Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Absorption Enhancement in Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskite Films with Embedded Plasmonic Gold Nanoparticles
Carretero-Palacios, S; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 18635-18640
Show abstract ▽
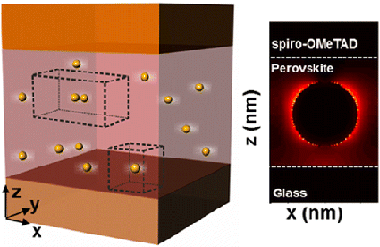
We report on the numerical analysis of solar absorption enhancement in organic-inorganic halide perovskite films embedding plasmonic gold nanoparticles. The effect of particle size and concentration is analyzed in realistic systems in which random particle location within the perovskite film and the eventual formation of dimers are also taken into account. We find a maximum integrated solar absorption enhancement of similar to 10% in perovskite films of 200 nm thickness and similar to 6% in 300 nm films, with spheres of radii 60 and 90 nm, respectively, in volume concentrations of around 10% in both cases. We show that the presence of dimers boosts the absorption enhancement up to,similar to 12% in the thinnest films considered. Absorption reinforcement arises from a double contribution of plasmonic near-field and scattering effects, whose respective weight can be discriminated and evaluated from the simulations.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06473
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Rapid Legionella pneumophila determination based on a disposable core–shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles immunoplatform
Martin, M; Salazar, P; Jimenez, C; Lecuona, M; Ramos, MJ; Ode, J; Alcoba, J; Roche, R; Villalonga, R; Campuzano, S; Pingarron, JM; Gonzalez-Mora, JLAnalytica Chimica Acta, 887 (2015) 51-58
Show abstract ▽
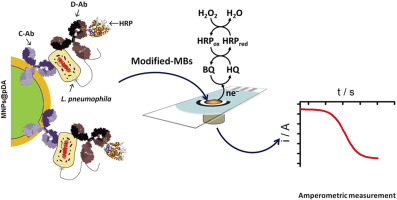
A novel amperometric magnetoimmunoassay, based on the use of core–shell magnetic nanoparticles and screen-printed carbon electrodes, was developed for the selective determination of Legionella pneumophila SG1. A specific capture antibody (Ab) was linked to the poly(dopamine)–modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs@pDA-Ab) and incubated with bacteria. The captured bacteria were sandwiched using the antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase (Ab-HRP), and the resulting MNPs@pDA-Ab-Legionella neumophila-Ab-HRP were captured by a magnetic field on the electrode surface. The amperometric response measured at −0.15 V vs. Ag pseudo-reference electrode of the SPCE after the addition of H2O2 in the presence of hydroquinone (HQ) was used as transduction signal. The achieved limit of detection, without pre-concentration or pre-enrichment steps, was 104 Colony Forming Units (CFUs) mL−1. The method showed a good selectivity and the MNPs@pDA-Ab exhibited a good stability during 30 days. The possibility of detecting L. pneumophila at 10 CFU mL−1 level in less than 3 h, after performing a membrane-based preconcentration step, was also demonstrated.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.048
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Viability of adding gypsum and calcite for remediation of metal-contaminated soil: laboratory and pilot plant scales
Gonzalez-Nunez, R; Alba, MD; Vidal, M; Rigol, AInternational Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12 (2015) 2697-2710
Show abstract ▽
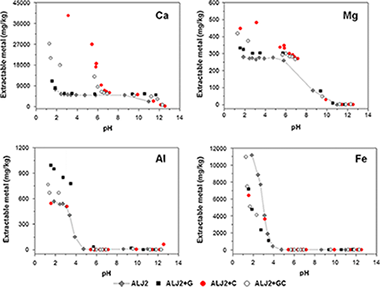
The effect of adding waste materials (gypsum and calcite) for the remediation of a soil contaminated by pyritic minerals was examined. Materials were characterised in terms of their acid neutralisation capacity (ANC), sorption capacity and structural components. Their effect on the contaminant leaching in soil + material mixtures over a wide range of pH was also evaluated. Results at laboratory and pilot plant scales were compared to account for the potential variability in the material efficiency when applied at larger scale. The use of gypsum permitted its valorisation, although calcite was a more effective amendment because its addition led to a greater increase in the pH and acid neutralisation capacity, and thus in the sorption capacity in the resulting soil + material mixture. In the same way, when the combination of gypsum + calcite was added to the soil, it led to an increase in the pH from 2.5 to 6.9 and in the ANC from −86 to 1,513 meq/kg. As a result, the concentration of extractable heavy metals and As was reduced, and they were successfully immobilised both at laboratory and at pilot plant scales. Thus, the use of these materials induced a significant reduction in the contaminant mobility and permitted the valorisation of waste materials.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1007/s13762-014-0671-3
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Direct observation of doping incorporation pathways in self-catalytic GaMnAs
Kasama, T.; Thuvander, M.; Siusys, A.; Gontard, L. C.; Kovacs, A.; Yazdi, S.; Duchamp, M.; Gustafsson, A.; Dunin-Borkowski, R. E.; Sadowski, J.Journal of Applied Physics, 118 (2015) 054302
Show abstract ▽
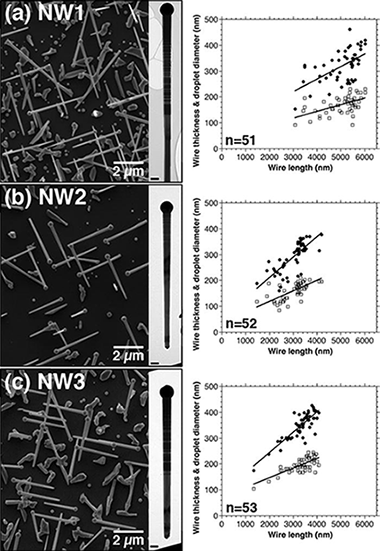
Doping mechanisms of Mn in GaAs nanowires (NWs) that have been grown self-catalytically at 600 °C by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) are investigated using advanced electron microscopy techniques and atom probe tomography. Mn is found to be incorporated primarily in the form of non-magnetic tetragonal Ga0.82Mn0.18 nanocrystals in Ga catalyst droplets at the ends of the NWs, while trace amounts of Mn (22 ± 4 at. ppm) are also distributed randomly in the NW bodies without forming clusters or precipitates. The nanocrystals are likely to form after switching off the reaction in the MBE chamber, since they are partially embedded in neck regions of the NWs. The Ga0.82Mn0.18 nanocrystals and the low Mn concentration in the NW bodies are insufficient to induce a ferromagnetic phase transition, suggesting that it is difficult to have high Mn contents in GaAs even in 1-D NW growth via the vapor-liquid-solid process.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1063/1.4927623
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Ultraviolet Pretreatment of Titanium Dioxide and Tin-Doped Indium Oxide Surfaces as a Promoter of the Adsorption of Organic Molecules in Dry Deposition Processes: Light Patterning of Organic Nanowires
Oulad-Zian, Y; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Parra-Barranco, J; Hamad, S; Espinos, JP; Barranco, A; Ferrer, J; Coll, M; Borras, ALangmuir, 31 (2015) 8294-8302
Show abstract ▽
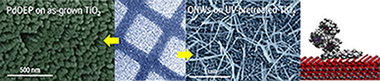
In this article we present the preactivation of TiO2 and ITO by UV irradiation under ambient conditions as a tool to enhance the incorporation of organic molecules on these oxides by evaporation at low pressures. The deposition of p-stacked molecules on TiO2 and ITO at controlled substrate temperature and in the presence of Ar is thoroughly followed by SEM, UV-vis, XRD, RBS, and photoluminescence spectroscopy, and the effect is exploited for the patterning formation of small-molecule organic nanowires (ONWs). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) in situ experiments and molecular dynamics simulations add critical information to fully elucidate the mechanism behind the increase in the number of adsorption centers for the organic molecules. Finally, the formation of hybrid organic/inorganic semiconductors is also explored as a result of the controlled vacuum sublimation of organic molecules on the open thin film microstructure of mesoporous TiO2.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01572
- ‹ anterior
- 244 of 420
- siguiente ›














