Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Oxodiperoxomolybdenum complex immobilized onto ionic liquid modified SBA-15 as an effective catalysis for sulfide oxidation to sulfoxides using hydrogen peroxide
Carrasco, Carlos J.; Montilla, Francisco; Bobadilla, Luis; Ivanova, Svetlana; Antonio Odriozola, Jose; Galindo, AgustinCatalysis Today, 255 (2015) 102-108
Show abstract ▽
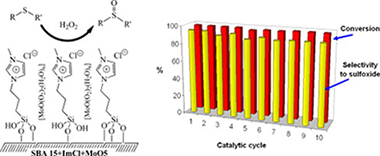
A supported ionic-liquid-phase (SILP) was prepared by the reaction of 1-methyl-3-(3-(triethoxysilyl) propyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride with a mesoporous SBA-15 silica and then an oxodiperoxomolybdenum complex was immobilized onto the obtained SILP. The resulting material, identified as SBA-15 + ImCl+ MoO5, was characterized by solid state NMR (H-1, C-13 and Si-29), and their textural and thermogravimetric properties were determined. The SBA-15 + ImCl+ MoO5 material was investigated as catalyst for the oxidation of methylphenylsulfide, as model reaction, with aqueous hydrogen peroxide as oxidant at room temperature. The presence of the molybdenum species was crucial for achieving good conversions and methanol was selected as the best solvent (conversion of 95% and selectivity toward sulfoxide 98%). The optimized reaction conditions were applied for the oxidation of several selected sulfides. In general, good catalytic activity and selectivity to sulfoxide were obtained and, remarkably, the selectivity toward sulfoxide is higher than those observed in the study of the same process carried out in [C(4)min][PF6] (C(4)mim = 1-buty1-3-methylimidazolium) and catalyzed by a molecular molybdenum complex, under the same reaction conditions. The importance of the IL-functionalization in the SBA-15 material was evidenced by recycling experiments. The SBA-15 + ImCl+ MoO5 catalyst was used for the sulfoxidation of the methylphenylsulfide substrate for ten reaction cycles without a significant change in conversion, selectivity to sulfoxide and molybdenum content.
Octubre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.10.053
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Facile Synthesis of Decahedral Particles of Anatase TiO2 with Exposed {001} Facets
Perales-Martinez, IA; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V; Obregon-Alfaro, S; Lee, SWJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 15 (2015) 7351-7356
Show abstract ▽
This paper reports a facile synthesis of decahedral particles of anatase TiO2 dominated by {101} and {001} faces. The decahedral particles has been enhanced by means a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method using TiF4 as a titanium precursor and HF as capping agent to promote oriented growth and formation of {001} faces in only 4 h. The prepared samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, high resolution of transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The morphology of anatase TiO2 particles is consisted of near-perfect-truncated-bipyramid-shape. Reaction time is a key factor to obtain truncated-bipyramid-shaped particles with sharp and well-defined edges. Reaction times longer than 4 h induce irregular particles. Decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are truncated bypiramid crystals which have eight {101} and two {001} facets at top/bottom surfaces. The average size of decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are similar to 250 nm for the samples obtained without applying the microwave irradiation and similar to 350 nm for reaction 4 h.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10578
Materiales Coloidales
Uniform Poly(acrylic acid)-Functionalized Lanthanide-Doped LaVO4 Nanophosphors with High Colloidal Stability and Biocompatibility
Nunez, NO; Zambrano, P; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 27 (2015) 4546-4554
Show abstract ▽
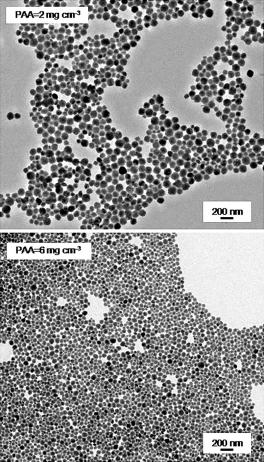
Ln-doped (Ln = Eu or Nd) LaVO4 nanoparticles functionalized with poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) were prepared from lanthanide and vanadate precursors in the presence of PAA by a simple one-pot method that consists of a homogeneous precipitation reaction in ethylene glycol/water at a moderate temperature (120 degrees C). The size of the nanoparticles could be modified in the 40-70 nm range by adjusting the amount of PAA added. The effects of the Eu and Nd contents of these nanomaterials on theirs optical properties (emission intensity and lifetime) were also analyzed to find the optimum nanophosphors. Finally, the nanoparticles showed negligible cytotoxicity for Vero cells at concentrations up to 0.05 mgmL(-1) and a high colloidal stability in physiological buffer solutions; therefore, they satisfy the most important requirements for in vitro biotechnological applications.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201500265
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Microstructure of mixed oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Gil-Rostra, J; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, FThin Solid Films, 591 (2015) 330-335
Show abstract ▽
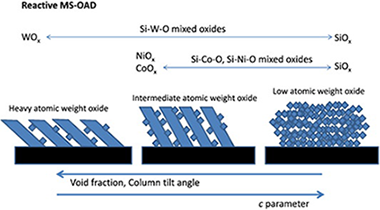
Several mixed oxide thin film series of samples (Si–Co–O, Si–Ni–O, Si–W–O) have been prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at oblique angle geometries. The paper focuses on the description of microstructure of the films as a function of their stoichiometry. It is found that for identical process parameters (gas mixture, pressure, magnetron-substrate distance, incidence angle of the vapour flux, etc.) the tilt angle of the developed columnar microstructure and the film porosity is strongly dependent on the stoichiometry of the films. The results are discussed in the framework of several theoretical models on this topic.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.01.058
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Microreactors technology for hydrogen purification: Effect of the catalytic layer thickness on CuOx/CeO2-coated microchannel reactors for the PROX reaction
Laguna, O. H.; Castano, M. Gonzalez; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Chemical Engineering Journal, 271 (2015) 45-52
Show abstract ▽
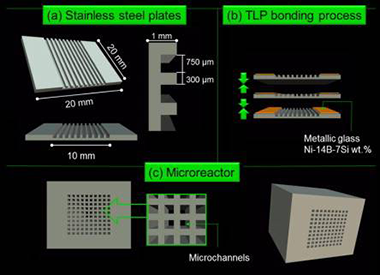
Two blocks of microreactors composed by 100 microchannels and coated, respectively, with 150 and 300 mg of a CuOx/CeO2 catalyst, were prepared and tested in the preferential oxidation of CO in presence of H2 (PROX). The deposition of different amount of catalyst resulted in different catalytic layer thicknesses thus modifying the catalytic performances of the microreactor. The evaluation of the main reaction variables (the space velocity, the O2-to-CO ratio and the presence of H2O and/or CO2 in the stream) was performed over both microreactors and compared to that of the parent powder catalyst. The least loaded microreactor, with a coating thickness around 10 μm, presented the highest CO conversion and selectivity levels at temperatures below 160 °C. This result evidences (i) the improvement of the catalytic performances got by the structuration of the powder catalyst and (ii) the importance of the selection of the adequate thickness of the catalytic layer on the microreactor, which have not to exceed and optimal value. An adequate coating thickness allows minimizing the mass and heat transport limitations, thus resulting in the enhancement of the catalytic performance during the PROX reaction.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.023
- ‹ anterior
- 241 of 420
- siguiente ›














