Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Materiales Avanzados
Phyllite clay-cement composites having improved engineering properties and material applications
Garzon, E; Cano, M; O'Kelly, BC; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 114 (2015) 229-233
Show abstract ▽
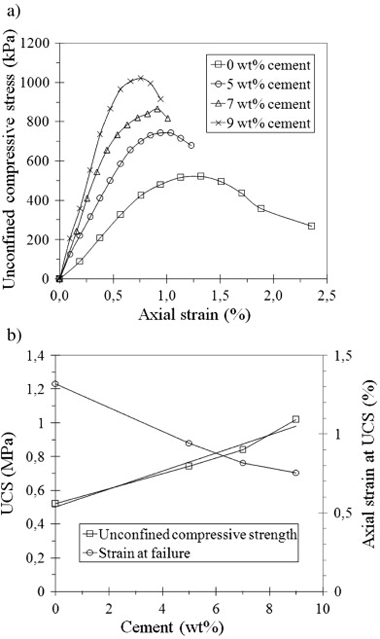
Phyllite clays contain clay minerals (chlorite, illite and mixed-layer illite smectite), quartz and feldspars. In this experimental laboratory study, new composites of phyllite clay and cement (5, 7 and 9 wt.%) were prepared and tested to determine their Atterberg limits, dry density and optimum water content for modified Proctor (MP) compaction, California Bearing ratio, swelling potential after soakage in water, unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and water-permeability coefficient. From the mixes investigated, the composite with 5 wt.% cement was deemed most suitable for certain construction material applications, having a plasticity index of 10.5%, maximum dry density of 2.17 Mg/m3 and optimum water content of 8% for MP compaction (undergoing no swelling under soakage), a UCS of 0.74 MPa, and a very low permeability coefficient value of 7.4 × 10− 11 m/s. Potential material applications for these new composites include for building construction, roofs, and flexible pavements.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.06.006
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Microstructure of mixed oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Gil-Rostra, J; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, FThin Solid Films, 591 (2015) 330-335
Show abstract ▽
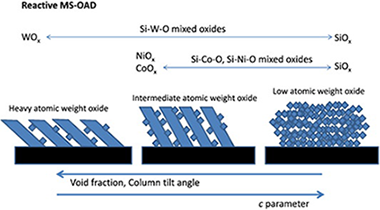
Several mixed oxide thin film series of samples (Si–Co–O, Si–Ni–O, Si–W–O) have been prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at oblique angle geometries. The paper focuses on the description of microstructure of the films as a function of their stoichiometry. It is found that for identical process parameters (gas mixture, pressure, magnetron-substrate distance, incidence angle of the vapour flux, etc.) the tilt angle of the developed columnar microstructure and the film porosity is strongly dependent on the stoichiometry of the films. The results are discussed in the framework of several theoretical models on this topic.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.01.058
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Facile Synthesis of Decahedral Particles of Anatase TiO2 with Exposed {001} Facets
Perales-Martinez, IA; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V; Obregon-Alfaro, S; Lee, SWJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 15 (2015) 7351-7356
Show abstract ▽
This paper reports a facile synthesis of decahedral particles of anatase TiO2 dominated by {101} and {001} faces. The decahedral particles has been enhanced by means a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method using TiF4 as a titanium precursor and HF as capping agent to promote oriented growth and formation of {001} faces in only 4 h. The prepared samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, high resolution of transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The morphology of anatase TiO2 particles is consisted of near-perfect-truncated-bipyramid-shape. Reaction time is a key factor to obtain truncated-bipyramid-shaped particles with sharp and well-defined edges. Reaction times longer than 4 h induce irregular particles. Decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are truncated bypiramid crystals which have eight {101} and two {001} facets at top/bottom surfaces. The average size of decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are similar to 250 nm for the samples obtained without applying the microwave irradiation and similar to 350 nm for reaction 4 h.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10578
Materiales Coloidales
Uniform Poly(acrylic acid)-Functionalized Lanthanide-Doped LaVO4 Nanophosphors with High Colloidal Stability and Biocompatibility
Nunez, NO; Zambrano, P; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 27 (2015) 4546-4554
Show abstract ▽
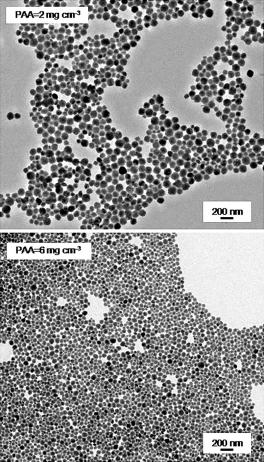
Ln-doped (Ln = Eu or Nd) LaVO4 nanoparticles functionalized with poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) were prepared from lanthanide and vanadate precursors in the presence of PAA by a simple one-pot method that consists of a homogeneous precipitation reaction in ethylene glycol/water at a moderate temperature (120 degrees C). The size of the nanoparticles could be modified in the 40-70 nm range by adjusting the amount of PAA added. The effects of the Eu and Nd contents of these nanomaterials on theirs optical properties (emission intensity and lifetime) were also analyzed to find the optimum nanophosphors. Finally, the nanoparticles showed negligible cytotoxicity for Vero cells at concentrations up to 0.05 mgmL(-1) and a high colloidal stability in physiological buffer solutions; therefore, they satisfy the most important requirements for in vitro biotechnological applications.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201500265
Reactividad de Sólidos
Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2 Thin Films Modified with Ag and Pt Nanoparticles Deposited by Gas Flow Sputtering
Maicu, M; Gloss, D; Frach, P; Hecker, D; Gerlach, G; Cordoba, JMJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 15 (2015) 6478-6486
Show abstract ▽
In this work, a gas flow sputtering (GFS) process which allows the production and deposition of metal nanoparticles (NPs) in a vacuum environment is described. Aim of the study is to prove the potential of this technology for the fabrication of new TiO2 films with enhanced photocatalytic properties. For this purpose, Ag and Pt NPs have been produced and deposited on photocatalytic float glass coated with TiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering. The influence of the process parameters and of the metal amount on the final properties of the particles (quantity, size, size distribution, oxidation state etc.,) was widely investigated. Moreover, the effect of the NPs on the photocatalytic activity of the resulting materials was evaluated for the case of the decomposition of stearic acid (SA) during UV-A irradiation. The reduction of the water contact angle (WCA) during the irradiation period was measured in order to test the photo-induced super-hydrophilicity (PSH).
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10873
- ‹ anterior
- 242 of 420
- siguiente ›














