Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Modulating Low Energy Ion Plasma Fluxes for the Growth of Nanoporous Thin Films
Alvarez, Rafael; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Ferrer, Francisco J.; Rico, Victor; Cotrino, Jose; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Palmero, AlbertoPlasma Processes and Polymers, 12 (2015) 719-724
Show abstract ▽
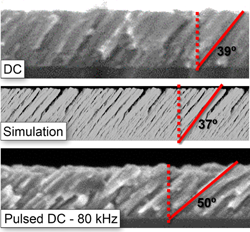
The growth of nanoporous layers by plasma-assisted deposition techniques is strongly mediated by the ion fluxes in the reactor. To analyze their influence we have deposited different nanostructured thin films by the magnetron sputtering technique at oblique angles, modulating the ion fluxes in the plasma by tuning the frequency of the electromagnetic signal from pure DC to 160 kHz DC pulsed mode. In the DC case, ions possess energies below 5 eV and do not induce noticeable changes in the film structure. However, when the signal is pulsed, ions with energies up to 40 eV impinge on the film, decreasing the porosity of the layers and tilting down the porous/nanocolumnar structures. As a result, we demonstrate that the overall porosity of the layers and the tilt angle of the columns can be tailored as two independent morphological quantities.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201400209
Reactividad de Sólidos
Preparation of phase pure, dense fine grained ceramics by conventional and spark plasma sintering of La-substituted BiFeO3 nanoparticles
Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Poyato, Rosalia; Maso, Nahum; West, Anthony R.; Criado, Jose M.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 35 (2015) 2283-2293
Show abstract ▽
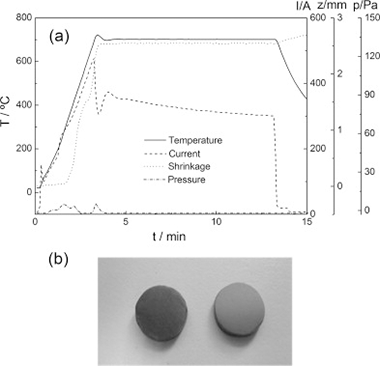
High density ceramics of the system Bi1-xLaxFeO3, 0 <= x <= 0.15, have been prepared starting from nanoparticles obtained by mechanosynthesis. The ceramics have been sintered conventionally at 850 degrees C and by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Sintering conditions have been optimized to obtain single phase ceramics, and the microstructure of the ceramics has been compared. Ceramics prepared conventionally present grain sizes from 5 mu m to less than 1 mu m, whereas grain sizes by SPS are in the range from 50 to 100 nm, which demonstrates that it is possible to obtain nanostructured ceramics of La-substituted BiFeO3 using mechanosynthesis followed by SPS at low temperature (625-650 degrees C). The as-prepared SPS ceramics show low resistivity, indicating some reduction in the samples. However, after an oxidative anneal in air, ceramics are highly insulating at room temperature and electrically homogeneous. The high quality of the ceramics has also been demonstrated by XRD, EDX, Raman and DSC.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.01.030
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanical and electrical properties of low SWNT content 3YTZP composites
Poyato, R; Macias-Delgado, J; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 35 (2015) 2351-2359
Show abstract ▽
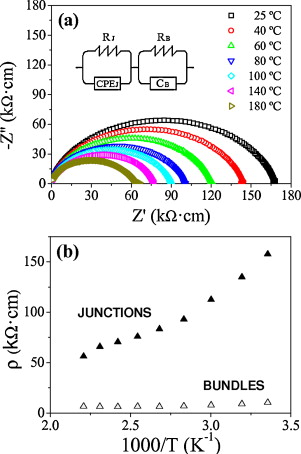
Fully dense 3 mol% Y2O3-ZrO2 (3YTZP) composites with low single wall carbon nanotube content (0.5, 1 and 1.5 vol% SWNT) were prepared by colloidal processing and spark plasma sintering (SPS). SWNT were distributed at ceramic grain boundaries and also into agglomerates. Characterization of SWNT agglomerates indicated that increase in SWNT vol% does not imply an increase in agglomeration. SWNT agglomerate density was related to the evolution of hardness and fracture toughness with SWNT vol%. Electrical properties of the composites were characterized in a wide temperature range, and percolation threshold was estimated. A model allowing separation of the individual SWNT bundles contribution to resistance from the resistance due to junctions between bundles was proposed for composites with a percolating SWNT network.
Agosto, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.02.022
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic propylene epoxidation on Bi2WO6-based photocatalysts
Murcia-Lopez, S.; Vaiano, V.; Sannino, D.; Hidalgo, M. C.; Navio, J. A.Research on Chemical Intermediates, 41 (2015) 4199-4212
Show abstract ▽
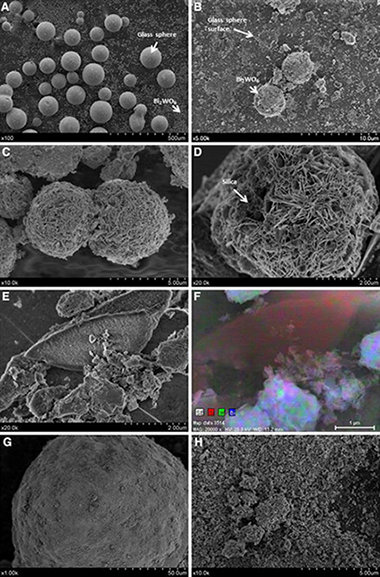
The photocatalytic epoxidation of propylene (PR) with molecular oxygen was carried out in a fluidized-bed reactor with several Bi2WO6-based materials under UV-A illumination. Three different photocatalysts were tested: one of single Bi2WO6 and two of coupled Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructures, thus showing that a mixed system of Bi2WO6 with commercial TiO2 Degussa-P25 leads to the best combination of conversion and PO selectivity. Then, direct support on glass spheres and silica gel was made, being a good alternative for improving the Bi2WO6 performance. Additionally, several reaction conditions of temperature and PR to O-2 feed ratio were studied.
Julio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1007/s11164-013-1523-3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
New Copper wide range nanosensor electrode prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for the non-enzimatic determination of glucose
Salazar, P; Rico, V; Rodriguez-Amaro, R; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 169 (2015) 195-201
Show abstract ▽
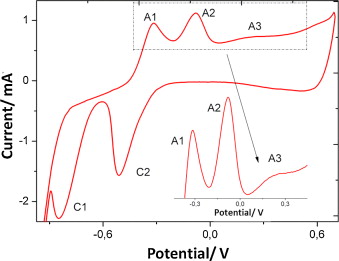
In this work a novel Cu nanostructured electrode is presented. Cu tilted nanocolumnar and porous thin films have been prepared by physical vapor deposition (PVD) in an oblique angle configuration and characterized by different techniques. Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry were used to study the sensing ability of the copper films deposited on ITO to quantitatively determine glucose and to optimize the experimental conditions of detection. Scanning electron microscopy data revealed that the film microstructure consists of tilted nanocolumns of around 70 nm of diameter and an inclination of 65° with respect to the surface normal that extend through the total thickness of the layer of ca. 300 nm. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman, used to determine the oxidation state of Cu, revealed that an oxy/hydroxide external layer formed around the nanocolumns is the active phase responsible for the electrocatalytic detection of glucose. Under optimized conditions, the CuO/Cu nanoporous/ITO electrode presented a sensitivity of 1.41 A mol dm−3 cm−2 (R2:0.999) with a limit of detection of 0.36 μmol dm−3 and a reproducibility of 3.42%.The selectivity of the proposed sensor was checked against various interferences, including physiological compounds, different sugars and ethanol, thereby showing excellent anti-interference properties. The CuO/Cu nanoporous/ITO electrode was also used successfully to determine glucose in blood samples showing a performance comparable to that of a commercial glucometer. An extended working range covering from 1 to 5 × 10−3 mol dm−3 was determined for these sensor films which, in this way, could be applied for different analytical purposes including agro industrial liquids.
Julio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.092
- ‹ anterior
- 245 of 420
- siguiente ›














