Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Boosting the activity of a Au/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst for the WGS reaction
Reina, T. R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Catalysis Today, 253 (2015) 149-154
Show abstract ▽
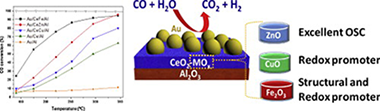
Herein a strategy to design highly efficient Au/CeO2/Al2O3 based WGS catalysts is proposed. The inclusion of transition metals, namely Fe, Cu and Zn as CeO2 dopant is considered. All the promoters successfully increased the WGS performance of the undoped sample. The activity improvement can be correlated to structural and/or redox features induced by the dopants. The comparative characterization of the doped samples by means of XRD, Raman spectroscopy and OSC evaluation permits an accurate understanding of the boosted WGS activity arising from the Ce-promoter interaction. This study establishes distinction among both, structural and redox sources of promotion and provides a useful strategy to develop highly active Au/CeO2 based catalysts for the WGS reaction.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.041
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Boosting the visible-light photoactivity of Bi2WO6 using acidic carbon additives
Carmona, RJ; Velasco, LF; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Ania, COApplied Catalysis A-General, 505 (2015) 467-477
Show abstract ▽
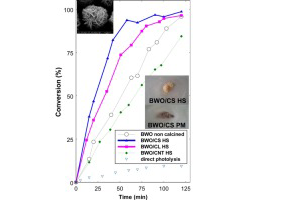
We have explored the role of the physicohemical properties of carbon materials as additives to bismuth tungstate on its structure, optical properties, and photocatalytic activity for the degradation of rhodamine B under visible light. For this purpose, C/Bi2WO6 hybrid composites were prepared following two different routes: (i) physical mixture of the catalyst components, and (ii) one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of the semiconductor in the presence of the carbon additive. Three carbons with different properties were selected as additives: biomass-derived activated carbon, carbon nanotubes and carbon spheres obtained from polysaccharides. Data has shown the outstanding role of the acidic/basic nature of the carbon additive, and of the synthetic method on the photocatalytic performance of the resulting composites. For a given additive, the degradation rate of RhB is greatly improved for the catalysts prepared through a one-step hydrothermal synthesis, where there is low shielding effect of the carbon matrix. Carbon additives of acidic nature boost the surface acidity of the hybrid photocatalyst, thereby enhancing the photodegradation of RhB under visible light via a coupled mechanism (photosensitization, semiconductor photocatalysis and carbon-photon mediated reactions).
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.05.011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Specific features of the electrical properties in partially graphitized porous biocarbons of beech wood
Popov, VV; Orlova, TS; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the solid state, 57 (2015) 1746-1751
Show abstract ▽
The electrical and galvanomagnetic properties of partially graphitized highly porous bioC(Ni) biocarbon matrices produced by pyrolysis (carbonization) of beech wood at temperatures T (carb) = 850-1600A degrees C in the presence of a Ni-containing catalyst have been studied in comparison with their microstructural features. The temperature dependences of the resistivity, the magnetoresistance, and the Hall coefficient have been measured in the temperature range of 4.2-300 K in magnetic fields to 28 kOe. It has been shown that an additional graphite phase introduction into samples with T (carb) a parts per thousand yen 1000A degrees C results in an increase in the carrier mobility by a factor of 2-3, whereas the carrier (hole) concentration remains within similar to 10(20) cm(-3), as in biocarbons obtained without catalyst. An analysis of experimental data has demonstrated that the features of the conductivity and magnetoresistance of these samples are described by quantum corrections related to their structural features, i.e., the formation of a globular graphite phase of nano- and submicrometer sizes in the amorphous matrix. The quantum corrections to the conductivity decrease with increasing carbonization temperature, which indicates an increase in the degree of structure ordering and is in good agreement with microstructural data.
Septiembre, 2015 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783415090280
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Absorption Enhancement in Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskite Films with Embedded Plasmonic Gold Nanoparticles
Carretero-Palacios, S; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 18635-18640
Show abstract ▽
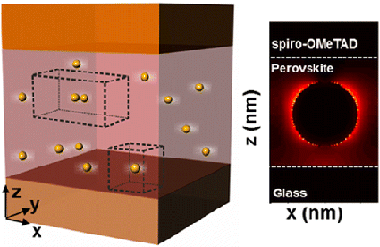
We report on the numerical analysis of solar absorption enhancement in organic-inorganic halide perovskite films embedding plasmonic gold nanoparticles. The effect of particle size and concentration is analyzed in realistic systems in which random particle location within the perovskite film and the eventual formation of dimers are also taken into account. We find a maximum integrated solar absorption enhancement of similar to 10% in perovskite films of 200 nm thickness and similar to 6% in 300 nm films, with spheres of radii 60 and 90 nm, respectively, in volume concentrations of around 10% in both cases. We show that the presence of dimers boosts the absorption enhancement up to,similar to 12% in the thinnest films considered. Absorption reinforcement arises from a double contribution of plasmonic near-field and scattering effects, whose respective weight can be discriminated and evaluated from the simulations.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06473
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Rapid Legionella pneumophila determination based on a disposable core–shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles immunoplatform
Martin, M; Salazar, P; Jimenez, C; Lecuona, M; Ramos, MJ; Ode, J; Alcoba, J; Roche, R; Villalonga, R; Campuzano, S; Pingarron, JM; Gonzalez-Mora, JLAnalytica Chimica Acta, 887 (2015) 51-58
Show abstract ▽
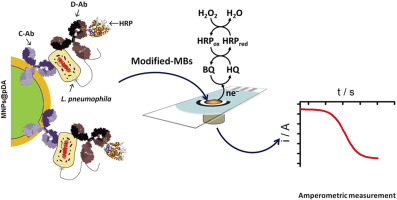
A novel amperometric magnetoimmunoassay, based on the use of core–shell magnetic nanoparticles and screen-printed carbon electrodes, was developed for the selective determination of Legionella pneumophila SG1. A specific capture antibody (Ab) was linked to the poly(dopamine)–modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs@pDA-Ab) and incubated with bacteria. The captured bacteria were sandwiched using the antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase (Ab-HRP), and the resulting MNPs@pDA-Ab-Legionella neumophila-Ab-HRP were captured by a magnetic field on the electrode surface. The amperometric response measured at −0.15 V vs. Ag pseudo-reference electrode of the SPCE after the addition of H2O2 in the presence of hydroquinone (HQ) was used as transduction signal. The achieved limit of detection, without pre-concentration or pre-enrichment steps, was 104 Colony Forming Units (CFUs) mL−1. The method showed a good selectivity and the MNPs@pDA-Ab exhibited a good stability during 30 days. The possibility of detecting L. pneumophila at 10 CFU mL−1 level in less than 3 h, after performing a membrane-based preconcentration step, was also demonstrated.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.048
- ‹ anterior
- 243 of 420
- siguiente ›














