectric-paraelectric transitions, respectively) decrease with increasing yttrium content. The nature of the ferroelectric paraelectric transition has been studied by temperature-dependent X-ray diffraction (XRD), which revealed rhombohedral R3c to orthorhombic Pbnm phase transitions for x = 0.07 and 0.10. On the other hand, for x = 0.02 the high-temperature phase was indexed as Pnma. Optical properties of the samples, as studied by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, showed low optical band gap that decreases with increasing yttrium content. Prepared ceramics were highly insulating at room temperature and electrically homogeneous, as assayed by impedance spectroscopy, and the conductivity increased with x.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b01654
- ‹ anterior
- 240 of 420
- siguiente ›














